Army MOS for Cyber Security: Protecting the Digital Battlefield

The Evolution of Cyber Security in the Military
The world of cyber security has become an integral part of modern warfare. As technology advances, the need for skilled professionals to protect the digital battlefield has increased. The United States Army has recognized this need and has developed various Military Occupational Specialties (MOS) to address the growing threat of cyber attacks.
What is an Army MOS for Cyber Security?

An Army MOS for cyber security is a specialized career path that focuses on protecting the Army’s digital assets from cyber threats. These specialists are responsible for designing, implementing, and maintaining the security measures that protect the Army’s computer systems, networks, and data.
Types of Army MOS for Cyber Security

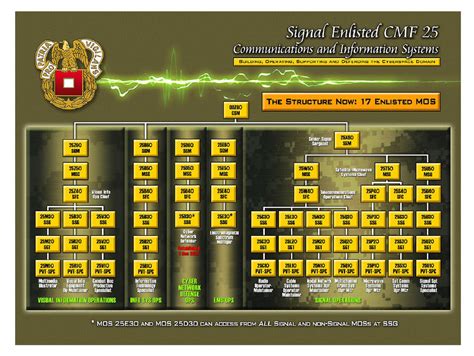
The Army offers several MOS options for individuals interested in pursuing a career in cyber security. Some of the most common MOS include:
- 25D: Cyber Network Defender: These specialists are responsible for protecting the Army’s computer networks from cyber threats. They use a variety of tools and techniques to detect and prevent attacks.
- 25B: Information Technology Specialist: These specialists are responsible for designing, implementing, and maintaining the Army’s computer systems and networks.
- 35T: Military Intelligence Systems Maintainer/Integrator: These specialists are responsible for maintaining and integrating the Army’s military intelligence systems.
- 25A: Signal Intelligence Analyst: These specialists are responsible for analyzing and interpreting signals intelligence data to identify potential cyber threats.
What are the Requirements for an Army MOS for Cyber Security?

To be eligible for an Army MOS for cyber security, individuals must meet certain requirements. These include:
- Age: Must be between 17 and 35 years old
- Citizenship: Must be a U.S. citizen
- Education: Must have a high school diploma or equivalent
- Physical Fitness: Must meet the Army’s physical fitness standards
- Background Check: Must undergo a background check and obtain a security clearance
- Training: Must complete the Army’s cyber security training program
What are the Benefits of an Army MOS for Cyber Security?

Pursuing an Army MOS for cyber security can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Job Security: The demand for cyber security specialists is high, and the Army offers job security and stability.
- Competitive Pay: The Army offers competitive pay and benefits, including education assistance and healthcare.
- Opportunities for Advancement: The Army offers opportunities for advancement and career growth.
- Hands-on Training: The Army provides hands-on training and experience in cyber security.
- Sense of Purpose: Serving in the Army provides a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
How to Pursue an Army MOS for Cyber Security

