5 California Salary Facts
Introduction to California Salary Facts
California is known for being one of the most expensive states to live in within the United States, with a high cost of living that affects various aspects of life, including salaries. Understanding the dynamics of salaries in California can provide valuable insights for both employers and employees. In this article, we will delve into five key facts about California salaries, exploring how they compare nationally, the impact of the cost of living, industry-specific salary trends, the role of education in determining salary, and the legal frameworks that govern salaries in the state.
Fact 1: California Salaries Compared to the National Average

California salaries tend to be higher than the national average across many industries. This is partly due to the state’s thriving economy, driven by sectors such as technology, entertainment, and healthcare. However, when adjusted for the cost of living, especially in areas like Silicon Valley and Los Angeles, the purchasing power of these salaries can be significantly reduced. The cost of living in California is among the highest in the country, which means that while salaries may be higher, the actual standard of living they afford can be comparable to, or sometimes even lower than, what one might experience in other states with lower salaries but a lower cost of living.
Fact 2: Impact of Cost of Living on Salaries

The cost of living in California varies significantly across different regions. Cities like San Francisco and San Jose have some of the highest costs of living in the country, with extremely high housing costs being a major factor. In contrast, areas like Fresno and Bakersfield have a lower cost of living, though still higher than many parts of the country. This variability means that salaries that might seem high in a national context can be barely sufficient in certain parts of the state. For example: - Housing costs in San Francisco can be more than twice as high as in other major cities in the United States. - The cost of groceries, transportation, and utilities also tends to be higher in California, especially in urban areas.
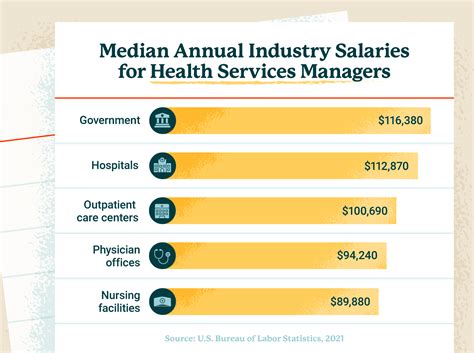
Fact 3: Industry-Specific Salary Trends

Different industries in California exhibit unique salary trends. The tech industry, for instance, is known for offering some of the highest salaries, with software engineers and data scientists often earning upwards of 200,000 per year in cities like Palo Alto and Mountain View. In contrast, salaries in the education and non-profit sectors tend to be lower, reflecting national trends but exacerbated by the high cost of living in California. Some of the key industries and their salary trends include: - Technology and Software: High salaries, often exceeding 150,000 per year for experienced professionals. - Healthcare: Salaries vary widely depending on specialization and experience but tend to be above the national average. - Entertainment: Highly variable, with potential for very high earnings but also significant competition and instability.
Fact 4: Role of Education in Determining Salary
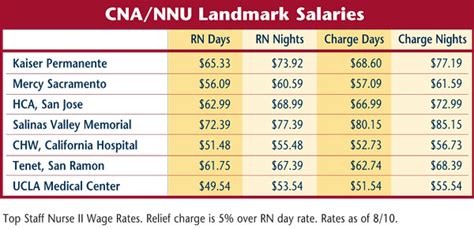
Education plays a critical role in determining salary potential in California, as it does nationally. However, the state’s unique economic landscape means that certain degrees and certifications can lead to particularly high salaries. For example: - Degrees in STEM fields (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) are highly valued and can lead to salaries well above $100,000 per year, even for entry-level positions. - Advanced degrees, such as MBAs, law degrees, and medical degrees, can also significantly increase earning potential, especially in industries like finance, law, and healthcare.
Fact 5: Legal Frameworks Governing Salaries

California has a robust set of laws governing employment and salaries, designed to protect workers’ rights and ensure fair compensation. Some key aspects include: - Minimum Wage: California has a higher minimum wage than the federal minimum, with annual increases to account for inflation. - Overtime Pay: California law requires overtime pay for work exceeding eight hours in a day or 40 hours in a week, with some exceptions. - Equal Pay: Laws are in place to prevent pay discrimination based on gender, race, and other protected characteristics.
📝 Note: Understanding and complying with these legal frameworks is crucial for employers in California to avoid legal issues and ensure a positive work environment.
In summary, California salaries are influenced by a complex interplay of factors including the cost of living, industry-specific trends, the role of education, and legal protections. While salaries in California can be high, especially in thriving industries like technology and healthcare, the state’s unique economic and regulatory environment means that both employers and employees must be aware of these factors to navigate the job market effectively.
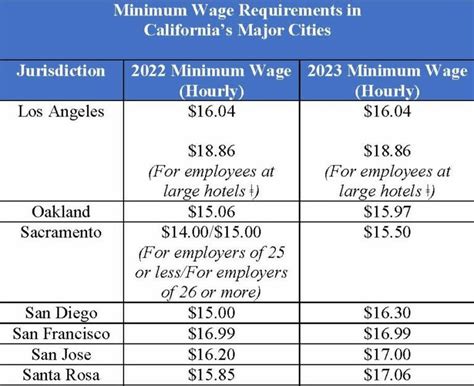
What is the current minimum wage in California?
+
The minimum wage in California varies by year and the size of the employer, with annual increases to account for inflation. As of the last update, the minimum wage for employers with 26 or more employees is higher than for those with 25 or fewer employees.
How does the cost of living in California affect salaries?
+
The high cost of living in California, particularly in housing, groceries, and transportation, means that even higher-than-average salaries can result in a standard of living that is not significantly better than in other parts of the country with lower costs of living.
What industries in California tend to offer the highest salaries?
+
Industries such as technology and software, healthcare, and finance tend to offer some of the highest salaries in California, with professionals in these fields often earning upwards of 100,000 to over 200,000 per year, depending on experience and specialization.