Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers: Clear and Simple Guide

Atomic structure is a foundational topic in chemistry that often causes confusion among students due to its intricate nature. Understanding the arrangement and behavior of atoms is crucial not only for academic purposes but also for comprehending various chemical reactions. This detailed guide aims to clarify the complex aspects of atomic structure with simple explanations and concise answers for worksheet queries.
What is an Atom?

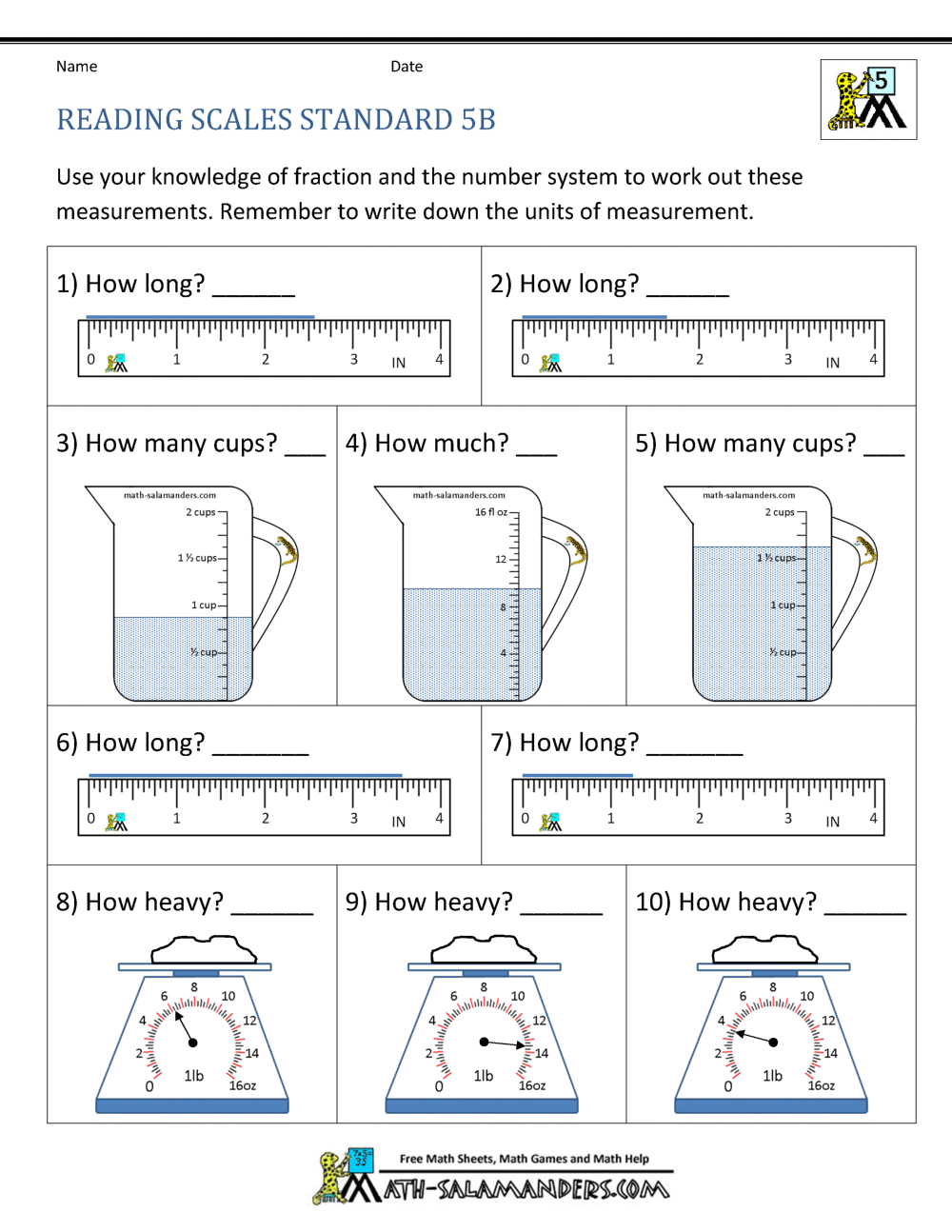
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Each atom consists of a central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons:
- Nucleus: Composed of protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral).
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
Atomic Number and Mass Number

The atomic number defines an element, indicating the number of protons in its nucleus:
- If an atom has an atomic number of 6, it is carbon.
The mass number, on the other hand, gives the total number of protons and neutrons:
- Subtracting the atomic number from the mass number provides the number of neutrons.
Isotopes, Ions, and the Periodic Table

