5 Tips for Mastering Ionic & Covalent Bonds
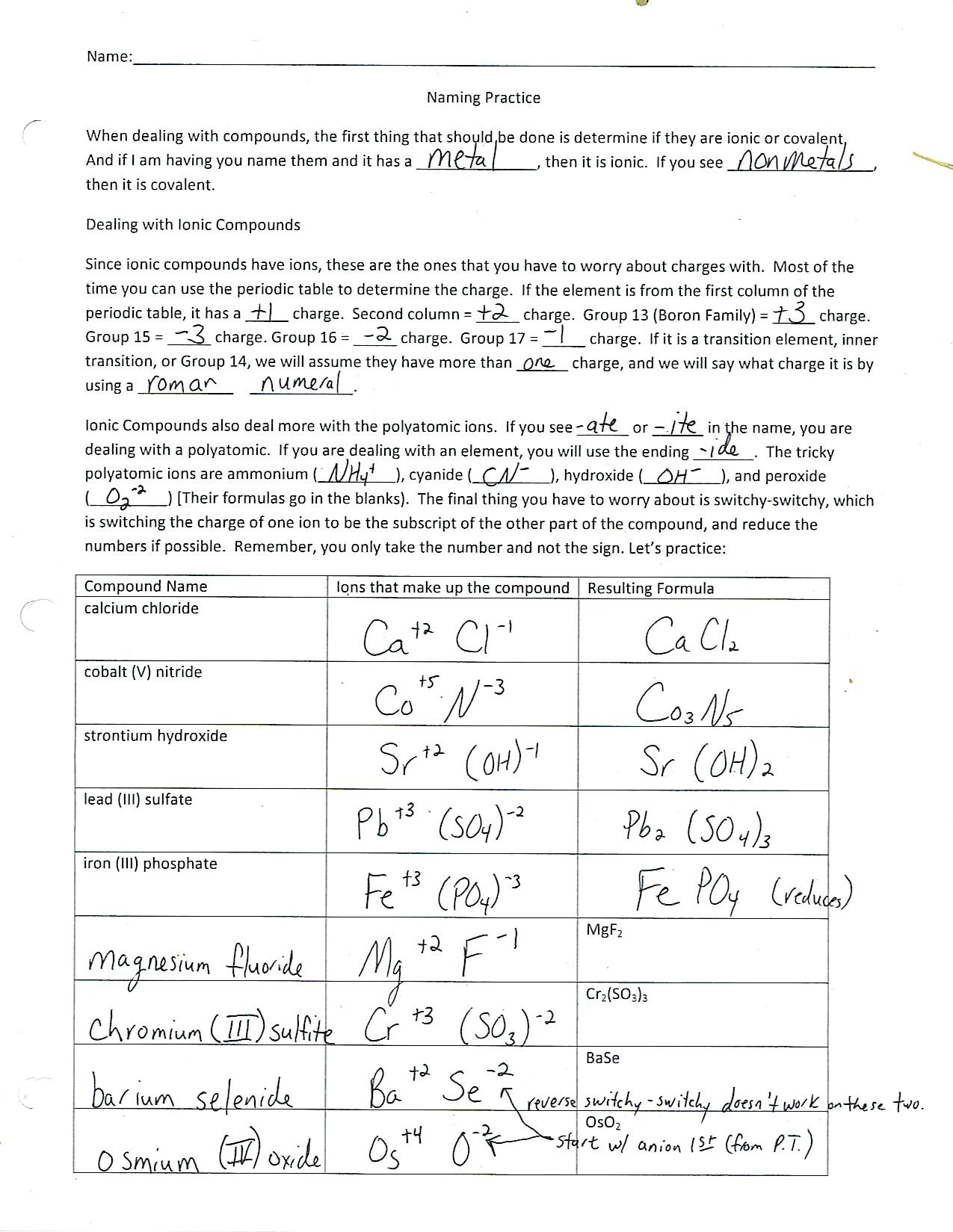
Understanding the distinctions between ionic and covalent bonds is fundamental to grasping how atoms interact and form compounds. These bonding types not only dictate the properties of elements and molecules but also play a critical role in various chemical reactions and structures. Here are five essential tips to master these bonding concepts:
1. Understand Electron Transfer and Sharing
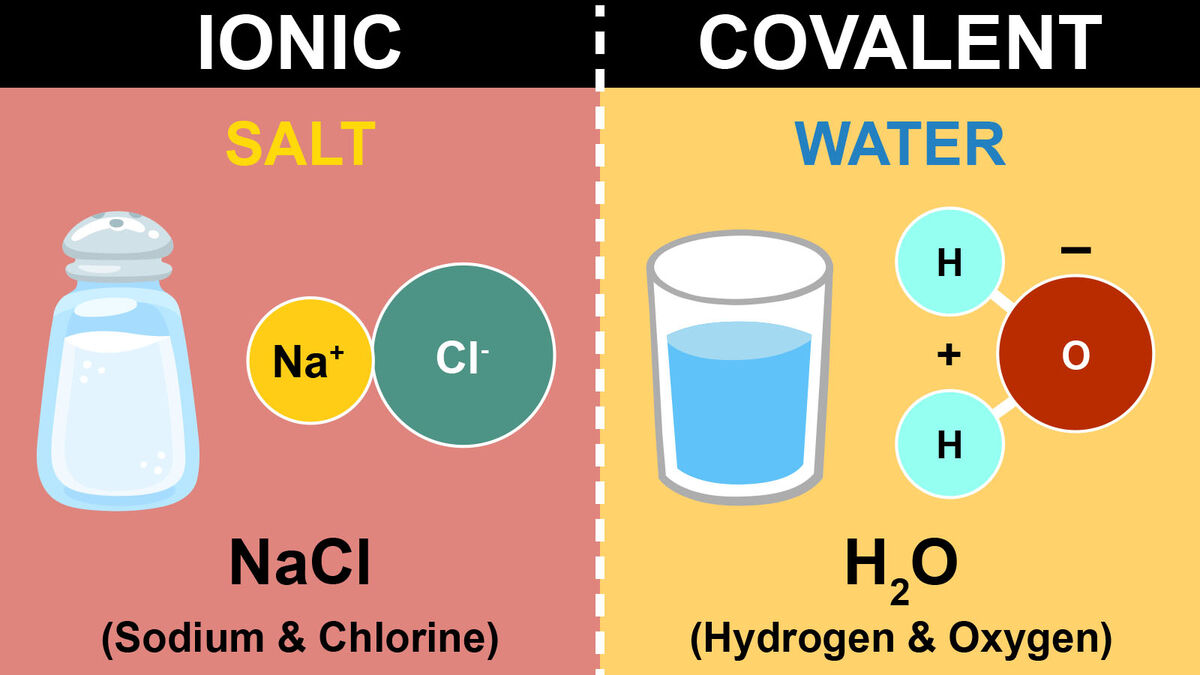
Ionic bonds involve the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another, typically between metals and non-metals. Here’s how to approach them:
- Focus on elements’ tendencies to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- Identify electron donors (usually metals) and electron acceptors (usually non-metals).
Covalent bonds, on the other hand, involve the sharing of electron pairs. Keep these points in mind:
- Non-metals bond with non-metals through electron sharing to achieve stability.
- Learn about electronegativity differences to understand the degree of electron sharing or inequality in covalent bonds.

