ATP Activity Worksheet Answer Key: Boost Your Biology Knowledge

ATP, or Adenosine Triphosphate, is fundamental to the energy dynamics of all living organisms. Understanding how ATP works and its role in cellular processes is crucial for students studying biology. To assist in this educational journey, we've compiled an ATP Activity Worksheet Answer Key to help clarify concepts and enhance your understanding of this essential molecule.
Overview of ATP


ATP is known as the “energy currency” of the cell. Here are some key points about ATP:
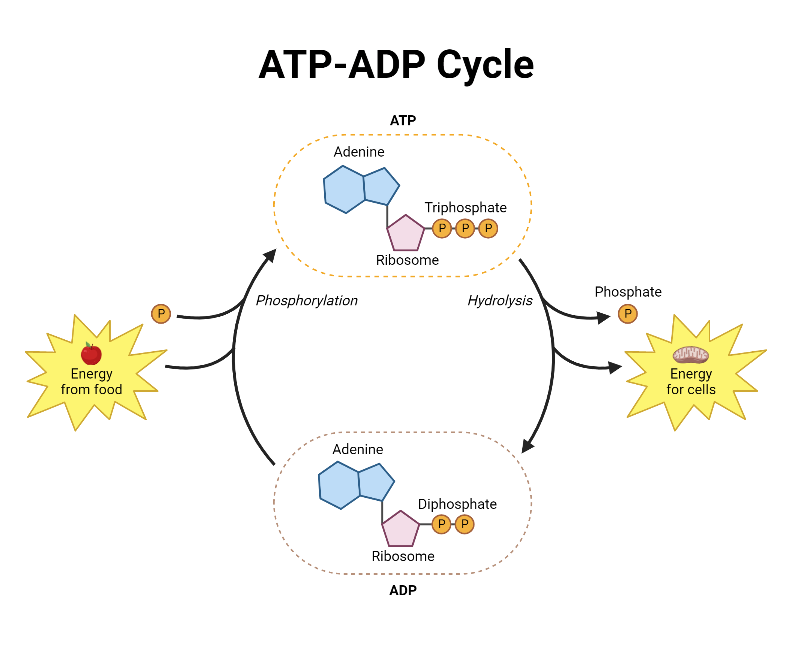
- ATP contains three phosphate groups. When it loses the outermost phosphate group, it becomes ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate), releasing energy.
- This process, known as hydrolysis, is reversible. When ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP, energy is released, which can be used for various cellular processes.
- The energy stored in ATP is in the form of potential chemical energy due to the high-energy bonds between the phosphate groups.
Worksheet Questions and Answers

Below are some common questions from an ATP activity worksheet, along with their answers:
What is ATP?

ATP is:
- Adenosine Triphosphate, a molecule that serves as the main energy source for cellular functions.
- Consists of adenine, ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups.
How does ATP provide energy?

ATP provides energy through:
- Hydrolysis of its terminal phosphate group to form ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi). This process releases energy:
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| ATP Hydrolysis | ATP + H2O ⇌ ADP + Pi + Energy |

💡 Note: This reaction is exergonic, meaning energy is released.
Why is ATP Considered an Energy Carrier?

ATP is:
- Stable enough to store energy for a short time.
- Reactive enough to release energy quickly when needed.
- Produced in high amounts, which makes it readily available in cells.
List the Steps of ATP Synthesis

ATP synthesis, known as oxidative phosphorylation, involves:
- Chemiosmosis: The electrochemical gradient drives protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space.
- Proton Motive Force: Protons flow back into the mitochondrial matrix through the ATP synthase complex.
- ATP Synthase: This enzyme rotates due to the flow of protons, converting ADP to ATP by attaching a phosphate group.
🔧 Note: ATP synthase acts like a molecular turbine powered by protons.
Final Insights
ATP’s role in cellular metabolism cannot be overstated. By understanding how ATP functions, you gain insights into:
- The mechanisms of energy transfer in cells.
- How metabolic pathways are interconnected.
- The importance of various enzymes in ATP production.
This ATP activity worksheet has shed light on the complexities of ATP and should now equip you with a better grasp of its significance in biology. Through this learning process, you not only boost your knowledge but also pave the way for exploring more intricate cellular processes.
What happens when ATP is hydrolyzed?

+
When ATP is hydrolyzed, it breaks down into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi), releasing energy. This energy can be used to perform work within the cell.
Can ATP be regenerated?

+
Yes, ATP can be regenerated from ADP through phosphorylation, primarily occurring during cellular respiration in mitochondria or through other metabolic pathways like glycolysis.
Why does ATP contain high-energy bonds?

+
The high-energy bonds in ATP are due to the electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged phosphate groups. When one is broken, the molecule relaxes to a more stable state, releasing energy.