Mastering Math with Base Ten Blocks Worksheets

Base ten blocks are a powerful educational tool for teaching and learning mathematics, particularly in the early education stages. These blocks visually represent numbers and place values, making abstract concepts more concrete and understandable for young learners. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into what base ten blocks are, why they're essential, and how you can effectively use base ten blocks worksheets to enhance mathematical learning.
Understanding Base Ten Blocks

Before diving into worksheets, let's understand base ten blocks:
- Units or Ones Block: Represents the number 1.
- Rods or Tens Block: Represents 10 units, equivalent to one ten.
- Flat or Hundreds Block: Represents 100 units or 10 rods.
- Cube or Thousands Block: Represents 1,000 units or 10 flats.

Why Use Base Ten Blocks?

- Visual Learning: They help in visualizing numbers and operations, which is crucial for conceptual understanding.
- Concrete to Abstract Transition: They bridge the gap between physical counting and abstract numeric operations.
- Hands-on Learning: Provides a tactile experience that can solidify mathematical concepts.
- Develop Number Sense: Enhances the understanding of place value and the numerical relationship.
Utilizing Base Ten Blocks Worksheets
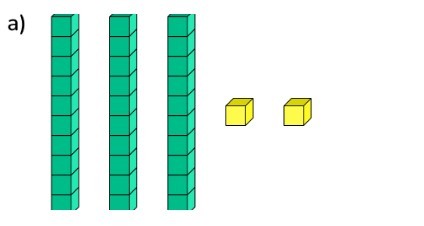
1. Introduction to Place Value

Begin with worksheets that introduce the concept of place value:
- Ask students to represent numbers using base ten blocks.
- Create exercises where students match physical models to written numbers.
Example Activities:
- Match the Number: Students draw blocks to match a given number.
- Identify the Number: Students look at block formations and write the corresponding number.
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Number Formation | Students use blocks to show numbers from 1 to 100 or beyond. |
| Place Value Chart | Complete charts where each block represents a place value. |

👉 Note: Always start with numbers less than 100 for beginners to keep it simple and clear.
2. Addition and Subtraction

Worksheets at this stage can introduce arithmetic operations:
- Use base ten blocks to physically add or subtract numbers.
- Create visual puzzles where addition or subtraction results in specific formations.
Sample Worksheets:
- Adding with Blocks: Students add numbers represented by blocks and write the sum.
- Subtraction Scenarios: Students remove blocks to represent subtraction and find the difference.
🗝️ Note: Introduce regrouping (carrying or borrowing) when students are comfortable with basic operations.
3. Multiplication and Division
As students progress:
- Use blocks to demonstrate multiplication as repeated addition.
- Introduce division as sharing blocks into equal groups.
Advanced Activities:
- Multiplication Grid: Students fill a grid by multiplying base ten blocks.
- Division Sharing: Students share blocks into groups to illustrate division.
Creating Effective Base Ten Blocks Worksheets

Design Principles:

- Gradual Progression: Start simple, increasing complexity as students show understanding.
- Interactive Learning: Allow students to physically manipulate blocks while solving problems.
- Variety: Include diverse problems to cover different aspects of math.
Worksheet Content:

- Number representation and identification.
- Basic operations (addition, subtraction) leading to multiplication and division.
- Advanced concepts like place value understanding, decimals, and fractions.
Key Benefits of Using Base Ten Blocks Worksheets

- Improves conceptual learning of numbers and arithmetic.
- Encourages problem-solving through physical manipulation.
- Builds confidence as students see results of their mathematical work.
- Helps in transitioning from concrete to abstract mathematical thinking.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, base ten blocks and accompanying worksheets offer a versatile and engaging method for teaching mathematics. They not only aid in learning fundamental number concepts but also support complex operations through tangible representations. By integrating these tools into your teaching strategy, you can foster a deeper understanding of math in your students, helping them to grasp both the 'what' and the 'why' behind numbers.
What age group is most suitable for base ten blocks?

+
Base ten blocks are particularly beneficial for students from kindergarten to third grade. However, they can be used effectively up to grade five or six to reinforce concepts.
Can base ten blocks help with learning disabilities?

+
Yes, base ten blocks provide a visual and tactile learning experience which can be very helpful for students with dyscalculia or other math-related learning challenges by making abstract math concepts more tangible.
How often should base ten blocks be used in lessons?

+
Incorporating base ten blocks at least once a week can provide consistent practice in visual mathematics. However, for students new to the concept or struggling, more frequent use could be beneficial.