5 Essential Answers to Atom Structure Worksheet Queries
Exploring the fundamental building blocks of matter can be both fascinating and challenging.
Whether you're a student striving to understand the basic principles of chemistry or an educator looking to assist students in grasping these concepts, the structure of an atom is a pivotal topic to master. This article delves deep into common queries surrounding atom structure worksheets, providing comprehensive answers to aid your learning or teaching journey.
What is an Atom Structure Worksheet?
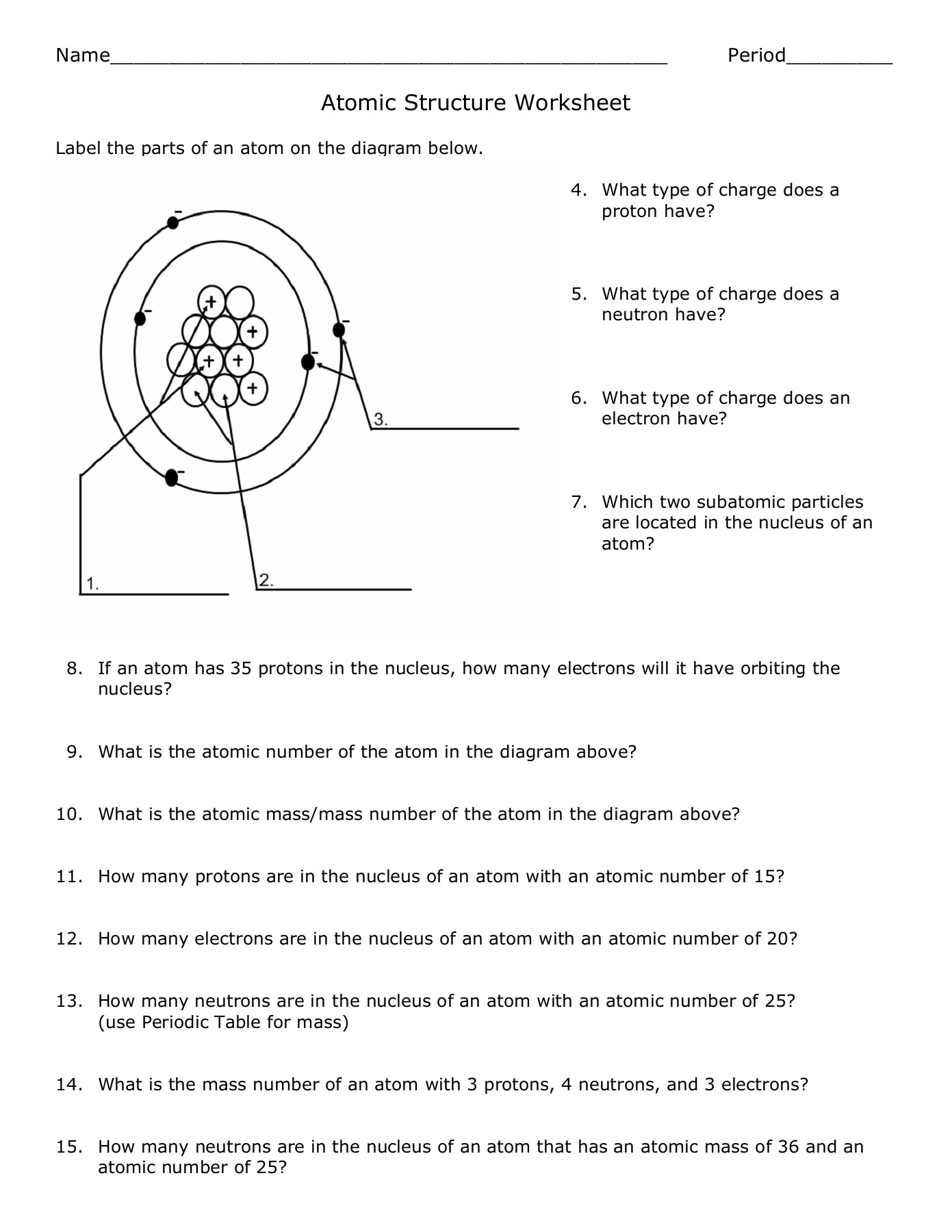
An atom structure worksheet serves as an educational tool designed to help students understand the composition of atoms. Here's what you can typically expect to find in such a worksheet:
- Atomic Models: Illustrations or diagrams of different atomic models, like the Bohr model or the Quantum Mechanical Model.
- Subatomic Particles: Questions related to protons, neutrons, and electrons, including their charges, locations within the atom, and their roles.
- Atomic Number and Mass: Problems that involve calculating atomic mass or understanding the significance of atomic numbers.
- Isotopes: Exploring variations within elements by discussing isotopes, their properties, and how to calculate isotopic abundance.
These worksheets aim to solidify the students' knowledge about atoms through hands-on activities and thought-provoking questions.
Understanding Atomic Structure