🔍 Note: Electron transfer occurs when the electronegativity difference is significant; electron sharing is observed when the electronegativity differences are small to moderate.
2. Recognize Electronegativity’s Role

Electronegativity is the key to understanding bond formation:
- Higher electronegativity means an atom attracts electrons more strongly.
- The difference in electronegativity helps in classifying bonds:
| Electronegativity Difference | Bond Type |
|---|---|
| 0.0 - 0.4 | Non-polar covalent |
| 0.5 - 1.7 | Polar covalent |
| 1.8 and above | Ionic |
🔬 Note: Electronegativity values can vary between different scales, but Pauling’s scale is widely used.
3. Use Lewis Structures to Visualize Bonds

Lewis dot structures provide a visual representation of electron distribution in molecules:
- Draw central atoms and count valence electrons for each atom.
- Arrange electrons to achieve octet rule (or duets in case of hydrogen).
- Understand the importance of lone pairs and bond types (single, double, triple) in these structures.

4. Relate Bonding to Molecular Properties

The type of bond directly influences the properties of compounds:
- Ionic Compounds: High melting and boiling points, brittle solids, conducts electricity when molten or dissolved.
- Covalent Compounds: Lower melting and boiling points, varied states of matter, generally do not conduct electricity.
💡 Note: Intermolecular forces like hydrogen bonding can significantly impact physical properties even among covalent compounds.
5. Practice With Real-Life Examples

The best way to solidify understanding is through practical examples:
- Compare the bonding in table salt (NaCl, ionic) versus water (H2O, covalent).
- Analyze the covalent nature of organic compounds and the ionic nature of salts in daily life.
- Understand how bonding influences reactions, for example, in acid-base chemistry.

In summary, mastering ionic and covalent bonds involves a nuanced understanding of electron behavior, electronegativity, and molecular structure visualization. By applying these tips, you'll be equipped to analyze chemical bonds and predict the properties of compounds with greater confidence.
What are the main differences between ionic and covalent bonds?

+
The primary difference is in how electrons are handled. In ionic bonds, electrons are transferred completely from one atom to another, creating ions with charges. In covalent bonds, electrons are shared between atoms, typically with non-metals.
Why does the electronegativity difference matter in bonding?

+
Electronegativity difference determines the nature of the bond. Large differences result in ionic bonds, while smaller differences lead to covalent bonds, which can be further classified as non-polar or polar based on the degree of sharing.
How can I identify the type of bond between two atoms?

+
By calculating the electronegativity difference. If the difference is less than 0.5, it’s likely a non-polar covalent bond; between 0.5 and 1.7, it’s polar covalent; and above 1.8, it becomes ionic.