Isotopes
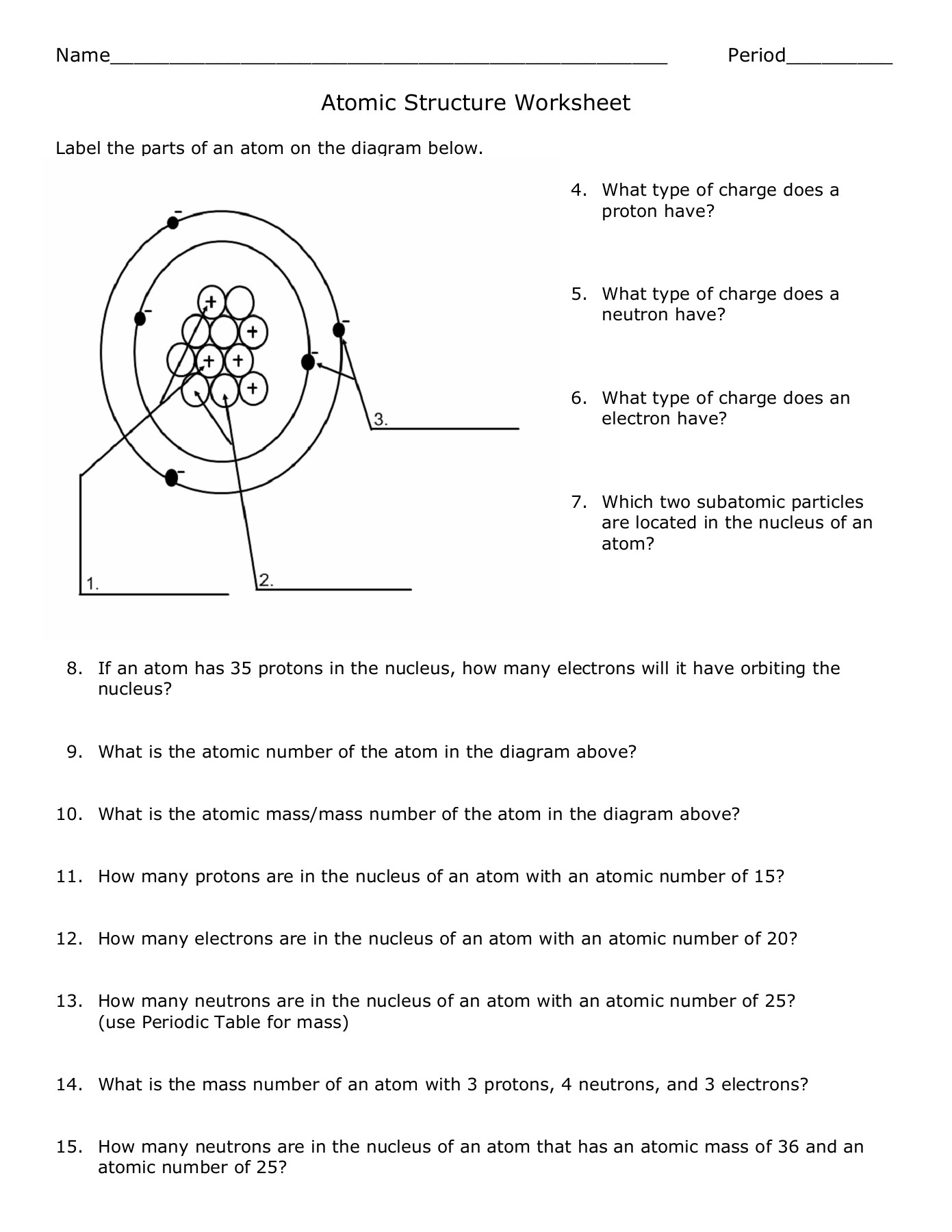
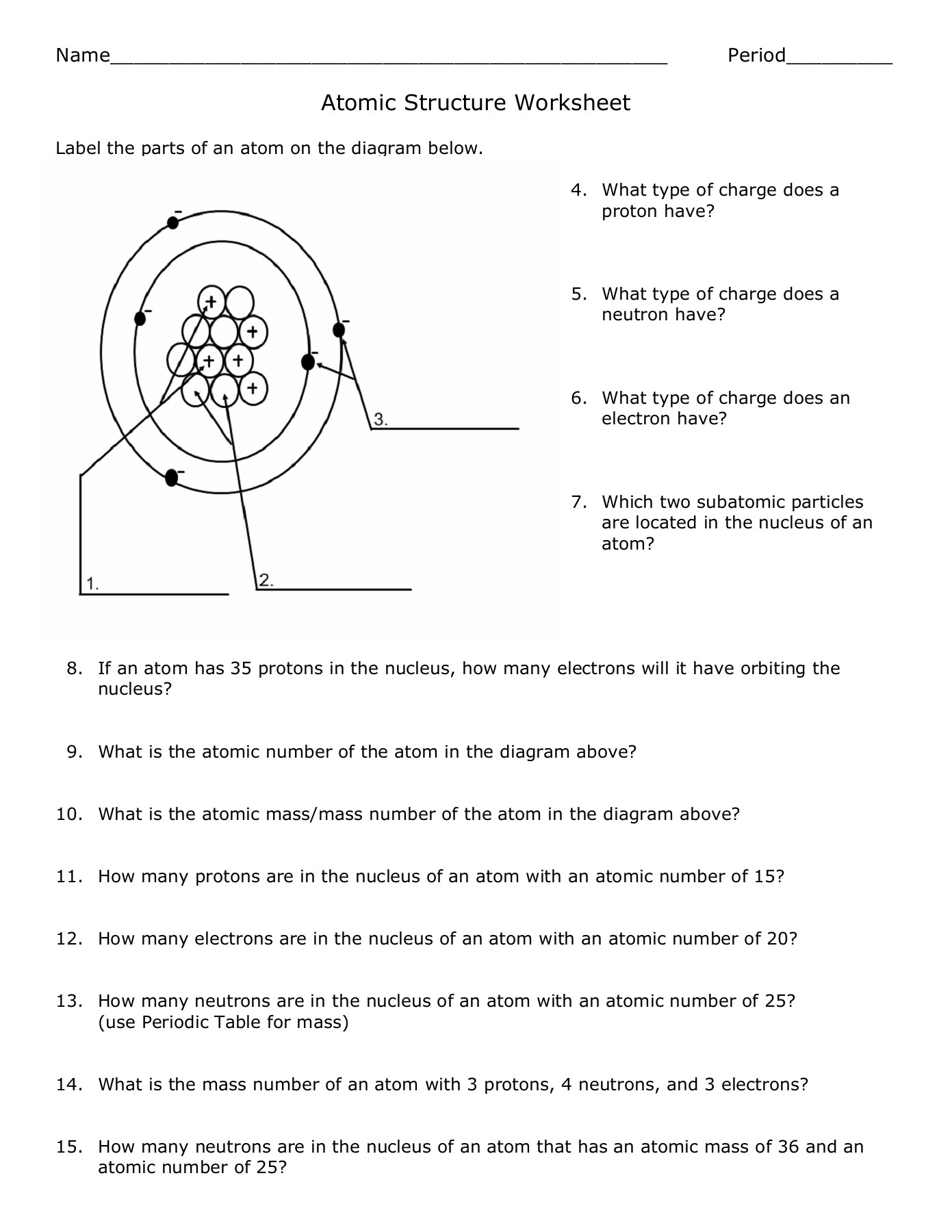
Isotopes are variations of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This leads to variations in mass number:
| Element | Isotopes | Atomic Number | Mass Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H-1, H-2, H-3 | 1 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Carbon | C-12, C-14 | 6 | 12, 14 |

