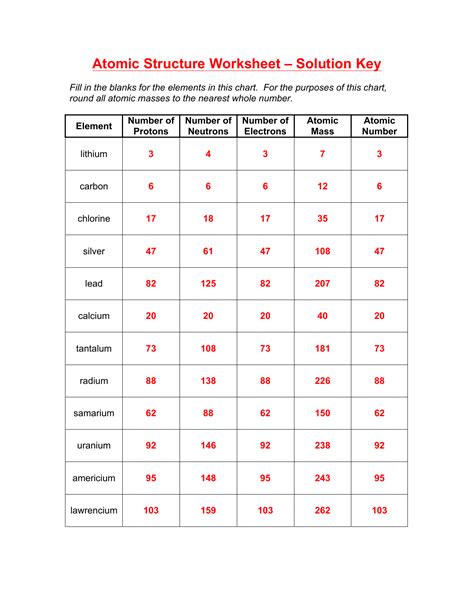
5 Ways to Master Atom Structure Worksheets
Understanding the Atom: A Fundamental Concept in Chemistry

The atom is the building block of matter, and understanding its structure is essential for any student of chemistry. Atom structure worksheets are an excellent way to help students visualize and comprehend the atom’s components and their relationships. In this article, we will explore five ways to master atom structure worksheets, making it easier for students to grasp this fundamental concept in chemistry.
1. Start with the Basics: Understanding the Subatomic Particles

Before diving into atom structure worksheets, it’s crucial to understand the three subatomic particles that make up an atom: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus (center) of the atom.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus along with protons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
| Subatomic Particle | Charge | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Proton | Positive | Nucleus |
| Neutron | Neutral | Nucleus |
| Electron | Negative | Orbits the nucleus |

🔍 Note: The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, while the number of neutrons can vary, leading to different isotopes of the same element.
2. Visualize the Atom: Using Diagrams and Models
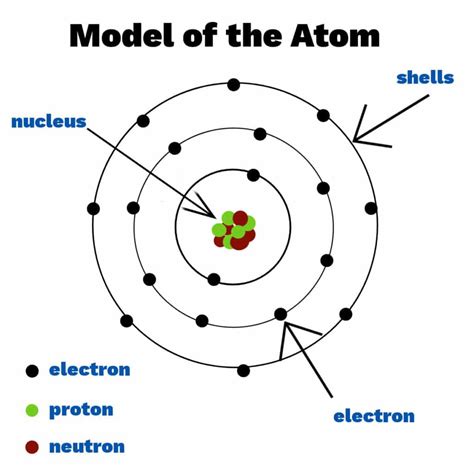
Atom structure worksheets often include diagrams or models of the atom. These visual aids help students understand the relationships between the subatomic particles and the overall structure of the atom.
- Bohr Model: A simplified model of the atom that shows the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, surrounded by electrons in energy levels or shells.
- Electron Cloud Model: A more advanced model that depicts the electrons as a cloud of probability around the nucleus.

3. Practice, Practice, Practice: Atom Structure Worksheets

The best way to master atom structure worksheets is through practice. Students can use online resources or worksheets provided by their teacher to practice drawing and labeling diagrams of the atom.
- Labeling Diagrams: Identify and label the subatomic particles, nucleus, and energy levels.
- Completing Tables: Fill in tables with information about the subatomic particles, such as charge, location, and number.
📝 Note: Encourage students to use different colors to highlight different parts of the atom, making it easier to visualize and understand the structure.
4. Apply Real-World Examples: Connecting the Atom to Everyday Life

To make the concept of atom structure more engaging and relevant, students can explore real-world examples that demonstrate the importance of understanding the atom.
- Materials Science: Understanding the atom’s structure helps us develop new materials with unique properties, such as nanomaterials and semiconductors.
- Energy Applications: Knowledge of the atom’s structure is crucial for developing new energy sources, such as nuclear power and solar cells.
5. Collaborate and Review: Working with Peers and Reviewing Key Concepts

Finally, students can benefit from collaborating with their peers and reviewing key concepts to reinforce their understanding of atom structure.
- Peer Review: Students can work in pairs or groups to review and provide feedback on each other’s worksheets.
- Key Concept Review: Regular review of key concepts, such as the subatomic particles and their relationships, can help solidify students’ understanding of the atom’s structure.
In summary, mastering atom structure worksheets requires a combination of understanding the basics, visualizing the atom, practicing with worksheets, applying real-world examples, and collaborating with peers. By following these five ways, students can develop a deeper understanding of the atom’s structure and its significance in chemistry.
In the end, a strong grasp of atom structure is essential for building a solid foundation in chemistry. By using these five strategies, students can develop a deeper understanding of the atom and its importance in the world around us.
Related Terms:
- Atomic Structure
- Periodic table
- Atom
- Chemical Bond
- Chemical reaction
- Chemical equilibrium