10 Essential Insights into Aquatic Ecosystems Worksheet Answers
Aquatic ecosystems are vast and varied, ranging from the deep sea to your local pond. They play a crucial role in the earth's biodiversity, climate regulation, and are fundamental in human life for water, food, and recreation. Here are 10 essential insights into the worksheets that help students understand these intricate systems better.
Understanding Aquatic Ecosystems

Aquatic ecosystems are water-based environments where organisms live. They are classified into two primary types:
- Freshwater Ecosystems: Including lakes, rivers, wetlands, and groundwaters.
- Marine Ecosystems: Encompassing oceans, coral reefs, and estuaries.
🌊 Note: Understanding the differences between freshwater and marine ecosystems is crucial for conserving both types effectively.
Key Components of Aquatic Ecosystems

The study of aquatic ecosystems involves understanding their:
- Biotic Components: All living organisms from bacteria to whales.
- Abiotic Components: Physical and chemical factors like temperature, salinity, pH, and light penetration.
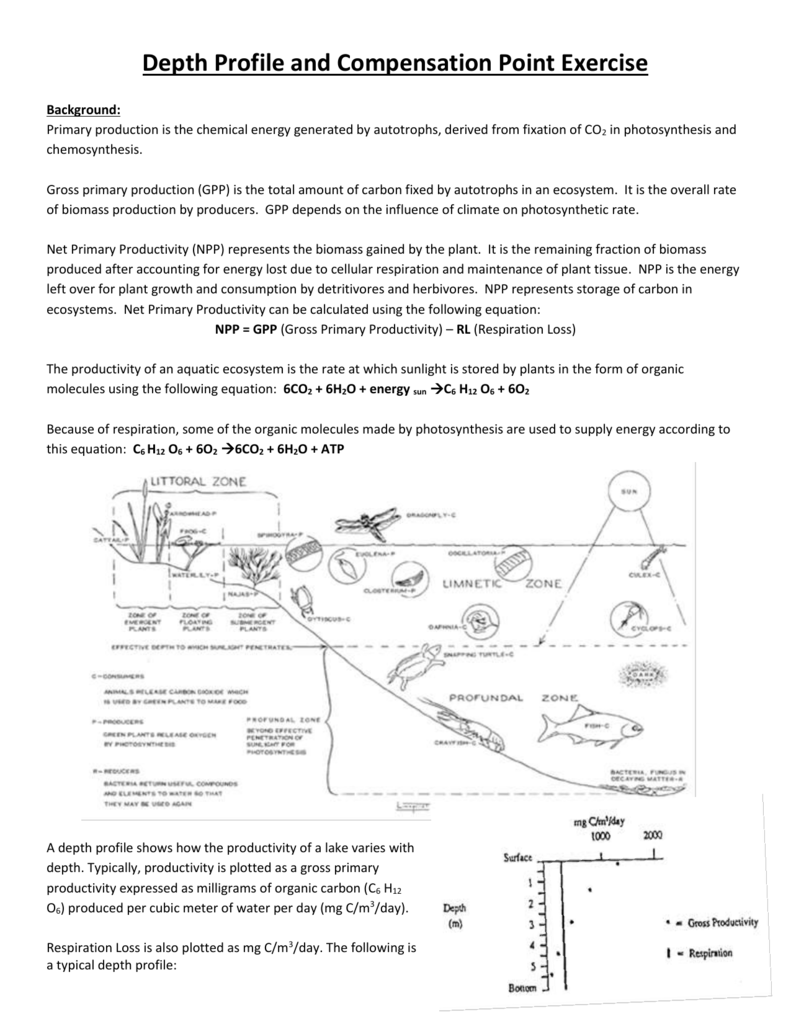
Food Web and Energy Flow

