Atomic Structure Worksheet: Easy Answers for Better Learning
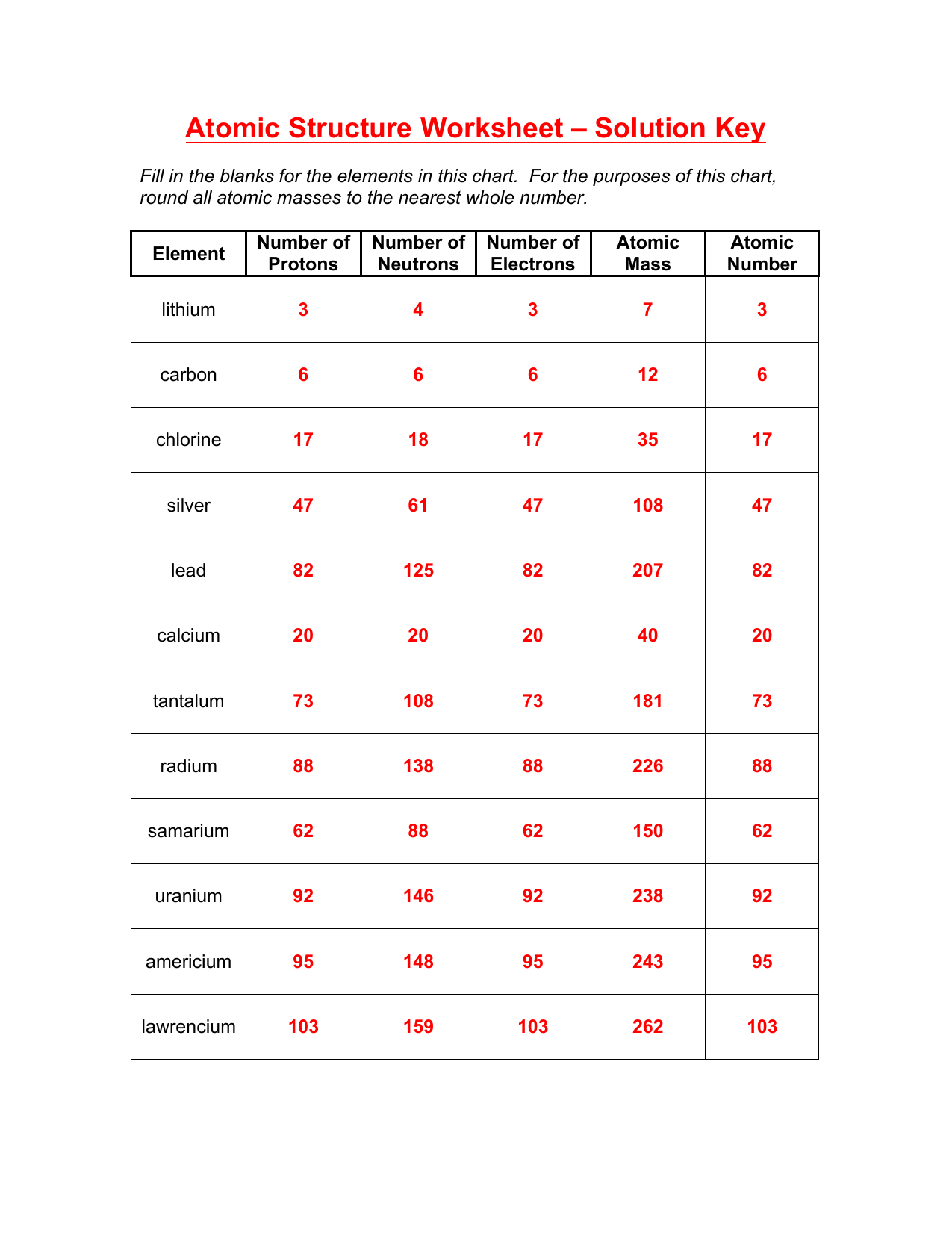
Understanding the atomic structure is fundamental in the field of chemistry. It serves as the building block for more complex chemical concepts and reactions. For students and enthusiasts alike, a worksheet on atomic structure provides a hands-on way to engage with these principles. In this blog post, we'll explore some easy and straightforward approaches to answering atomic structure questions, making the learning process more accessible and enjoyable.
Key Components of an Atom

