3 Simple Steps for Mastering Autosomal Pedigrees
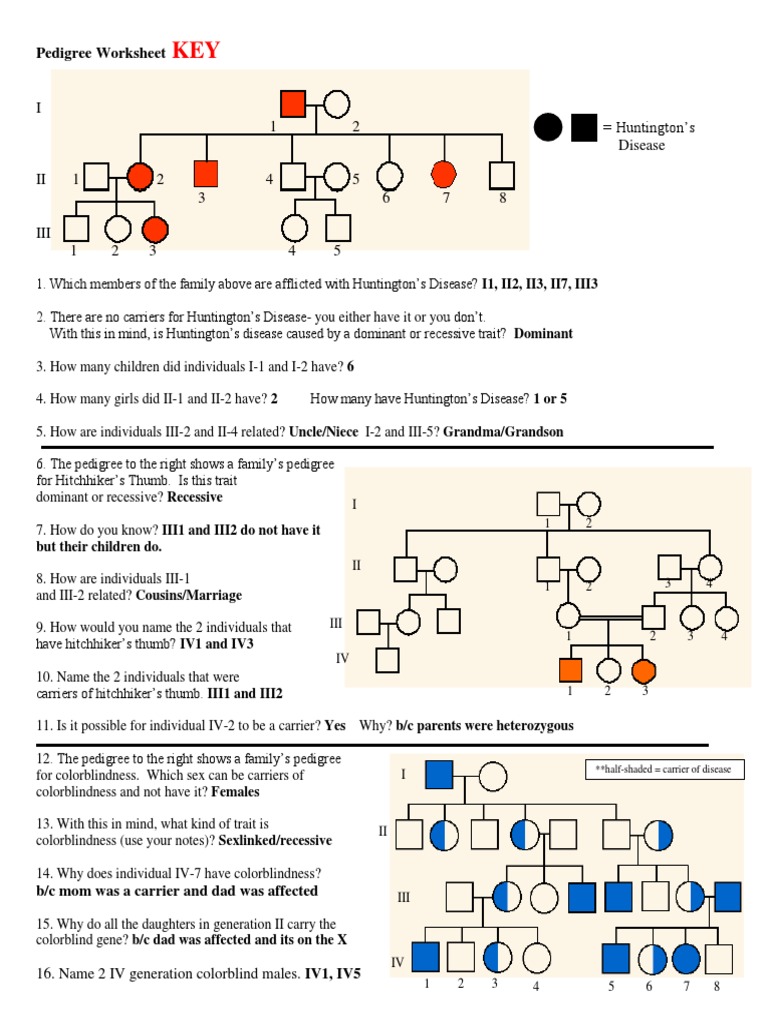
Understanding autosomal pedigrees is a cornerstone for students and professionals in genetics, evolutionary biology, and related fields. Whether you're studying for an exam or trying to understand complex inheritance patterns in a family, mastering the interpretation of autosomal pedigrees can be a game-changer. In this detailed guide, we'll walk through the three simple steps that will help you decipher these fascinating diagrams with ease. Let's dive in!
Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with Pedigree Symbols

Before interpreting any pedigree, it's crucial to understand the symbols and notations commonly used:
- Males are represented by squares, and females by circles.
- Shaded shapes indicate individuals affected by the trait or disease in question.
- Half-shaded shapes might mean carriers in recessive traits or reduced penetrance.
- Lines between symbols represent biological parent-child relationships; a vertical line shows descent, a horizontal line indicates a mating.
To better visualize this:
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| □ | Male |
| ○ | Female |
| Affected Female | |
| Affected Male | |
| Carrier or Reduced Penetrance Female | |
| Carrier or Reduced Penetrance Male |

