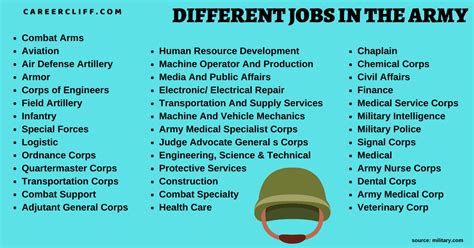
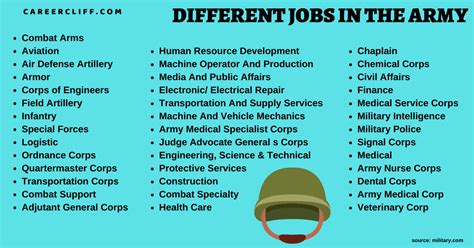
Army Reserve Officer Jobs

As a member of the Army Reserve, you have the opportunity to serve your country while also pursuing a civilian career. The Army Reserve offers a wide range of officer jobs, known as Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), that cater to various skills and interests. In this article, we will explore the different types of Army Reserve officer jobs, their responsibilities, and the requirements for each.
Combat Arms

Combat Arms officers lead soldiers in combat and are responsible for the planning and execution of military operations. Some examples of Combat Arms officer jobs in the Army Reserve include:
- Infantry Officer (11A): Leads infantry soldiers in combat and is responsible for the planning and execution of infantry operations.
- Field Artillery Officer (13A): Leads field artillery soldiers in combat and is responsible for the planning and execution of artillery operations.
- Armor Officer (19A): Leads armor soldiers in combat and is responsible for the planning and execution of armor operations.
Combat Support

Combat Support officers provide support to combat units and are responsible for the planning and execution of operations that enable combat success. Some examples of Combat Support officer jobs in the Army Reserve include:
- Military Police Officer (31A): Leads military police soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for law and order, and area security.
- Signal Officer (25A): Leads signal soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for the planning and execution of communications operations.
- Intelligence Officer (35A): Leads intelligence soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for the collection, analysis, and dissemination of intelligence.
Combat Service Support
Combat Service Support officers provide support to combat units and are responsible for the planning and execution of operations that sustain combat success. Some examples of Combat Service Support officer jobs in the Army Reserve include:
- Logistics Officer (92A): Leads logistics soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for the planning and execution of logistics operations.
- Finance Officer (36A): Leads finance soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for the planning and execution of financial operations.
- Human Resources Officer (42A): Leads human resources soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for the planning and execution of personnel operations.
Specialized Branches
The Army Reserve also offers a range of specialized branches that cater to specific skills and interests. Some examples include:
- Medical Corps Officer (62A): Leads medical soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for the planning and execution of medical operations.
- Chaplain Officer (56A): Leads chaplain soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for the planning and execution of spiritual operations.
- Judge Advocate General (JAG) Officer (27A): Leads JAG soldiers in support of combat operations and is responsible for the planning and execution of legal operations.
💡 Note: The above list is not exhaustive and there are many more officer jobs available in the Army Reserve.
Requirements

To become an officer in the Army Reserve, you must meet certain requirements, including:
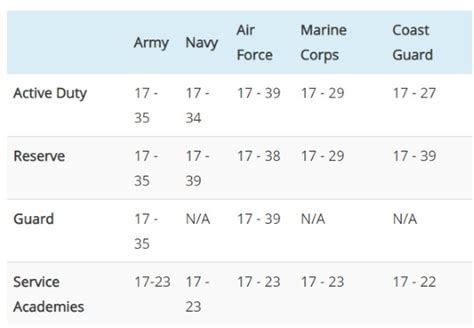
- Age: Be between the ages of 17 and 35 (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Citizenship: Be a U.S. citizen
- Education: Have a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution
- Physical Fitness: Meet the Army’s physical fitness standards
- Background Check: Pass a background check
Additionally, you must also complete Officer Candidate School (OCS) or receive a commission through another program, such as the Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC) or the United States Military Academy (USMA).
📝 Note: Requirements may vary depending on the specific MOS and the needs of the Army Reserve.
Conclusion

The Army Reserve offers a wide range of officer jobs that cater to various skills and interests. Whether you’re interested in combat, combat support, or combat service support, there’s an officer job in the Army Reserve that’s right for you. By meeting the requirements and completing the necessary training, you can serve your country while also pursuing a civilian career.
What is the difference between the Army Reserve and the Regular Army?
+
The main difference between the Army Reserve and the Regular Army is the level of commitment. Army Reserve soldiers serve part-time, typically one weekend a month and two weeks a year, while Regular Army soldiers serve full-time.
How do I join the Army Reserve?
+
To join the Army Reserve, you must meet the eligibility requirements, complete the enlistment process, and attend Basic Combat Training (BCT) and Advanced Individual Training (AIT).
Can I serve in the Army Reserve while also having a civilian career?

+
Yes, many Army Reserve soldiers serve part-time while also pursuing a civilian career. The Army Reserve offers a range of programs and benefits to help soldiers balance their military and civilian careers.
Related Terms:
- Army Reserve Officer eligibility requirements
- Army Reserve Officer training
- Army Reserve Officer Roles
- Army Reserve jobs
- Army Reserve roles
- Reserve Officer requirements