5 Easy Steps to Create Bar Graph Worksheets

Creating bar graph worksheets can be a fantastic way to teach students about data representation and interpretation. These visual tools make abstract data more tangible, aiding in the development of critical thinking and analytical skills. Let's explore five straightforward steps to create bar graph worksheets that are both educational and engaging.
1. Determine the Purpose

Before you start creating your bar graph worksheet, decide what it’s meant to achieve. Here’s what to consider:
- Learning Objective: What specific skills do you want your students to learn or practice? This could be reading bar graphs, interpreting data, or even comparing data sets.
- Subject and Topic: Will it be for math, science, or another subject? Is there a specific theme or real-world data you want to introduce?
2. Gather or Create Data
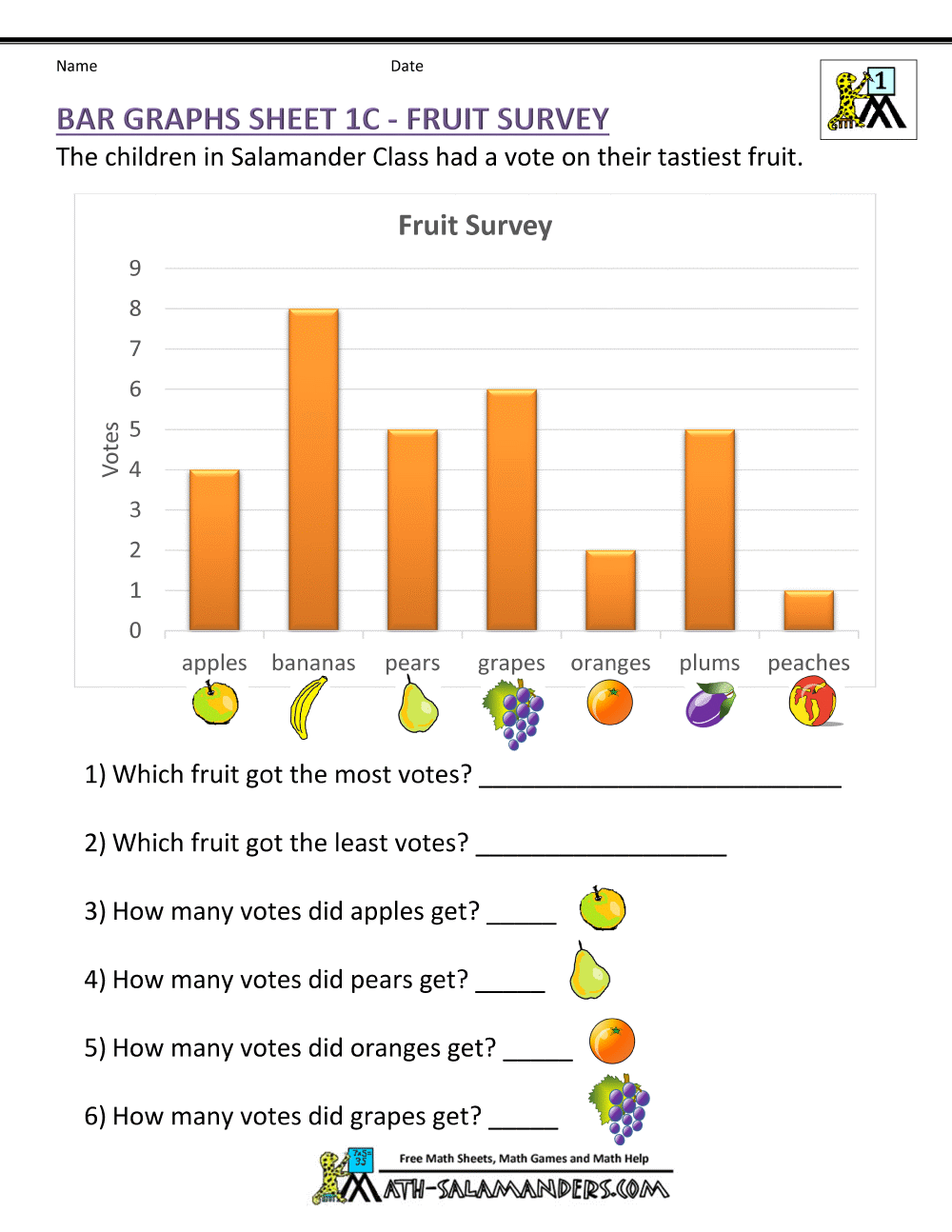
Deciding on the data for your bar graph is crucial:
- Choose Relevant Data: Ensure the data relates to your teaching goals. For instance, if you’re teaching population growth, collect data on different cities or countries.
- Make it Age-Appropriate: The complexity of the data should match the student’s age and ability. Younger students might compare basic things like favorite fruits or animals.
- Use Real or Hypothetical Data: While real data adds authenticity, you can also craft hypothetical data to simplify or focus on specific concepts.
3. Design the Bar Graph


