Army Special Forces Medic: Elite Warrior Healers
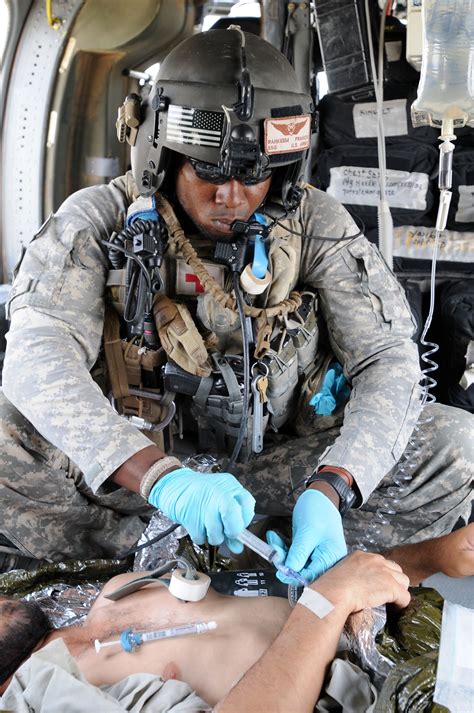
Army Special Forces Medic: Elite Warrior Healers

In the world of special operations, the Army Special Forces Medic is a highly trained and elite warrior-healer. These medics are part of the United States Army Special Forces, also known as the Green Berets, and are trained to provide medical care in the most challenging and hostile environments. Their unique blend of combat and medical skills makes them an invaluable asset to their teammates and a force to be reckoned with on the battlefield.
Selection and Training

To become an Army Special Forces Medic, a candidate must first meet the basic requirements of the Army Special Forces. This includes being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 20 and 35, and scoring a minimum of 110 on the general technical section of the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test. Candidates must also complete Basic Combat Training (BCT), Advanced Individual Training (AIT), and the Special Forces Assessment and Selection (SFAS) course.
Once selected, candidates attend the Special Forces Qualification Course (SFQC), also known as the “Q Course,” which is a grueling 53-week training program that pushes candidates to their limits. The course includes training in unconventional warfare, foreign languages, and advanced first aid.
Medics who complete the SFQC are then assigned to a Special Forces Operational Detachment-Alpha (ODA), also known as an “A-Team.” These teams are the basic building block of the Special Forces and consist of 12-15 soldiers, each with a unique skill set.
Skills and Qualifications

Army Special Forces Medics are trained in a wide range of skills, including:
- Advanced first aid and trauma care
- Surgery and suturing
- Pharmacology and medication administration
- Medical evacuation and transportation
- Patient assessment and diagnosis
- Disease prevention and control
- Combat skills, including marksmanship and tactics
They are also qualified in a variety of specialized skills, such as:
- Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS)
- Pediatric advanced life support (PALS)
- Basic life support (BLS)
- Combat casualty care (C4)
- Tactical combat casualty care (TCCC)
Equipment and Resources

Army Special Forces Medics are equipped with a variety of medical supplies and equipment, including:
- Individual first aid kits (IFAKs)
- Squad-level medical kits
- Team-level medical kits
- Portable defibrillators
- Ventilators
- Suture kits
- Medications and pharmaceuticals
They also have access to a range of medical resources, including:
- Medical evacuation aircraft (MEDEVAC)
- Forward operating bases (FOBs)
- Combat support hospitals (CSH)
- Field hospitals
Tactical Medicine

Army Special Forces Medics are trained in the principles of tactical medicine, which emphasizes the importance of providing medical care in a combat environment while also taking into account the tactical situation. This includes:
- Providing medical care under fire
- Evacuating patients in a combat environment
- Using cover and concealment to protect patients
- Working with limited resources and equipment
- Making tough decisions in high-stress situations
Combat Experience

Army Special Forces Medics have seen extensive combat in a variety of theaters, including:
- Afghanistan
- Iraq
- Vietnam
- Korea
- Latin America
They have worked alongside other special operations forces, including the Navy SEALs, the Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), and the Marine Corps Forces Special Operations Command (MARSOC).
Conclusion

The Army Special Forces Medic is a highly trained and elite warrior-healer who plays a critical role in the success of special operations missions. With their advanced medical skills and combat training, they are able to provide life-saving care in the most challenging environments. Whether working in a combat zone or providing humanitarian aid, the Army Special Forces Medic is a true hero and a credit to the U.S. military.
What is the role of an Army Special Forces Medic?

+
The role of an Army Special Forces Medic is to provide medical care to their teammates and allies in a combat environment. They are trained in advanced first aid and trauma care, as well as combat skills and tactics.
How do Army Special Forces Medics receive their training?

+
Army Special Forces Medics receive their training through the Special Forces Qualification Course (SFQC), also known as the “Q Course.” This 53-week training program includes training in unconventional warfare, foreign languages, and advanced first aid.
What kind of equipment and resources do Army Special Forces Medics have access to?

+
Army Special Forces Medics have access to a range of medical supplies and equipment, including individual first aid kits (IFAKs), squad-level medical kits, and team-level medical kits. They also have access to medical evacuation aircraft (MEDEVAC), forward operating bases (FOBs), and combat support hospitals (CSH).