Mastering Chemical Equations: Balancing Worksheet with Answers

Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental skill for anyone diving into the world of chemistry. At its core, a balanced chemical equation reveals the law of conservation of mass, showing that atoms aren't created or destroyed in chemical reactions; they merely rearrange. Today's guide will walk you through the intricacies of balancing chemical equations, providing worksheets and answers to enhance your comprehension and practice.
Why Balancing is Crucial in Chemistry

The balance of a chemical equation:
- Ensures the equation abides by the law of conservation of mass.
- Shows us the mole ratios of reactants to products.
- Enables us to calculate reactant quantities needed for a complete reaction.
- Is essential for stoichiometry, where we predict amounts of substances involved in a reaction.
Steps for Balancing Chemical Equations

Here is a step-by-step process for balancing chemical equations:
- Write out the unbalanced equation: Begin with the reactants on the left and products on the right, e.g., H2 + O2 → H2O.
- Identify all the elements: List each element involved in the reaction.
- Count the atoms: Count the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
- Balance the equation:
- Start with the element that appears in the least number of compounds.
- Add coefficients (numbers in front of chemical formulas) to equalize the number of atoms of each element on both sides.
- Make sure not to change subscripts (the small numbers within formulas).
- Check your work: Verify that all atoms are equal on both sides. Recount to ensure every element is balanced.
- Reduce coefficients if necessary: If possible, reduce the equation to the lowest whole numbers by dividing all coefficients by their greatest common divisor.
🧪 Note: Don’t alter the chemical formulas when balancing; only use coefficients to balance.
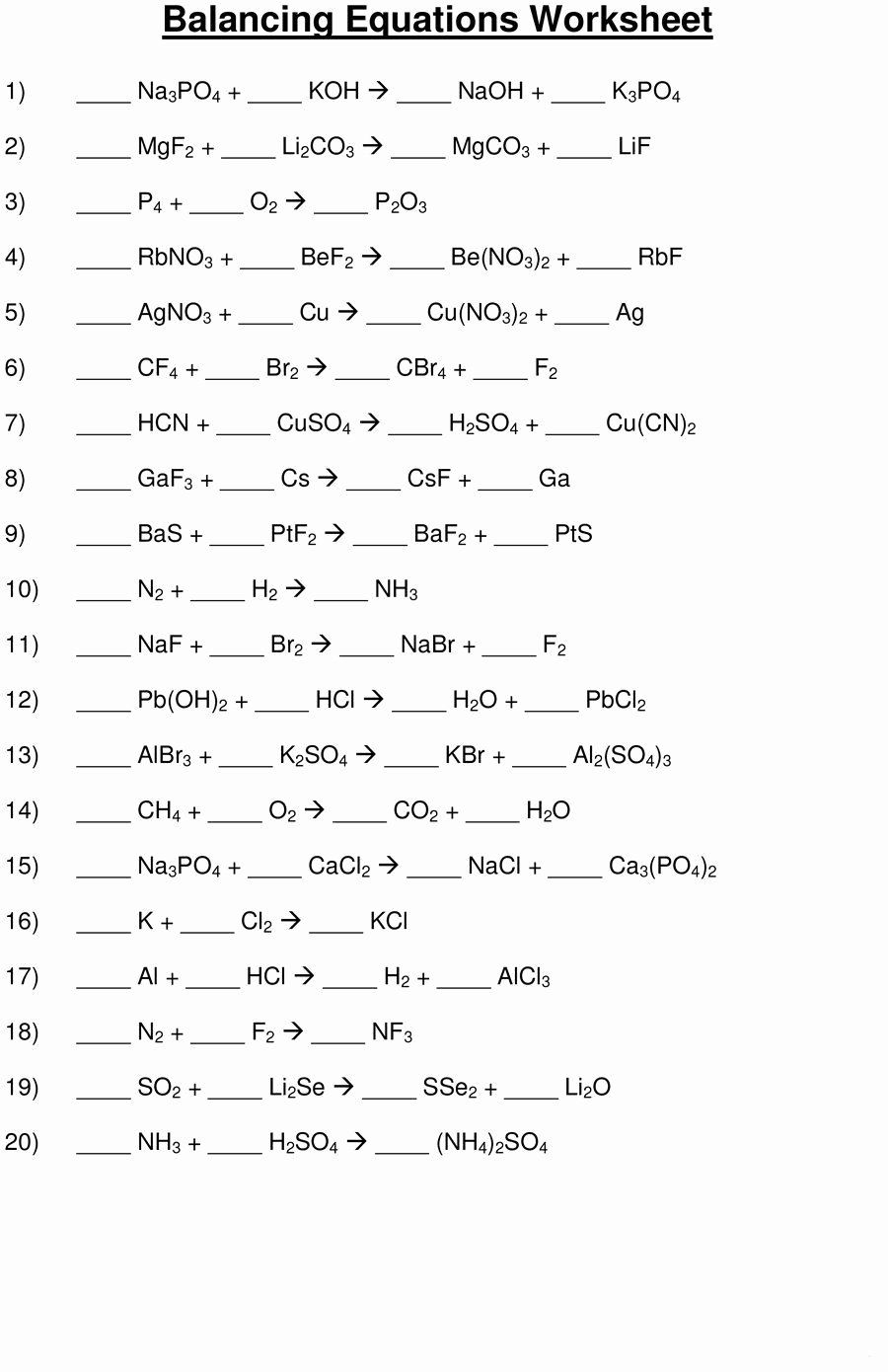
Worksheet on Balancing Chemical Equations

Try your hand at balancing these chemical equations:
| Unbalanced Equation |
|---|
| Al + O2 → Al2O3 |
| Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2 |
| C3H8 + O2 → CO2 + H2O |
| NH3 + O2 → NO + H2O |
Answers to the Worksheet

Let’s balance the equations from the worksheet:
- Al + O2 → Al2O3 balances to 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3
- Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2 balances to 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
- C3H8 + O2 → CO2 + H2O balances to C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
- NH3 + O2 → NO + H2O balances to 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
⚗️ Note: Practice makes perfect. Balancing chemical equations takes time to master.
Balancing chemical equations allows us to understand the quantitative aspects of chemical reactions, which is essential not only for academic purposes but also in applied chemistry fields. From ensuring the correct proportions in chemical synthesis to preparing solutions in labs, the ability to balance equations accurately is indispensable. Keep practicing with these worksheets, and soon you'll find that what once seemed complex becomes second nature. Remember, in chemistry, balance is everything.
Why must chemical equations be balanced?

+
Balancing ensures that the law of conservation of mass is not violated. Each atom must appear on both sides of the equation in equal numbers.
Can I balance an equation by changing subscripts?

+
Never change subscripts as this alters the compound. Balance equations using coefficients only.
What is the significance of coefficients in balancing equations?

+
Coefficients represent the number of moles of each substance involved in the reaction, allowing us to relate reactants and products stoichiometrically.