Here’s how to design your bar graph:
- Title: Give your graph a clear and informative title that explains what the data represents.
- Labels:
- Label the x-axis and y-axis. The x-axis typically represents the categories, while the y-axis represents values or counts.
- Scale:
- Set an appropriate scale for the y-axis to ensure readability. If the data varies widely, consider breaking the y-axis into segments for clarity.
- Bar Sizes: Each bar should accurately reflect its value. Make sure the bars are of equal width and properly spaced.
- Colors or Patterns: Use different colors or patterns to distinguish between data sets or categories for easy interpretation.
⚠️ Note: Keep the design simple and avoid cluttering the graph with too much information, as this can overwhelm students.
4. Create Questions

Design questions to guide students’ interaction with the bar graph:
- Direct Interpretation: Ask students to read specific values from the graph.
- Analysis:
- Pose questions that require students to analyze trends or compare categories. Example: “Which category has the highest/lowest value?”
- Data Manipulation:
- Encourage calculations, like finding the total, average, or percentage of a category.
- Open-Ended: Allow for personal insights by asking what students can infer from the data or how they might collect similar data.
5. Test and Refine

Before distributing your bar graph worksheet:
- Check for Errors: Ensure there are no mistakes in the data presentation or questions.
- Review Comprehensibility: Can students easily understand and answer the questions? If not, adjust the level of complexity.
- Engage Feedback:
- Seek feedback from colleagues or test the worksheet with a small group of students to see how it performs.
- Iterate: Based on feedback, make necessary changes. This could involve tweaking the graph design, simplifying or expanding questions, or adjusting the data.
💡 Note: Remember, your bar graph worksheet is a tool for learning; make sure it remains fun and engaging, not just another task.
The process of creating bar graph worksheets can be as rewarding for the teacher as it is for the student. By following these five steps, educators can effectively design worksheets that not only meet educational objectives but also capture students' interest. Bar graphs offer a clear visualization of data, promoting skills in data interpretation, comparison, and even prediction. With the right data and carefully crafted questions, students can explore the world of numbers in a visual and interactive way.
Why are bar graphs useful in education?

+
Bar graphs provide a visual representation of data, making it easier for students to understand and compare quantities. They foster skills in data interpretation, analysis, and comparison, which are fundamental in many subjects.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating bar graph worksheets?

+
Common mistakes include overloading the graph with too much data, using inappropriate scales, not labeling axes clearly, and posing questions that do not match the students’ level of understanding.
Can I use real data for my bar graph worksheet?

+
Absolutely, using real-world data can make the worksheet more relevant and engaging. It also provides a practical context for learning about data representation and analysis.
How do I ensure the worksheet is suitable for different ability levels?

+
Create versions of the worksheet with varying levels of complexity. Offer simpler graphs or fewer questions for less advanced students, and more complex analysis or open-ended questions for advanced learners.