Before diving into worksheets and quizzes, let’s quickly review the basic elements of atomic structure:
- Nucleus: Contains protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral).
- Protons: Determine the element’s atomic number.
- Neutrons: Help stabilize the nucleus and can vary, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Orbit the nucleus in shells, contributing to the atom’s reactivity and chemical properties.

Atomic Structure Worksheet: Easy Steps to Follow

Here are some steps you can take when tackling an atomic structure worksheet:
- Identify the Element: Look for the atomic number to determine which element you’re dealing with.
- Count Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons:
- Protons = atomic number
- Neutrons = mass number - atomic number
- Electrons = number of protons for a neutral atom
- Determine the Atomic Mass: This is often given or you can find it on a periodic table.
- Isotope Considerations: Remember isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
📌 Note: If the mass number is not given, you might have to work with the atomic weight to approximate the most common isotope.
Common Questions and Answers

Here are some common questions students might encounter on atomic structure worksheets, along with easy answers:
How do you determine the number of neutrons?

The number of neutrons is the mass number of the element (A) minus the atomic number (Z). Here’s how you can represent this:
| Element | Atomic Number (Z) | Mass Number (A) | Number of Neutrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen-14 | 7 | 14 | 7 |
| Carbon-12 | 6 | 12 | 6 |

What is an isotope?

Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. For example, both hydrogen-1 and hydrogen-2 (deuterium) are isotopes of hydrogen.
📌 Note: Understanding isotopes is crucial in fields like nuclear chemistry and radiology.
Visualizing Atomic Structure
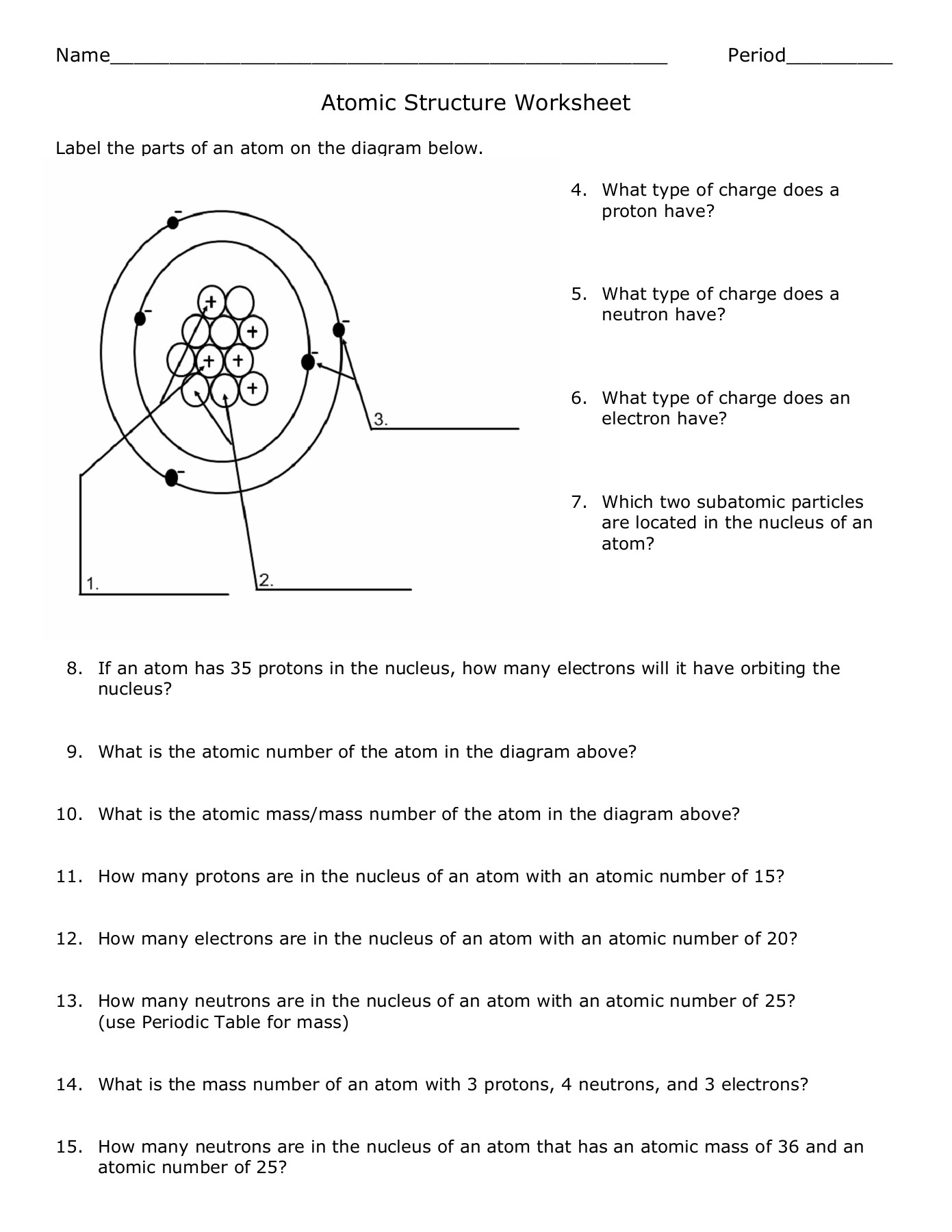
Visual aids can significantly enhance the learning experience. Here’s how to visualize an atom:
- Bohr Model: Depicts electrons in fixed orbits around the nucleus.
- Electron Cloud Model: Represents probability clouds where electrons are likely to be found.

