Battle of the Rosebud Creek
Introduction to the Battle of the Rosebud Creek

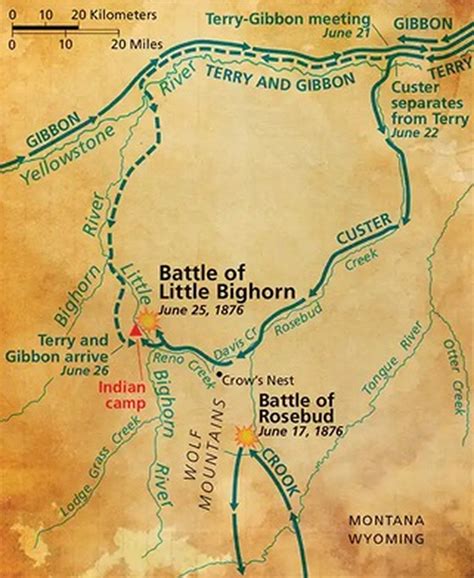
The Battle of the Rosebud Creek, also known as the Battle of Rosebud, was a pivotal battle fought on June 17, 1876, in Montana Territory, during the Great Sioux War of 1876. This battle was a precursor to the more famous Battle of Little Bighorn, which occurred just eight days later. The battle was a clash between the United States Army’s 2nd and 3rd Cavalry regiments, led by Brigadier General George Crook, and a combined force of Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho warriors. The battle was a significant event in the history of the American West and had a profound impact on the outcome of the Great Sioux War.
Background of the Battle

In the early 1870s, the discovery of gold in the Black Hills of South Dakota led to a significant influx of white settlers and miners into the region. This influx encroached on the land guaranteed to the Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes by the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868. The tribes, led by notable chiefs such as Crazy Horse, Sitting Bull, and Dull Knife, resisted the encroachment, leading to increased tensions between the tribes and the United States government. The government responded by dispatching a series of military expeditions to the region, with the aim of forcing the tribes onto reservations.
Preparations for Battle

In the spring of 1876, Brigadier General George Crook was tasked with leading an expedition against the Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes. Crook’s force consisted of approximately 1,300 men, including cavalry, infantry, and artillery units. The tribes, aware of the approaching army, gathered a large force of warriors, estimated to be between 1,000 to 1,500 strong. The warriors were a mix of experienced fighters and young men eager to prove themselves in battle.
The Battle

The battle began on the morning of June 17, 1876, when Crook’s scouts detected a large force of warriors gathered near Rosebud Creek. The warriors, led by Crazy Horse, launched a surprise attack on Crook’s force, hoping to catch them off guard. However, Crook’s men were well-trained and quickly formed a defensive line. The battle raged on for several hours, with both sides suffering significant casualties. Despite being outnumbered, the warriors fought bravely, using their knowledge of the terrain to their advantage. The battle ultimately ended in a stalemate, with both sides withdrawing from the field.
Aftermath of the Battle

The Battle of the Rosebud Creek was a significant defeat for the United States Army, as it prevented Crook’s force from joining up with the 7th Cavalry Regiment, led by Lieutenant Colonel George Armstrong Custer. This meant that Custer’s force would face the combined tribes alone at the Battle of Little Bighorn, which would prove disastrous for the army. The battle also marked a turning point in the Great Sioux War, as it showed that the tribes were capable of resisting the army’s advances. The tribes, however, would ultimately be forced to surrender and relocate to reservations.
Key Players in the Battle

Some key players in the Battle of the Rosebud Creek include: * Brigadier General George Crook: Led the United States Army’s 2nd and 3rd Cavalry regiments during the battle. * Crazy Horse: Led the combined force of Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho warriors during the battle. * Sitting Bull: A prominent chief of the Lakota tribe, who played a significant role in the Great Sioux War. * Dull Knife: A chief of the Cheyenne tribe, who fought alongside Crazy Horse during the battle.
Importance of the Battle

The Battle of the Rosebud Creek was a significant event in the history of the American West, as it marked a turning point in the Great Sioux War. The battle showed that the tribes were capable of resisting the army’s advances, but ultimately, they would be forced to surrender and relocate to reservations. The battle also had a profound impact on the outcome of the Great Sioux War, as it prevented Crook’s force from joining up with Custer’s force at the Battle of Little Bighorn.
📝 Note: The Battle of the Rosebud Creek is often overlooked in favor of the more famous Battle of Little Bighorn, but it was a significant event in the history of the American West and the Great Sioux War.
In the end, the Battle of the Rosebud Creek was a pivotal moment in the history of the American West, marking a significant turning point in the Great Sioux War. The battle highlighted the bravery and resilience of the Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes, who fought to protect their land and way of life. Despite their ultimate defeat, the tribes’ resistance would be remembered as a testament to their strength and determination.
What was the main cause of the Battle of the Rosebud Creek?

+
The main cause of the Battle of the Rosebud Creek was the discovery of gold in the Black Hills of South Dakota, which led to an influx of white settlers and miners into the region, encroaching on the land guaranteed to the Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes by the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868.
Who were the key players in the Battle of the Rosebud Creek?

+
The key players in the Battle of the Rosebud Creek included Brigadier General George Crook, Crazy Horse, Sitting Bull, and Dull Knife.
What was the outcome of the Battle of the Rosebud Creek?

+
The Battle of the Rosebud Creek ended in a stalemate, with both sides suffering significant casualties and withdrawing from the field.