Balanced Vs Unbalanced Forces Worksheet

Understanding forces and their effects on objects is fundamental in the study of physics. Forces can either be balanced, keeping an object in its current state of motion, or unbalanced, leading to changes in the object's movement or shape. This blog post delves into the nuances of balanced versus unbalanced forces, providing insights through examples and practical applications. Let's explore how these forces influence everyday life and why they are crucial in understanding physical phenomena.
What Are Forces?

Force is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. Here are key points about forces:
- Definition: A push or pull upon an object resulting from interaction with another object.
- Measurement: Force is typically measured in newtons (N).
- Types: Contact forces (like friction, air resistance) and non-contact forces (like gravity, magnetic force).

🧲 Note: Forces are responsible for all changes in motion and shape in our physical world.
Balanced Forces

When the forces acting on an object are balanced, the net force on the object is zero. This means:
- The object’s velocity remains constant.
- If it was stationary, it will remain stationary.
- If it was moving, it continues moving at the same speed and direction.
Examples of Balanced Forces

- Book on a Table: The weight of the book pulling down is exactly balanced by the normal force from the table pushing up.
- Tug of War: When two teams exert equal force, the rope does not move.
- Car on Cruise Control: Once set, the engine force matches the air resistance and friction, keeping the car at a constant speed.
Unbalanced Forces

When forces are unbalanced, there is a net force acting on the object, which results in:
- Acceleration or deceleration of the object.
- Change in direction of motion.
- Possible deformation if the forces are strong enough.
Examples of Unbalanced Forces
- Car Acceleration: When a car accelerates, the engine provides a forward force greater than the opposing forces.
- Falling Object: An object falling near the Earth’s surface experiences unbalanced gravitational force, accelerating until air resistance balances it out.
- Kicking a Ball: The force from the kick is unbalanced, sending the ball in motion.
⚽ Note: Understanding unbalanced forces is key to sports physics, engineering, and many other fields.
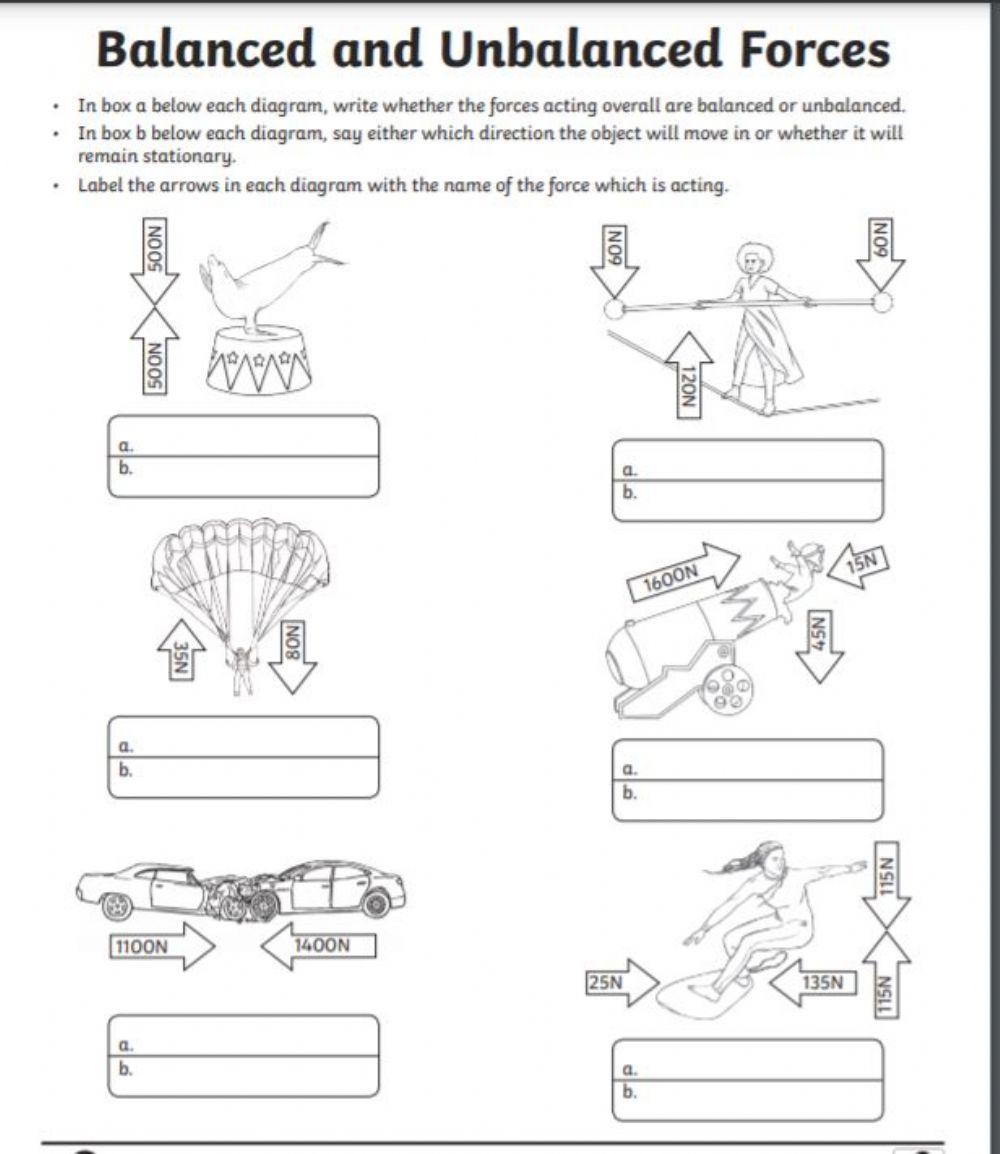
Worksheet for Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces

To better grasp these concepts, here’s a practical worksheet that can help you:
| Scenario | Forces Involved | Balanced or Unbalanced? | Resulting Motion/State |
|---|---|---|---|
| An object at rest on a flat surface | Weight vs. Normal force | Balanced | Stays at rest |
| A parachutist falling from a plane | Weight (gravity) vs. Air resistance | Unbalanced initially, then balanced as air resistance increases | Accelerates, then constant velocity |
| Pushing a stalled car | Push force vs. Friction, Air resistance | Can be balanced or unbalanced | Depends on the strength of the push relative to opposing forces |

The distinction between balanced and unbalanced forces is not just academic; it has practical implications in designing structures, predicting motion in sports, and even in understanding our daily activities like walking or driving.
What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces?

+
Balanced forces keep an object in its current state of motion (either stationary or moving at a constant speed in a straight line), while unbalanced forces cause the object to accelerate, decelerate, or change direction.
How can you determine if forces are balanced?

+
If the sum of all forces acting on an object is zero, the forces are balanced. This means no net force is acting, and the object will not change its motion.
Can an object be at rest with unbalanced forces?

+
Not under normal circumstances. If forces on a static object are unbalanced, the object will start moving or experience acceleration.
What role does friction play in balancing forces?

+
Friction often acts as the opposing force to maintain balance, for example, when walking, the friction between your feet and the ground keeps you from slipping.
Why is understanding balanced and unbalanced forces important?

+
It's crucial in fields like engineering for stability and safety, in sports to optimize performance, and in everyday life to predict and control motion.
In summary, the principles of balanced and unbalanced forces are not only intriguing from a scientific standpoint but also essential in numerous practical applications. Recognizing and analyzing these forces can help us design better systems, understand the mechanics of sports, and even move through our daily activities with greater ease and understanding. This knowledge empowers us to predict outcomes, control motion, and innovate in technology and sports.