Before we proceed to the detailed answers, let's briefly review what constitutes an atom:
- Nucleus: Central part of the atom containing protons and neutrons. It's positively charged due to protons and is heavy compared to the rest of the atom.
- Protons: Positively charged particles with a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
- Neutrons: Neutral particles, also with a mass of about 1 amu, present in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in electron shells. They have negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons.
This basic understanding is essential for answering questions typically found on atom structure worksheets.
Essential Answers to Common Atom Structure Worksheet Queries

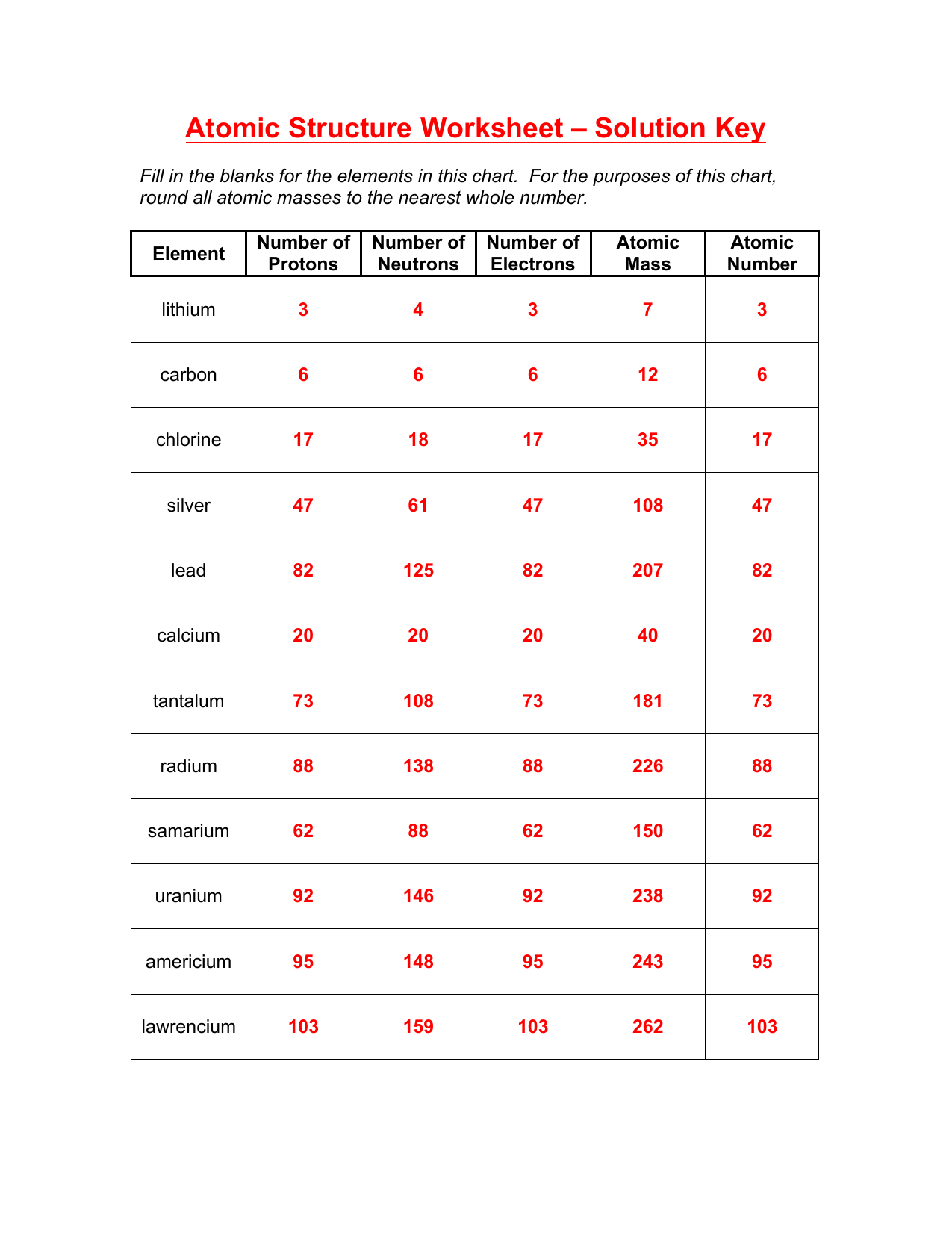
1. How Do You Determine the Number of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons in an Atom?