Identifying Patterns

Once you understand the symbols, look for patterns:
- Is the trait appearing in every generation or skipping generations? This can indicate dominant or recessive inheritance.
- Do unaffected individuals have affected children? This might suggest a recessive inheritance.
- Is the trait transmitted only through males? This could indicate Y-linked inheritance.
🧬 Note: Autosomal dominant traits are not necessarily dominant in all aspects; they simply require one allele to express the phenotype.
Step 2: Determine the Mode of Inheritance

With basic symbols and patterns in mind, you can start pinpointing the mode of inheritance:
Autosomal Dominant

- Both males and females are equally affected.
- Every affected individual has at least one affected parent.
- Skipping generations is not typical unless penetrance is incomplete.
Autosomal Recessive

- Unrelated parents can produce an affected child if both are carriers.
- The trait often skips generations.
- Parents of an affected child are usually not affected themselves but are carriers.
X-Linked Inheritance
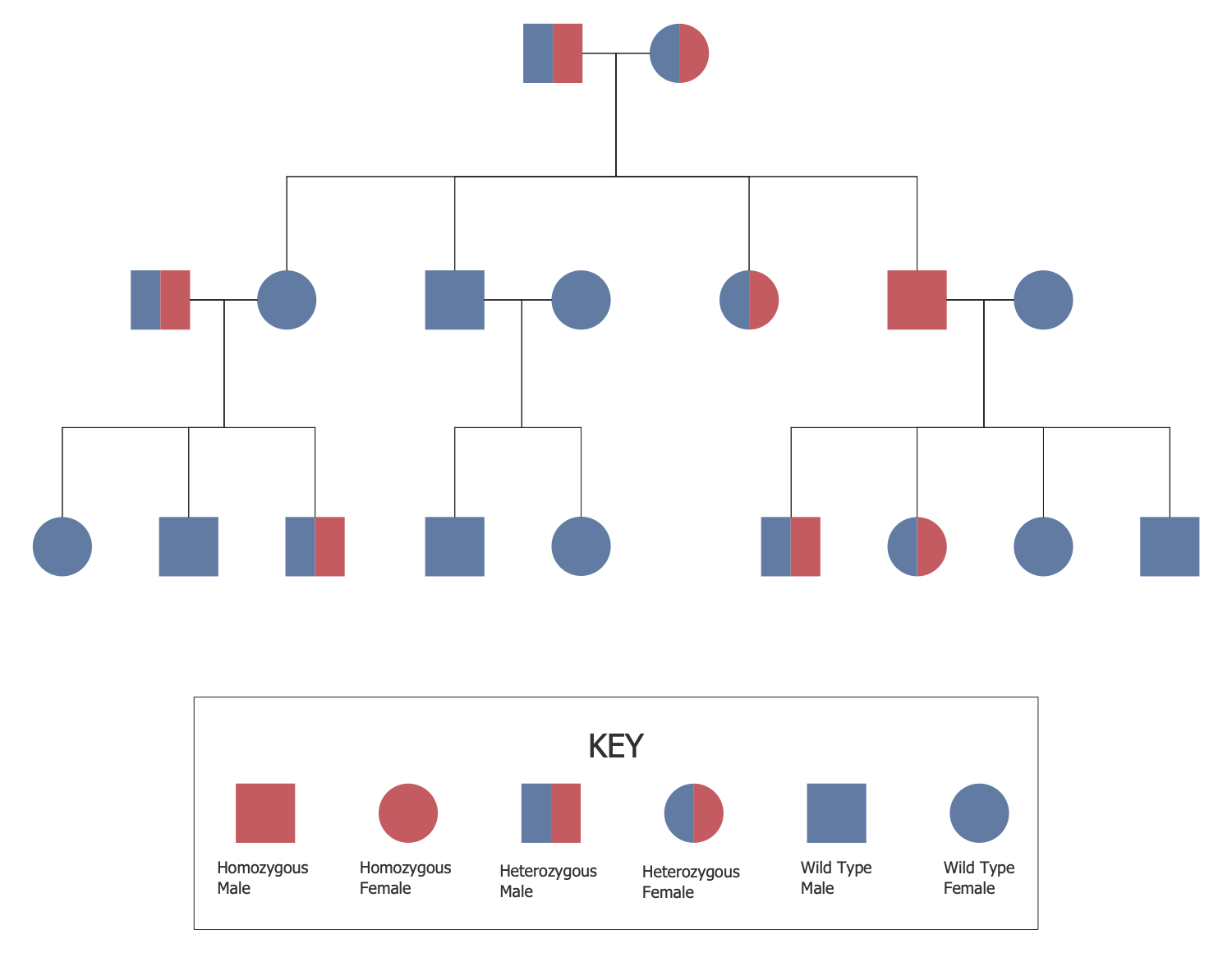
- Males are more commonly affected due to having only one X chromosome.
- Females can be affected if they are homozygous for the mutant allele.
Y-Linked Inheritance
- Only males are affected, and it is passed from father to son.
💡 Note: Remember that Y-linked inheritance is rare and limited to genes on the Y chromosome.
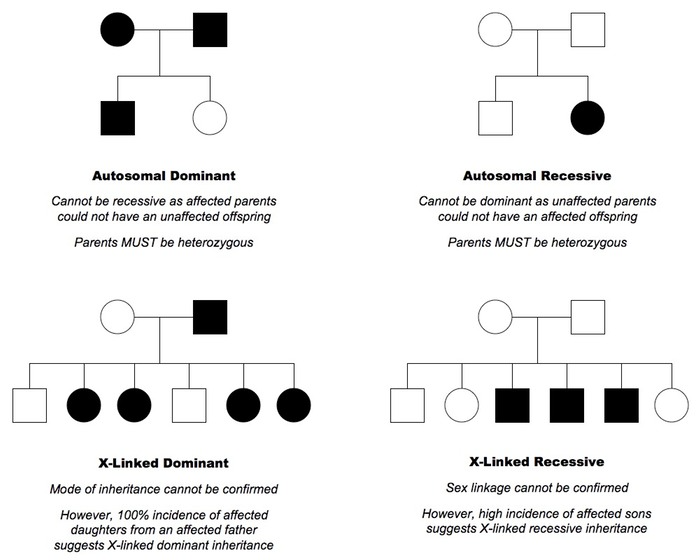
Using Punnett Squares for Confirmation