Ions

An ion forms when an atom gains or loses electrons, leading to a charge:
- Cation: Positively charged ions due to the loss of electrons.
- Anion: Negatively charged ions due to the gain of electrons.
Electron Configuration
Electrons are arranged in energy levels or shells around the nucleus. The configuration can be represented in various ways:
- Orbital Diagrams: Visualizes how electrons occupy orbitals.
- Electron Configuration Notation: 1s2 2s2 2p6…
Valence Electrons and Reactivity

Valence electrons are those in the outermost shell of an atom, playing a critical role in:
- Chemical bonding
- Reactivity
The number of valence electrons dictates an element’s chemical behavior, influencing its ability to form bonds:
- Metals: Generally lose electrons to achieve stability.
- Non-metals: Usually gain or share electrons.
🚀 Note: The Periodic Table groups elements by their electron configurations, which can help in understanding valence electrons.
Worksheet Answers

Here are straightforward answers to common atomic structure worksheet questions:
- Question 1: What is the atomic number of Oxygen?
- Answer: 8
- Question 2: How many neutrons does a Carbon-14 atom have?
- Answer: Mass Number (14) - Atomic Number (6) = 8 neutrons
- Question 3: Define isotope and provide an example.
- Answer: Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. Example: Oxygen-16 and Oxygen-18.
- Question 4: Explain why atoms are neutral.
- Answer: Atoms have an equal number of protons (positively charged) and electrons (negatively charged), resulting in overall neutrality.
Understanding atomic structure allows us to appreciate the complexity of matter and the foundation of chemical reactions. By mastering these concepts, students can better comprehend why elements behave the way they do, their placement in the Periodic Table, and their interactions in forming compounds. This knowledge is fundamental for anyone venturing into the realms of chemistry and beyond. Keep in mind that chemistry is an ever-evolving field, and keeping up with advances will continue to deepen our understanding of atomic structures.
Why do different isotopes have different mass numbers?

+
Different isotopes of the same element have varying numbers of neutrons. Since neutrons contribute significantly to the mass of an atom (protons and neutrons both have roughly the same mass), changing the number of neutrons directly alters the atom’s mass number.
How does the loss or gain of electrons affect an atom’s charge?

+
When an atom loses electrons, it has more protons than electrons, resulting in a positive charge, forming a cation. Conversely, when an atom gains electrons, it has more electrons than protons, creating a negative charge, forming an anion.
What is the significance of electron configuration?

+
Electron configuration gives insights into how electrons fill up energy levels or orbitals within an atom. This arrangement influences an element’s properties, like its reactivity, bond formation, and chemical behavior.