Type 2 Diabetes Overview
Introduction to Type 2 Diabetes

Type 2 diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to a variety of complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. In this article, we will provide an overview of type 2 diabetes, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
Causes and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes

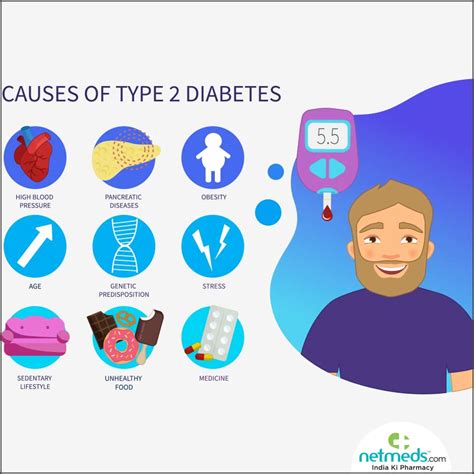
Type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Some of the key risk factors include: * Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. * Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. * Family history: Having a family history of type 2 diabetes can increase an individual’s risk. * Age: The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases with age. * Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. * Previous history of gestational diabetes: Women who have had gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. * Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes

The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include: * Increased thirst and urination: High blood sugar levels can cause increased thirst and urination. * Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can cause fatigue and weakness. * Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can cause blurred vision. * Slow healing of cuts and wounds: High blood sugar levels can cause slow healing of cuts and wounds. * Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet: High blood sugar levels can cause tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Some common tests used to diagnose type 2 diabetes include: * Fasting plasma glucose test: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. * Oral glucose tolerance test: This test measures blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink. * Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test: This test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes

Treatment for type 2 diabetes typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medications. Some common treatment options include: * Dietary changes: Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in sugar and saturated fat can help manage blood sugar levels. * Exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels. * Medications: Medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and pioglitazone can help manage blood sugar levels. * Insulin therapy: In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels.
Management Strategies for Type 2 Diabetes

Managing type 2 diabetes requires a long-term commitment to lifestyle modifications and ongoing monitoring of blood sugar levels. Some key management strategies include: * Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels can help identify any changes or trends. * Maintaining a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can help improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels. * Staying physically active: Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels. * Getting enough sleep: Getting enough sleep can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
📝 Note: It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan for type 2 diabetes.
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes

If left unmanaged, type 2 diabetes can lead to a variety of complications, including: * Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease. * Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can cause kidney damage and increase the risk of kidney failure. * Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage and increase the risk of neuropathy. * Blindness: High blood sugar levels can cause blindness and increase the risk of retinopathy.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Heart disease | High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease. |
| Kidney damage | High blood sugar levels can cause kidney damage and increase the risk of kidney failure. |
| Nerve damage | High blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage and increase the risk of neuropathy. |
| Blindness | High blood sugar levels can cause blindness and increase the risk of retinopathy. |

In summary, type 2 diabetes is a chronic health condition that requires ongoing management and lifestyle modifications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies for type 2 diabetes, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of complications.
What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
+
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?

+
Type 2 diabetes is typically diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including fasting plasma glucose test, oral glucose tolerance test, and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test.
What are the treatment options for type 2 diabetes?

+
Treatment for type 2 diabetes typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medications, including dietary changes, exercise, medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and pioglitazone, and insulin therapy.



