Atomic Basics Worksheet Answer Key Revealed: Master Chemistry Easily
If you're struggling with the concept of atomic structure and the periodic table, you're not alone. Mastering chemistry can seem daunting, but understanding the atomic basics is crucial for success. In this post, we'll dive deep into the Atomic Basics Worksheet Answer Key, providing clear explanations and insights to help you easily grasp fundamental chemistry concepts.
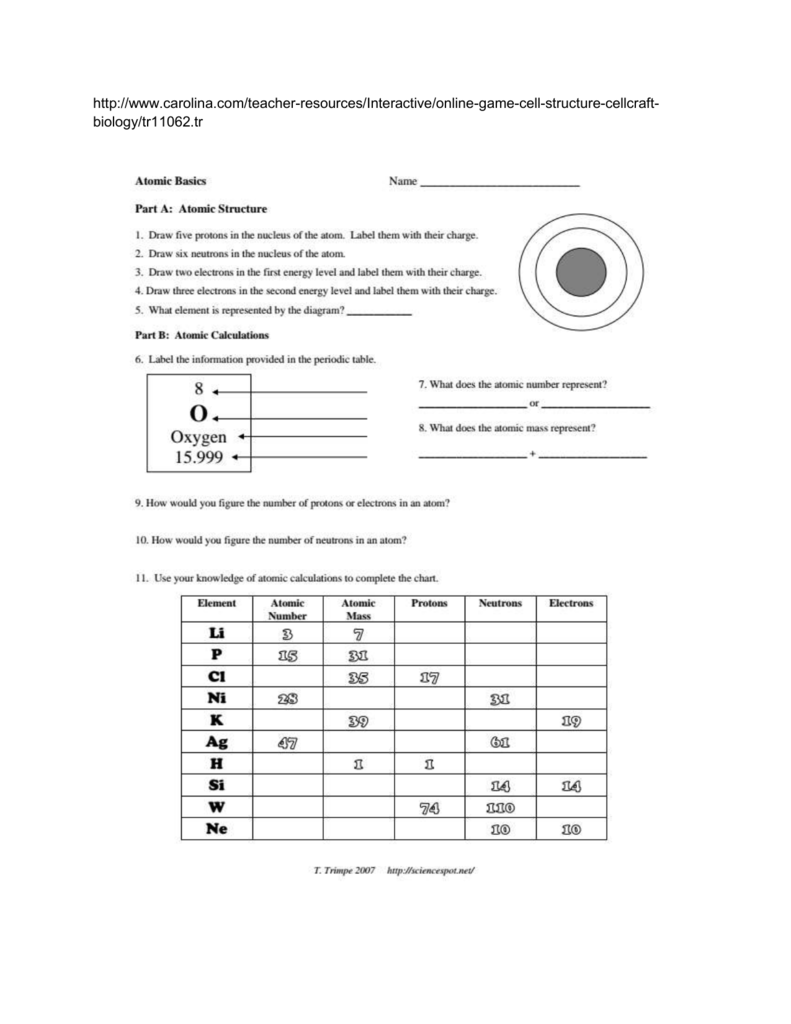
What are Atoms and Their Subatomic Particles?

An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Each atom consists of three primary types of subatomic particles:
- Protons: These positively charged particles reside in the nucleus of the atom. They help determine the atomic number.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbit the nucleus. Their interaction is what primarily determines an atom's chemical behavior.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles found in the nucleus alongside protons. They affect the atom's mass without altering its chemical properties.

Understanding Atomic Mass and Atomic Number

Atoms are characterized by their atomic number and atomic mass:
- Atomic Number: This is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, uniquely defining the element. For example, Hydrogen has an atomic number of 1.
- Atomic Mass: The sum of protons and neutrons within an atom's nucleus. It's crucial for understanding isotopic variations. Here's a simple table to illustrate:
| Element | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1.008 |
| Helium (He) | 2 | 4.003 |
| Carbon (C) | 6 | 12.011 |

🔍 Note: While the atomic number is always an integer, the atomic mass can be a decimal due to isotopic presence in natural samples.
Isotopes: The Same Element, Different Masses

Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This variation does not change the chemical properties but alters the atom's mass:
- For instance, 12C and 14C are isotopes of carbon. Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons, while Carbon-14 has 8 neutrons.
Periodic Table Organization

The periodic table is organized based on atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties:
- Periods: Rows on the table, where elements within the same row have the same number of electron shells.
- Groups: Columns that indicate elements with similar chemical properties due to the same number of valence electrons.
- Elements are also categorized into metals, non-metals, and metalloids based on their physical and chemical behaviors.

Working Through the Atomic Basics Worksheet

Here's how you might answer key questions in an atomic basics worksheet:
- Identify the element: Given the atomic number, locate it on the periodic table.
- Calculate the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons:
- Protons = Atomic Number
- Electrons = Protons (for neutral atoms)
- Neutrons = Atomic Mass - Protons
- Isotope identification: Recognize that elements might have different isotopes by comparing their atomic masses to their atomic numbers.
To illustrate, let's work through an example:
- Element A has an atomic number of 15. What is the element, and how many protons, electrons, and neutrons does its neutral atom have if its atomic mass is 30.97?
- Element: Phosphorus (P)
- Protons: 15
- Electrons: 15 (assuming the atom is neutral)
- Neutrons: 30.97 - 15 ≈ 16
Conclusion

We've navigated through the atomic basics by dissecting the answer key of an atomic basics worksheet. Understanding protons, electrons, and neutrons, along with atomic numbers and masses, provides the foundation for more complex chemical concepts. Isotopes introduce the idea that not all atoms of an element are identical, and the periodic table organizes these elements in a meaningful way. By focusing on these fundamentals, you'll find that mastering chemistry becomes significantly more manageable. Keep practicing with these worksheets, and soon, the language of atoms will become second nature to you.
What’s the difference between an element’s atomic number and atomic mass?

+
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which defines the element. The atomic mass, however, includes the sum of protons and neutrons, providing a measure of the atom’s mass.
Why do isotopes have the same atomic number but different masses?

+
Isotopes have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons, which doesn’t change the element’s identity but affects its mass.
How does the periodic table help in understanding atomic basics?

+
The periodic table organizes elements by their atomic number, electron configuration, and shared properties, making it easier to grasp trends and relationships among elements.