5 Essential Facts About Atoms and Isotopes
Have you ever wondered what makes up everything around us, from the air we breathe to the walls of our homes? Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, and understanding them is key to unlocking the mysteries of the universe. In this article, we dive into the fascinating world of atoms and isotopes, revealing five essential facts that shape our understanding of matter and its behavior.
1. The Structure of an Atom

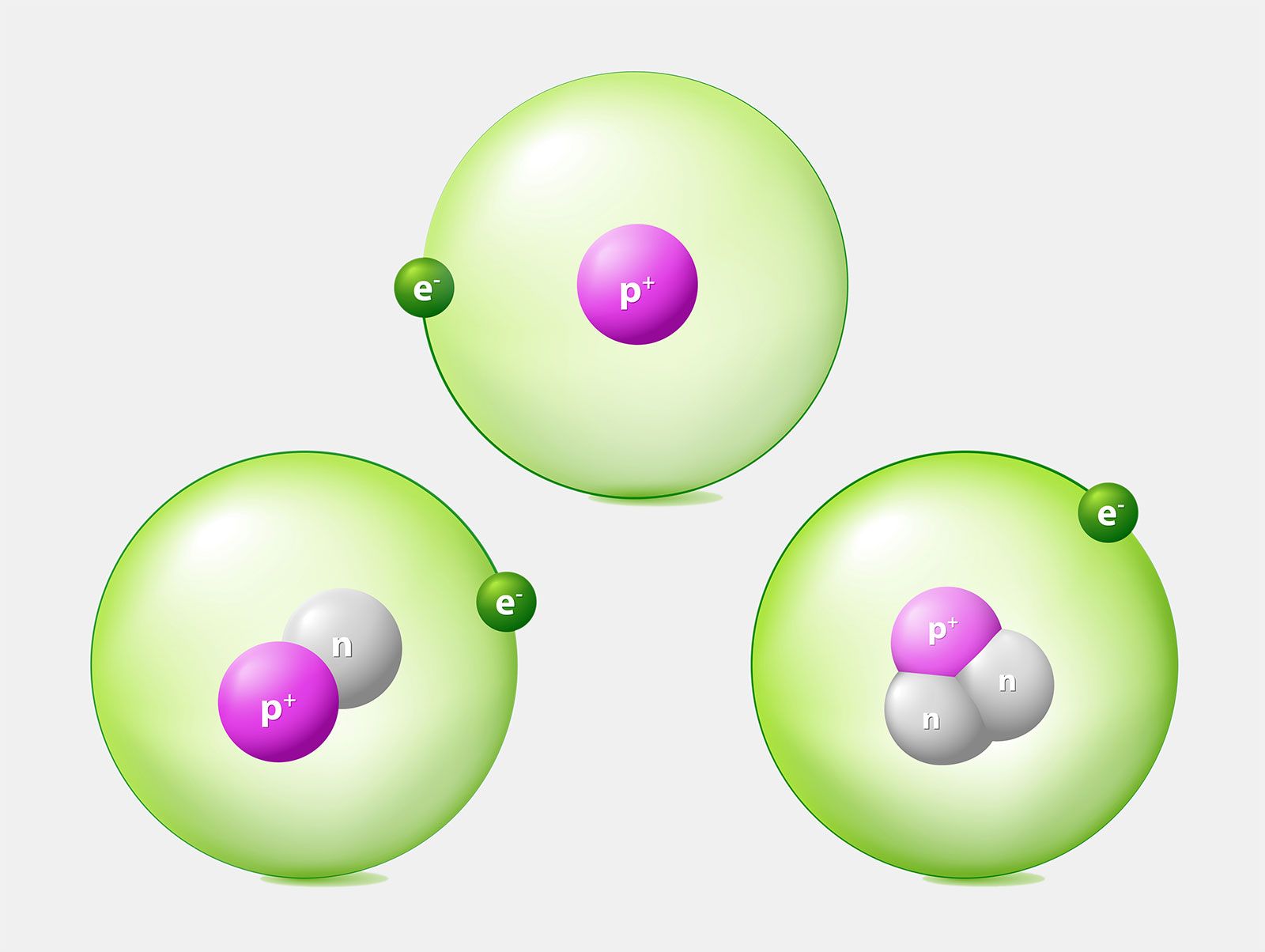
Atoms are incredibly small, so small that they cannot be seen with a traditional microscope. Each atom consists of three primary types of particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the nucleus, the dense center of the atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles also found in the nucleus that add to the atom's mass without affecting its charge.
The number of protons defines the element. For example, all hydrogen atoms have one proton, while oxygen has eight.
🔍 Note: Electrons have a very low mass, with each proton being approximately 1836 times heavier than an electron.

2. What Are Isotopes?

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element. While all isotopes of an element share the same number of protons, they differ in the number of neutrons. Here's what makes them special:
- Isotopes have the same chemical properties since the number of electrons (which governs chemical behavior) remains the same.
- They can have different physical properties due to the difference in atomic mass.
Some well-known isotopes include:
| Element | Isotopes |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H-1 (protium), H-2 (deuterium), H-3 (tritium) |
| Carbon | C-12 (stable), C-14 (radioactive) |
3. The Role of Isotopes in Nature and Science
Isotopes play critical roles in both natural phenomena and scientific research:
- Stable Isotopes: Elements like oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon exist as different isotopes in nature, which helps in climate studies and biological processes.
- Radioactive Isotopes: These isotopes decay over time, which is useful in dating materials, medical diagnostics, and treatment (like cancer therapies).
- Nuclear Reactions: Understanding isotopes is key to nuclear energy and weapons.
🔬 Note: Isotope analysis can reveal secrets about ancient civilizations through techniques like radiocarbon dating.
4. Atomic Number vs. Mass Number

Here's how these concepts differ:
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus, which defines the element.
- Mass Number: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom, also known as the nucleon number.
Although these two numbers might look similar, they have distinct roles:
- Atomic number is constant for a given element.
- Mass number can vary among isotopes, leading to slight variations in atomic mass.
5. The Quantum Nature of Atoms

Quantum mechanics provides a framework for understanding the behavior of atoms at a fundamental level:
- Atoms can exist in various energy states, not just a single state, as predicted by classical physics.
- Electrons occupy orbitals within shells, not precise orbits as might be traditionally visualized.
- The uncertainty principle implies that exact positions and velocities of particles within an atom cannot be simultaneously known with perfect accuracy.
🌀 Note: This quantum nature explains phenomena like atomic spectra and chemical bonding.
As we wrap up our exploration into atoms and isotopes, we recognize their fundamental importance in the fabric of our existence. From the smallest particle to the vast cosmos, the story of atoms is one of transformation, discovery, and an ongoing quest to understand the very essence of the universe. Whether you're studying chemistry, physics, or simply curious about the building blocks of life, these five facts provide a solid foundation for appreciating the intricacies of matter. So next time you take a breath or touch an object, remember the billions of atoms and isotopes that make that experience possible, each with its own unique story to tell.
What defines an element?

+
An element is defined by the number of protons in its nucleus, also known as the atomic number. For example, an atom with one proton is always hydrogen, regardless of its neutron count.
Can isotopes change into each other?

+
While isotopes of an element can naturally exist in different forms, one isotope cannot directly transform into another isotope with a different number of neutrons. However, through nuclear reactions or radioactive decay, changes can occur.
How do isotopes affect everyday life?

+
Isotopes impact our lives in numerous ways: from energy production in nuclear power plants to medical imaging, treatment of diseases, and even preserving food. They are also crucial in archeology and forensics for dating materials.



