Army Reserve Pay Scale
Understanding the Army Reserve Pay Scale

The Army Reserve is a part of the United States Army that allows individuals to serve their country on a part-time basis. Members of the Army Reserve typically attend drills one weekend per month and participate in a two-week annual training session. In return for their service, Army Reserve members are paid according to a specific pay scale. This pay scale is based on a variety of factors, including the member’s rank, time in service, and the number of drill periods attended.
Factors Affecting Army Reserve Pay

There are several factors that affect the pay of Army Reserve members. These include: * Rank: The member’s rank is a major factor in determining their pay. Higher-ranked members earn more than lower-ranked members. * Time in Service: The amount of time a member has served in the Army Reserve also affects their pay. Members with more time in service earn more than those with less time in service. * Drill Periods: Army Reserve members are paid for each drill period they attend. A drill period is typically one weekend per month. * Annual Training: Members are also paid for their annual training sessions, which are usually two weeks long.
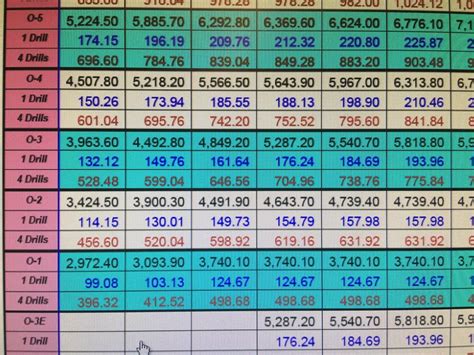
Army Reserve Pay Scale

The Army Reserve pay scale is based on the member’s rank and time in service. The following table shows the typical pay scale for Army Reserve members:
| Rank | Drill Pay per Month | Annual Training Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Private (E-1) | 262.20</td> <td>3,146.40 | |
| Private Second Class (E-2) | 309.30</td> <td>3,711.60 | |
| Private First Class (E-3) | 357.40</td> <td>4,288.80 | |
| Specialist/Corporal (E-4) | 406.50</td> <td>4,878.00 | |
| Sergeant (E-5) | 457.60</td> <td>5,471.20 | |
| Staff Sergeant (E-6) | 513.70</td> <td>6,164.40 | |
| Sergeant First Class (E-7) | 573.80</td> <td>6,865.60 | |
| Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (E-8) | 637.90</td> <td>7,674.80 | |
| Sergeant Major (E-9) | 705.00</td> <td>8,460.00 |

Note that these figures are subject to change and may not reflect the current pay scale.
Benefits of Serving in the Army Reserve

In addition to the pay, there are several benefits to serving in the Army Reserve. These include: * Education Benefits: The Army Reserve offers education benefits, including the Montgomery GI Bill and the Army Reserve Education Assistance Program. * Healthcare Benefits: Army Reserve members are eligible for healthcare benefits through TRICARE. * Retail Benefits: Members can shop at military bases and take advantage of tax-free shopping. * Civilian Career Opportunities: Serving in the Army Reserve can provide valuable skills and experience that can be applied to civilian careers.
💡 Note: The pay scale and benefits of serving in the Army Reserve are subject to change, so it's essential to check with the Army Reserve for the most up-to-date information.
How to Join the Army Reserve
To join the Army Reserve, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements, including: * Being a U.S. citizen or permanent resident * Being between the ages of 17 and 35 * Meeting physical and medical standards * Having a high school diploma or equivalent * Passing the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test * Completing basic training and advanced individual training
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
The Army Reserve pay scale is an important consideration for individuals who are thinking about joining the Army Reserve. While the pay may not be as high as that of active duty soldiers, it can still provide a valuable source of income and benefits. Additionally, serving in the Army Reserve can provide a sense of pride and fulfillment, as well as opportunities for education and career advancement. By understanding the factors that affect Army Reserve pay and the benefits of serving, individuals can make informed decisions about their military service.
How often do Army Reserve members get paid?

+
Army Reserve members are paid for each drill period they attend, which is typically one weekend per month. They also receive pay for their annual training sessions.
Can Army Reserve members use their education benefits to pursue higher education?
+
Yes, Army Reserve members can use their education benefits to pursue higher education. The Montgomery GI Bill and the Army Reserve Education Assistance Program provide financial assistance for tuition, fees, and other education-related expenses.
How long do Army Reserve members typically serve?

+
Army Reserve members typically serve for a minimum of six years, although some may choose to serve for longer periods of time. The length of service can vary depending on the individual’s circumstances and the needs of the Army Reserve.