To pursue an Army MOS for cyber security, individuals can follow these steps:
- Meet the Requirements: Ensure you meet the requirements for an Army MOS for cyber security.
- Take the ASVAB Test: Take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test to determine your eligibility for an Army MOS.
- Enlist in the Army: Enlist in the Army and choose the cyber security MOS you are interested in.
- Complete Training: Complete the Army’s cyber security training program.
- Gain Experience: Gain experience in the field by participating in training exercises and real-world missions.
💡 Note: The Army offers various training programs and certifications for cyber security, including CompTIA Security+ and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
Challenges and Opportunities in Army Cyber Security
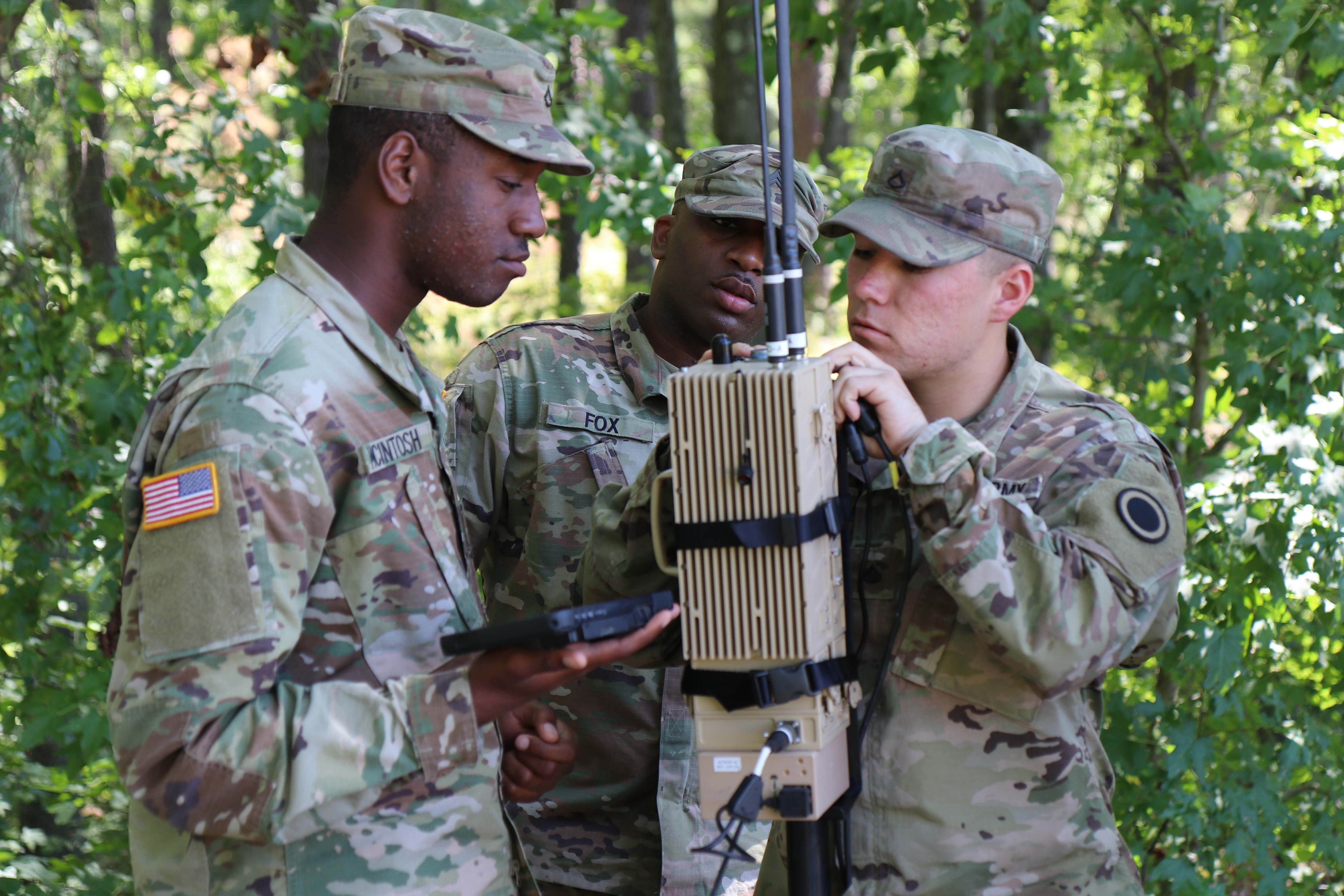

Pursuing an Army MOS for cyber security can be challenging, but it also provides numerous opportunities. Some of the challenges include:
- Continuous Learning: The field of cyber security is constantly evolving, and specialists must stay up-to-date with the latest threats and technologies.
- High-Stress Environment: Cyber security specialists often work in high-stress environments, where they must respond quickly to emerging threats.
- Limited Resources: The Army may have limited resources, which can make it difficult for specialists to access the latest tools and technologies.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities in Army cyber security are numerous. Some of the opportunities include:
- Job Variety: Cyber security specialists can work in a variety of roles, from network defense to incident response.
- Opportunities for Advancement: The Army offers opportunities for advancement and career growth.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Serving in the Army provides a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment.
Conclusion
Pursuing an Army MOS for cyber security can be a rewarding and challenging career path. The Army offers various MOS options, including 25D, 25B, 35T, and 25A. To be eligible, individuals must meet certain requirements, including age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness. The Army provides hands-on training and experience in cyber security, as well as opportunities for advancement and career growth.
What is the job outlook for Army cyber security specialists?

+
The job outlook for Army cyber security specialists is high, with the demand for skilled professionals expected to increase in the coming years.
What kind of training does the Army provide for cyber security specialists?

+
The Army provides hands-on training and experience in cyber security, including certification programs such as CompTIA Security+ and CISSP.
What are the benefits of pursuing an Army MOS for cyber security?

+
The benefits of pursuing an Army MOS for cyber security include job security, competitive pay, opportunities for advancement, hands-on training, and a sense of purpose.
Related Terms:
- Army Cyber MOS list
- Army 17 series MOS list
- Army Cyber Security salary
- 17C MOS reclass requirements
- Cyber security job in Army
- 17C MOS Army