Memory Aids and Mnemonics

To make learning atomic structure more engaging, you can use memory aids:
- PEN: Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons - easy to remember as “Protons Enter Nucleus”.
- Atomic Number vs. Mass Number: Think “Z” for zip code (atomic number) and “A” for apartment number (mass number).
📌 Note: These mnemonics not only help in memorizing but also in understanding the roles of protons, electrons, and neutrons.
Common Misconceptions

Here are some common misconceptions about atomic structure:
- Electrons orbit the nucleus like planets: Electrons exist in probability clouds.
- Neutrons determine element: Protons, not neutrons, determine what element it is.
- All atoms are neutral: This is true only for uncharged atoms. Ions have a net charge due to unequal electron-proton balance.
📌 Note: Dispelling these misconceptions early can prevent confusion as more advanced concepts are introduced.
By following these easy steps and understanding the key components of atomic structure, you can tackle atomic structure worksheets with confidence. This foundational knowledge will serve as a bedrock for further exploration into the fascinating world of chemistry. Whether you're a student, a hobbyist, or an enthusiast, a clear grasp of atomic structure enhances the understanding of how our physical world functions at the most basic level. Remember, chemistry is all about making connections between atoms, and with each worksheet, you're building those connections one atom at a time.
Why are neutrons important in an atom?

+
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus of an atom by balancing the repulsion between protons, making the atom more stable. They also play a critical role in nuclear reactions and determining isotopes.
How do you find the atomic number of an element?

+
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which can be found on the periodic table as the number above or beside the element symbol.
What’s the difference between an atom and an ion?
+
An atom is neutral with an equal number of protons and electrons. An ion has either gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
How can I visualize the electron cloud?

+
Electron clouds can be visualized as probability distributions or densities of where electrons might be found around the nucleus, as opposed to fixed orbits.
Is the atomic weight the same as the mass number?

+
No, the atomic weight (or atomic mass) is the average mass of all the element’s isotopes, weighted by their natural abundance. The mass number refers to the sum of protons and neutrons in a specific isotope.