5 Essential Biochemistry Basics Worksheet Answers You Need
Delving into biochemistry requires understanding foundational concepts that act as the building blocks of life. Whether you're a student brushing up on fundamentals or a hobbyist intrigued by the science of life processes, knowing the essential biochemistry basics is crucial. This blog post explores the 5 vital biochemistry worksheets and their answers, ensuring you grasp the key concepts behind biological molecules, metabolic pathways, enzyme kinetics, and much more.
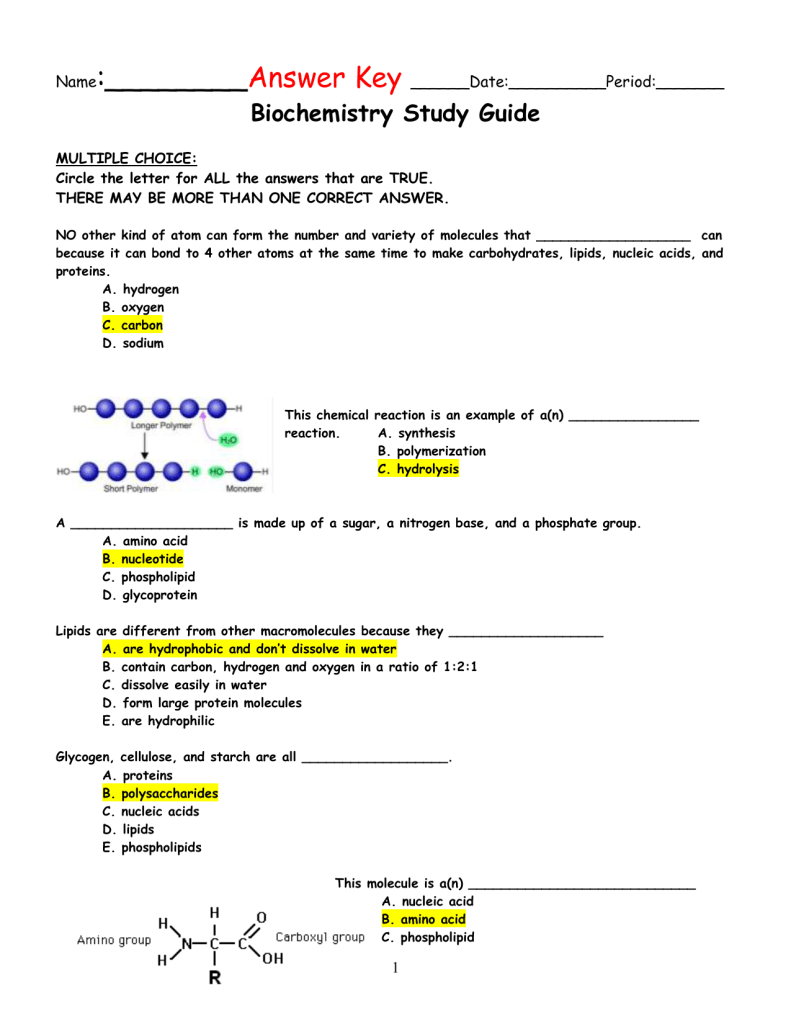
Worksheet 1: Biological Molecules

Biological molecules form the basis of all living organisms. Here’s what you need to know:
- Carbohydrates: They provide energy. Monosaccharides like glucose are the simplest form.
- Proteins: Made from amino acids, they play roles from enzymatic catalysis to structural support.
- Lipids: Essential for energy storage, hormones, and membrane structure.
- Nucleic acids: DNA and RNA store and transmit genetic information.
Table of Essential Macromolecules:
| Macromolecule | Monomers | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Sugars | Energy storage |
| Proteins | Amino acids | Enzyme activity, structural support |
| Lipids | Glycerol, fatty acids | Energy storage, membrane formation |
| Nucleic acids | Nucleotides | Genetic storage |

💡 Note: The functions listed here are not exhaustive; macromolecules often have multiple roles in biological systems.
Worksheet 2: Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics

Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in cells. Here are some key concepts:
- Active Sites: Specific regions where substrates bind.
- Enzyme-Substrate Complex: Temporary complex that forms during catalysis.
- Michaelis-Menten Kinetics: A model to describe the rate of enzyme reactions.
- Inhibition: Enzyme function can be inhibited by various substances.
Worksheet 3: Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis

These are fundamental processes for energy production:
- Glycolysis: Converts glucose into pyruvate, generating ATP.
- Krebs Cycle: Oxidation of pyruvate to CO2, producing ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
- Electron Transport Chain: Generates most of the ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
- Photosynthesis: Plants convert light energy into chemical energy, storing it in glucose.
Worksheet 4: Metabolic Pathways

Metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions within a cell:
- Anabolism: Synthesis of complex molecules from simple ones.
- Catabolism: Breakdown of complex molecules to simpler ones, releasing energy.
- Feedback Inhibition: Regulation mechanism to control the rate of metabolic pathways.
- Central Metabolic Pathways: Including glycolysis, TCA cycle, and pentose phosphate pathway.
Worksheet 5: Biochemistry Concepts and Experiments

This worksheet focuses on practical biochemistry:
- Experimental Techniques: Including spectroscopy, chromatography, and centrifugation.
- Bioenergetics: Understanding energy transfer in biological systems.
- Analyzing Biochemical Data: Interpreting results from experiments and understanding trends.
🔬 Note: Practicing with actual experiments or simulations can enhance your understanding of these biochemical concepts.
In this comprehensive journey through the essential biochemistry basics, we've covered the building blocks of life, the role of enzymes, energy production mechanisms, metabolic pathways, and practical techniques. These foundational principles are not only vital for academic studies but also for anyone interested in how life functions at a molecular level. This knowledge illuminates the complexity and beauty of biological systems, providing a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living things.
What are the primary functions of nucleic acids in cells?

+
Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are crucial for storing and transmitting genetic information. DNA carries the genetic code for making all proteins, while RNA translates this code into amino acid sequences, playing key roles in gene expression.
How do enzymes speed up reactions?

+
Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. They do this by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower energy barrier, thus allowing the substrate to transform into the product more readily.
What is the difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?

+
Photosynthesis is an anabolic process where plants convert light energy into chemical energy in glucose, using CO2 and H2O. In contrast, cellular respiration is a catabolic process where glucose is broken down to produce ATP, releasing CO2 and H2O.