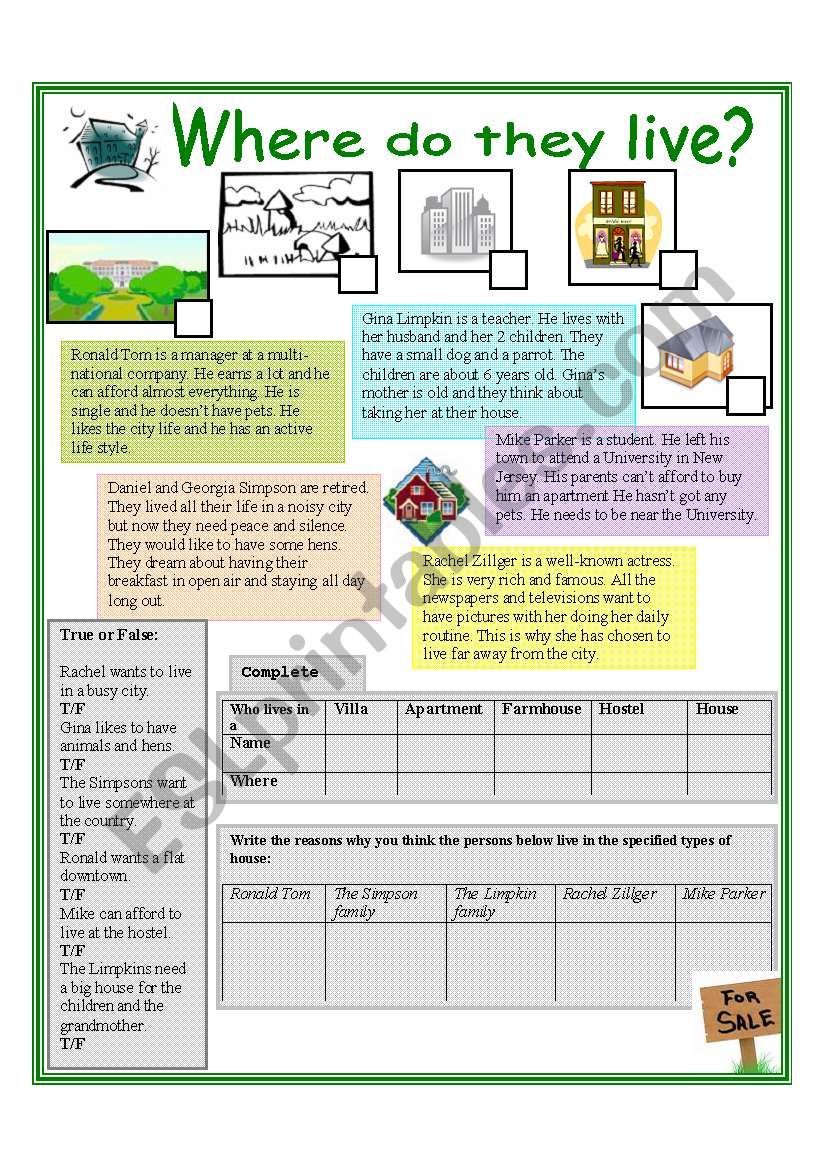
Balancing Equations Practice Problems: Solved Worksheet

Balancing chemical equations is a foundational skill in chemistry, crucial for understanding reactions, stoichiometry, and quantitative analysis. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed worksheet of practice problems, ranging from beginner to advanced levels, to help you master the art of balancing chemical equations. By following these steps and examples, you will not only improve your skills but also gain a deeper understanding of chemical reactions.
Understanding the Basics of Balancing Equations


Balancing an equation involves adjusting the coefficients of the reactants and products to ensure that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides. Here are the fundamental steps:
- Write down the unbalanced equation: Start with the chemical formula of each compound in the reaction.
- Count the atoms: List the number of atoms for each element on both the reactants and products sides.
- Adjust coefficients: Begin with the most complex molecule or the element appearing least frequently. Adjust coefficients step by step to balance atoms.
- Verify: Recount the atoms to ensure that the equation is now balanced.
- Reduce coefficients if necessary: Ensure that the coefficients are in their simplest ratio.
🧪 Note: Always balance compounds first, then focus on elements that appear in one molecule on each side, and then finally on the most common elements like hydrogen and oxygen.
Beginner Level Practice Problems

Let’s start with some simple equations suitable for beginners:
| Unbalanced Equation | Balanced Equation |
|---|---|
| H2 + O2 → H2O | 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O |
| N2 + H2 → NH3 | N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 |
| Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 | Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 |

🔬 Note: When you encounter a fraction in balancing, always multiply everything by the smallest integer to remove the fraction.
Intermediate Level Problems

Here are some problems where the process might require a bit more thought:
- Balance: K + O2 → K2O
- 2K + O2 → 2K2O
- Balance: Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + Fe
- 2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe
- Balance: C2H6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
- 2C2H6 + 7O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O
Advanced Level Problems

For those ready to tackle more complex reactions:
- Balance: Ca(NO3)2 + Na3PO4 → Ca3(PO4)2 + NaNO3
- 3Ca(NO3)2 + 2Na3PO4 → Ca3(PO4)2 + 6NaNO3
- Balance: Fe + O2 + H2O → Fe2O3 + H2
- 4Fe + 3O2 + 6H2O → 2Fe2O3 + 6H2
Final Thoughts

In summary, mastering the skill of balancing chemical equations is crucial for chemistry students. It not only helps in understanding the stoichiometry of reactions but also prepares you for more complex chemical calculations. Through this practice, you’ve seen how to approach equations systematically, starting with simple to more complex reactions. Remember, the key to success in balancing equations lies in methodical practice and attention to detail.
Why is it important to balance chemical equations?

+
Balancing ensures that the law of conservation of mass holds true for a chemical reaction, meaning the number of atoms of each element is the same before and after the reaction.
What should I do if I cannot balance an equation easily?

+
Start with the most complex molecule or the element with the lowest frequency. If difficulties persist, try listing the atoms in a table format to better visualize the changes needed.
How can I check if my equation is correctly balanced?

+
Count the atoms on both sides of the equation to ensure they match. Additionally, using a chemical equation balancer or double-checking your work step by step can help.