To solidify your hypotheses about the mode of inheritance:
- Identify potential carriers from the pedigree.
- Construct Punnett squares to predict progeny phenotypes.
- Check if the offspring ratios align with observed patterns.
Understanding these probabilities helps reinforce your interpretation:
- Autosomal dominant: 50% of offspring will have the trait if one parent is affected.
- Autosomal recessive: 25% of offspring will have the trait if both parents are carriers.
Step 3: Analyze for Penetrance and Variable Expressivity

Not all traits are straightforward in their expression:
- Penetrance: The proportion of individuals carrying a trait who express it.
- Expressivity: The degree to which the trait is expressed among individuals.
Complete Penetrance

- If the trait is always expressed in those with the genotype, it has complete penetrance.
Incomplete Penetrance
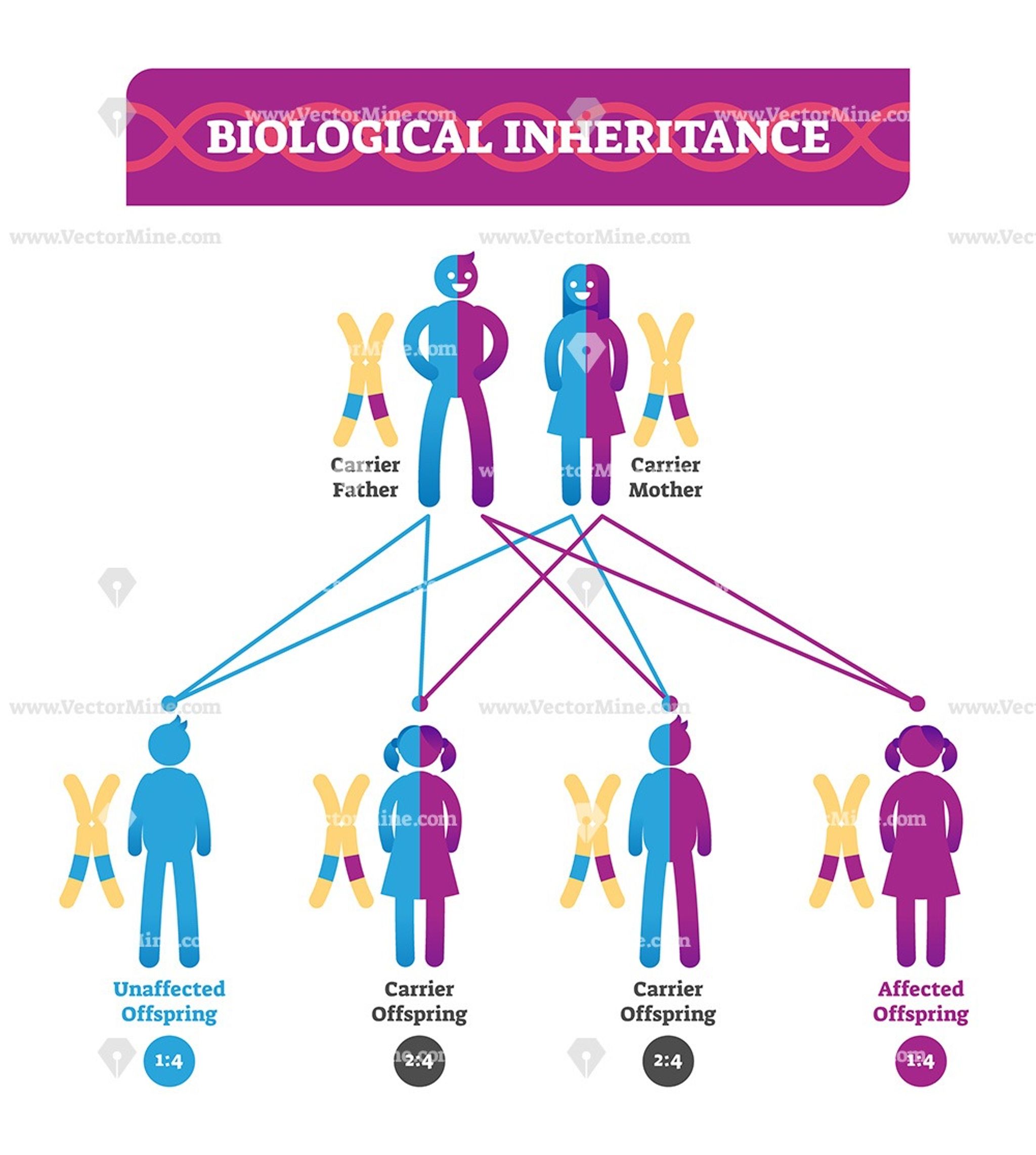
- If some individuals with the genotype do not express the trait, then penetrance is incomplete.
Variable Expressivity

