Breaking Down Anti-Access/Area Denial Strategies
Understanding Anti-Access/Area Denial Strategies
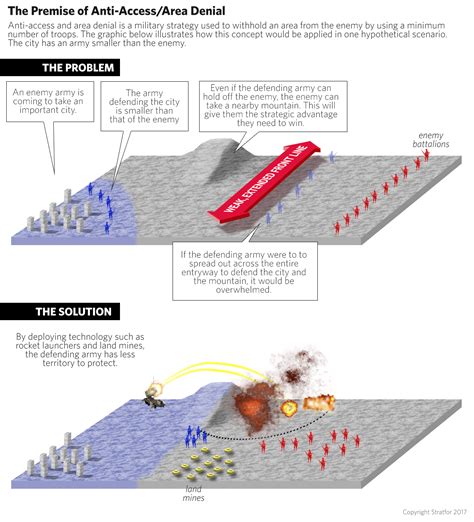
In the realm of military strategy, Anti-Access/Area Denial (A2/AD) has emerged as a critical concept that challenges the conventional military superiority of dominant powers. A2/AD strategies aim to prevent or restrict an adversary’s ability to access and operate within a specific geographic area. This blog post will delve into the intricacies of A2/AD strategies, exploring their components, applications, and implications.
Components of Anti-Access/Area Denial Strategies

A2/AD strategies typically comprise a combination of the following components:
- Anti-Access (A2) Measures: These are designed to prevent an adversary from entering a specific area or theater of operation. A2 measures include:
- Surface-to-air missile systems (SAMs)
- Anti-ship missiles (AShMs)
- Submarines and minefields
- Area Denial (AD) Measures: These aim to restrict an adversary’s ability to operate within a specific area, even if they manage to access it. AD measures include:
- Advanced air defense systems (AADS)
- Electronic warfare (EW) capabilities
- Cyber warfare tools
- Special operations forces (SOF)
Applications of Anti-Access/Area Denial Strategies

A2/AD strategies have been employed in various contexts, including:
- Territorial Defense: Countries like China, Russia, and Iran have developed A2/AD capabilities to protect their territorial integrity and sovereignty.
- Asymmetric Warfare: Non-state actors, such as terrorist organizations, have used A2/AD tactics to counter conventional military forces.
- Expeditionary Operations: A2/AD strategies can be used to challenge the deployment of expeditionary forces in distant theaters of operation.
Implications of Anti-Access/Area Denial Strategies

The proliferation of A2/AD strategies has significant implications for military planning and operations:
- Reduced Freedom of Action: A2/AD capabilities can restrict the ability of military forces to operate freely in a given area.
- Increased Risk: The deployment of A2/AD systems increases the risk of conflict escalation and raises the stakes for military operations.
- New Technologies and Doctrine: The development of A2/AD strategies has driven the creation of new technologies and doctrine, such as the use of drones, EW, and cyber warfare.
🔒 Note: The increasing use of A2/AD strategies has led to a shift in military doctrine, with a greater emphasis on speed, agility, and stealth.
Countering Anti-Access/Area Denial Strategies

To counter A2/AD strategies, military forces can employ various tactics, including:
- Network-Centric Warfare: This approach emphasizes the use of networked systems and sensors to detect and neutralize A2/AD threats.
- Electronic Warfare: EW capabilities can be used to disrupt or destroy A2/AD systems.
- Stealth and Low-Observability: The use of stealth and low-observable technologies can reduce the effectiveness of A2/AD systems.
- Special Operations Forces: SOF can be used to conduct reconnaissance, sabotage, or direct action against A2/AD systems.
| Strategy | Components | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| A2/AD | Anti-Access (A2) Measures, Area Denial (AD) Measures | Territorial Defense, Asymmetric Warfare, Expeditionary Operations |
| Network-Centric Warfare | Networked Systems, Sensors | Countering A2/AD Strategies |

The evolution of A2/AD strategies has significant implications for military planning and operations. Understanding the components, applications, and implications of A2/AD strategies is essential for developing effective countermeasures and maintaining military superiority in the face of emerging threats.
Military forces must adapt to the changing nature of modern warfare, incorporating new technologies and doctrine to counter the proliferation of A2/AD strategies. By understanding the intricacies of A2/AD strategies, military planners can develop effective countermeasures to ensure continued freedom of action and military superiority in the face of emerging threats.
What is Anti-Access/Area Denial (A2/AD) strategy?

+
A2/AD strategy aims to prevent or restrict an adversary’s ability to access and operate within a specific geographic area.
What are the components of A2/AD strategies?

+
A2/AD strategies typically comprise a combination of Anti-Access (A2) Measures and Area Denial (AD) Measures.
How can military forces counter A2/AD strategies?

+
Military forces can employ various tactics, including Network-Centric Warfare, Electronic Warfare, Stealth and Low-Observability, and Special Operations Forces.