Atomic Number: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus is the atomic number. This is also the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
Mass Number: The sum of protons and neutrons gives the mass number. To find the number of neutrons, subtract the atomic number from the mass number.
Neutrons Calculation: Mass Number - Atomic Number = Number of Neutrons
Electrons: In neutral atoms, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. For ions, adjust based on the ion charge.
2. What are Isotopes and How Do We Represent Them?

Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, leading to different mass numbers but identical chemical properties due to the same number of protons:
- Representation: Isotopes are written in the form Element Symbol Mass Number-Atomic Number. For example, Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are 12C and 14C.
- Isotopic Abundance: This refers to the natural occurrence percentages of an isotope of an element.
3. How Does Electron Configuration Work?

Electron configuration describes how electrons are distributed into the various atomic orbitals. Here are key points:
- Principal Energy Levels: Electrons occupy shells (K, L, M, N, etc.), each with an increasing number of electrons it can hold.
- Subshells: Within each energy level, subshells (s, p, d, f) are present, each with different energy and shape.
- Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill lower energy orbitals before higher ones.
- Hund’s Rule: When filling orbitals, electrons occupy each with one electron before pairing up.
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two electrons can have identical quantum numbers, thus sharing the same energy level.
Example of electron configuration for neon (Atomic Number 10): 1s22s22p6.
4. What are the Differences Between Atomic Models?

Here’s a table comparing major atomic models:
| Model | Description | When |
|---|---|---|
| Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model | Atom is a positively charged sphere with embedded electrons. | Early 20th century |
| Rutherford’s Planetary Model | Atom has a small, dense, positively charged nucleus with electrons orbiting. | 1911 |
| Bohr’s Model | Electrons orbit the nucleus in defined energy levels or orbits. | 1913 |
| Quantum Mechanical Model | Electrons exist in probability clouds or orbitals, with energy levels and subshells. | Mid-20th century |

Each model contributes to our understanding of atomic structure, showing the progression from simple to complex atom descriptions.
5. How Do You Balance Nuclear Reactions?

Balancing nuclear reactions involves ensuring conservation of charge (atomic number) and mass (mass number). Here are the steps:
- Write out the equation, including the unknown particle.
- Sum the atomic numbers (protons) on both sides.
- Sum the mass numbers on both sides.
- Solve for the unknown particle using the balance equations.
An example:
238U 92 -> 4He 2 + 234Th 90 + X
Balancing the atomic and mass numbers gives you the identity of X as a gamma ray (γ).
Understanding these concepts will aid in tackling complex atom structure worksheet queries effectively.
How do I calculate the atomic mass of an element?

+
To calculate the atomic mass of an element, multiply the mass of each isotope by its relative abundance and then sum these products. The formula is:
Atomic Mass = (Isotope 1 Mass × Isotope 1 Abundance) + (Isotope 2 Mass × Isotope 2 Abundance) + …
⚗️ Note: The abundances should be expressed as decimal fractions, not percentages.
Why is electron configuration important?

+
Electron configuration determines an atom’s chemical properties, reactivity, and how it will form bonds. It also gives insights into the atom’s energy levels, ionization energy, and the types of reactions it can undergo.
What are some applications of isotopes?
+
Isotopes have numerous applications:
- Medical: Used in radioactive tracers for diagnosis and in treatment.
- Industrial: For leak detection, measuring thickness or level, and as radiation sources.
- Environmental: For dating purposes like carbon-14 dating or tracing water movement.
- Nuclear Energy: Heavy isotopes like uranium-235 are used for nuclear fission.