- This occurs when different individuals with the same genotype have varying degrees of the trait expression.
👁️ Note: Recognizing penetrance and expressivity can help in counseling families about genetic risks and understanding disease severity.
Interpreting Complex Pedigrees
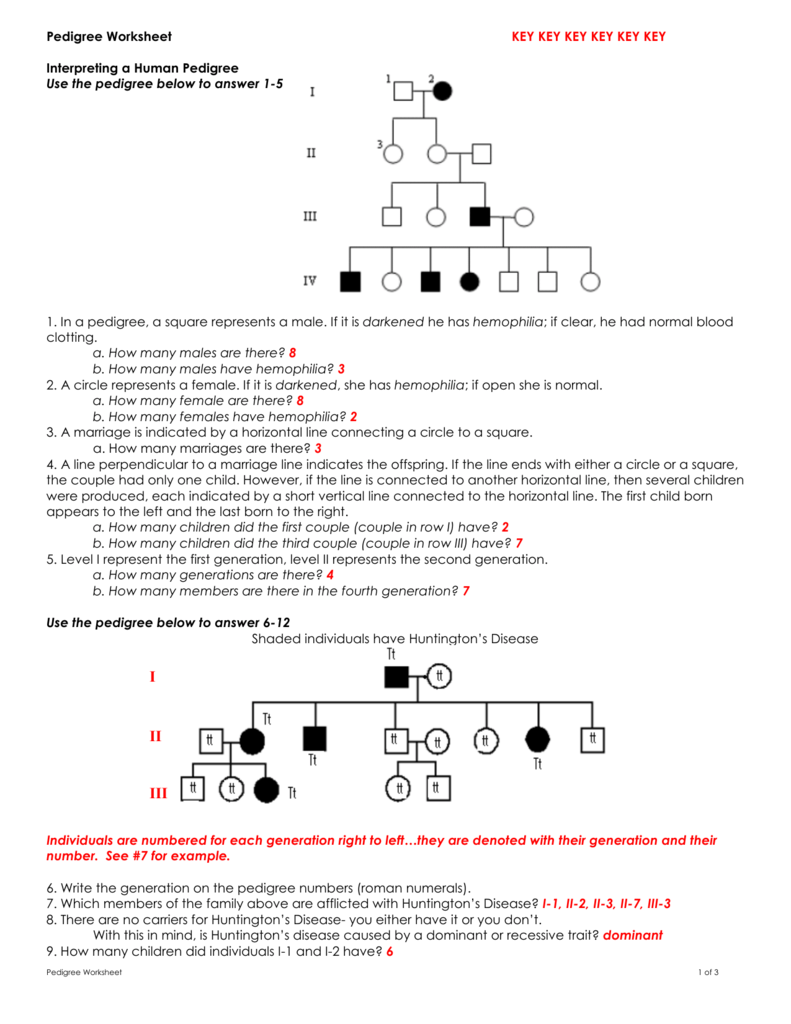
In real-world scenarios, pedigrees often exhibit complexities:
- Multiple affected genes.
- Environmental influences.
- Modifier genes.
Understanding how these factors interplay is essential:
- Identify if the trait seems to have variable expressivity or incomplete penetrance.
- Look for signs of epigenetic factors or gene-environment interactions.
- Use the pedigree to guide genetic testing or to suggest further research.
Remember, pedigree analysis is not just about simple Mendelian inheritance but about understanding the complexities of human genetics.
In conclusion, mastering autosomal pedigrees involves a systematic approach: knowing the symbols, discerning patterns, confirming inheritance modes, and considering the nuances of gene expression. By following these three steps, you'll be well on your way to becoming proficient in interpreting these diagrams, providing invaluable insights into genetic inheritance. Whether for academic pursuits or practical applications in genetic counseling, your ability to analyze pedigrees accurately will be a crucial asset.
What is the difference between autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive inheritance?
+Autosomal dominant inheritance means that only one copy of the gene is needed to express the trait, and typically, each affected person has an affected parent. Autosomal recessive inheritance requires both copies of the gene to be mutated for the trait to be expressed; parents can be carriers without showing symptoms.
Why might a pedigree not show a clear inheritance pattern?
+Pedigrees might not show clear inheritance patterns due to factors like incomplete penetrance, variable expressivity, gene interactions, or environmental influences that can mask or modify trait expression.
How can pedigrees help with genetic counseling?
+Pedigrees can help genetic counselors assess the risk of inheriting or transmitting a genetic condition, predict the likelihood of occurrence in future generations, and guide decisions about genetic testing and family planning.