Aquatic food webs show the complex interactions of:
- Primary Producers: Phytoplankton, algae, and macrophytes which photosynthesize to produce food.
- Herbivores: Zooplankton, some fish, and larger herbivorous animals that eat the producers.
- Carnivores and Omnivores: Predatory fish, birds, and mammals.
- Decomposers: Fungi, bacteria, and detritus feeders that break down dead material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Energy flows through this web in an often pyramid-shaped structure where each level supports less biomass than the one below it.
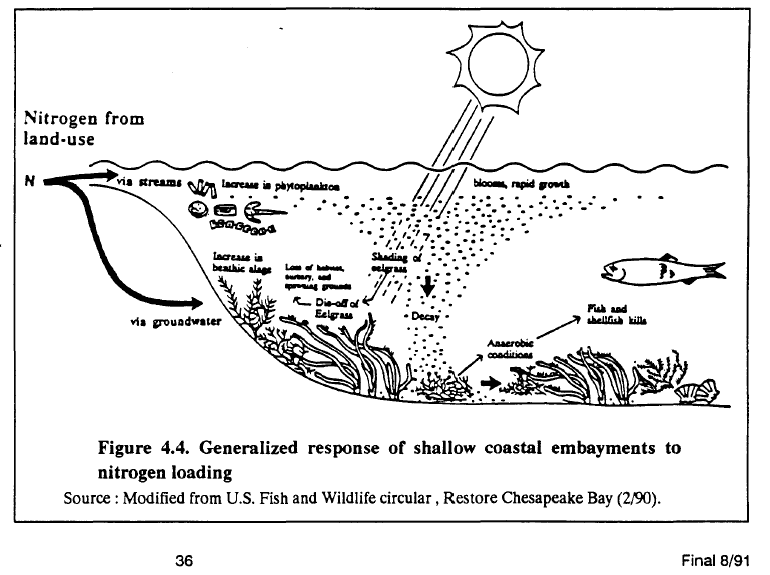
Human Impact on Aquatic Ecosystems

Human activities have a profound impact on aquatic systems:
- Pollution: From industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and urban pollution, affecting water quality and life forms.
- Overfishing: Depleting fish populations and disrupting the food chain.
- Habitat Destruction: Dredging, coastal development, and dam construction.
🌱 Note: Sustainable practices and conservation efforts are vital to mitigate these impacts and preserve these fragile ecosystems.
Aquatic Ecosystem Services

| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Provisioning | Water supply, food (fish, shellfish), minerals, and genetic resources. |
| Regulating | Climate regulation, water purification, and waste treatment. |
| Supporting | Nutrient cycling, oxygen production, and habitat provision. |
| Cultural | Recreational, aesthetic, spiritual, and educational values. |

Conservation and Restoration Efforts

To protect and restore aquatic ecosystems:
- Protected Areas: Establishing marine reserves and sanctuaries.
- Restoration Projects: Reviving degraded habitats like wetlands or coral reefs.
- Legislation: Enforcing laws to reduce pollution and regulate fishing.
Efforts also include community involvement to foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards local aquatic ecosystems.
Teaching About Aquatic Ecosystems

Educational tools like worksheets play a significant role in:
- Engaging Students: With interactive activities, simulations, and case studies.
- Understanding Complexity: By breaking down large systems into manageable parts.
- Encouraging Conservation: Through awareness and involvement in conservation activities.
📚 Note: Worksheets that incorporate real-world examples and hands-on activities can greatly enhance students' understanding and appreciation of aquatic ecosystems.
In summary, the study of aquatic ecosystems via worksheets not only provides students with essential scientific knowledge but also nurtures an understanding of ecological interdependence and the importance of conservation. By engaging with these complex systems, students gain insights into how their actions can influence water environments, fostering a lifelong commitment to environmental stewardship.
What are some common mistakes students make when filling out aquatic ecosystem worksheets?

+
Students often overlook the interconnectedness of biotic and abiotic factors. They might focus solely on the animals or plants without considering how water temperature, pH, or light affects these organisms.
How can one identify the health of an aquatic ecosystem?

+
Signs of a healthy aquatic ecosystem include diverse wildlife, clear water, stable populations of key species, and the presence of certain sensitive organisms which thrive in unpolluted conditions.
What role does biodiversity play in an aquatic ecosystem?

+
Biodiversity promotes stability, resilience against environmental changes, and maintains ecosystem services. It allows for a balanced food web where no single species dominates to the detriment of others.
How do climate changes affect aquatic ecosystems?

+
Changes in climate can lead to water temperature increases, altering species distributions, acidification of oceans, changes in water levels, and the timing of seasonal events, which impacts the survival and reproduction of aquatic life.
What can individuals do to contribute to the health of aquatic ecosystems?
+
Individuals can reduce their environmental footprint by conserving water, reducing pollution, participating in clean-up drives, supporting conservation efforts, and educating others about the importance of aquatic ecosystems.