Angle Measurement Worksheet: Free Practice for Geometry Mastery

Geometry, as a cornerstone of mathematical education, plays a critical role in our understanding of the physical world around us. For students, mastering geometry involves not only understanding the theory but also practicing through exercises that reinforce this knowledge. One fundamental skill in geometry is the ability to accurately measure angles. This blog post delves into how students can harness angle measurement worksheets to improve their geometric proficiency.
What is Angle Measurement?
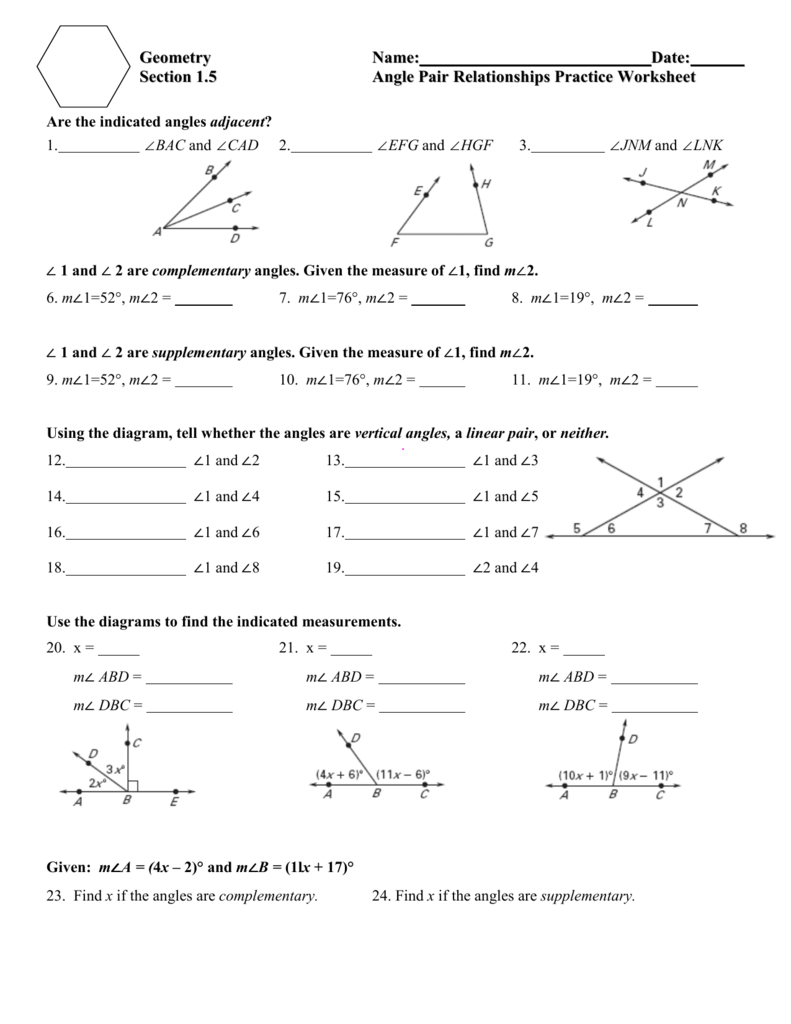

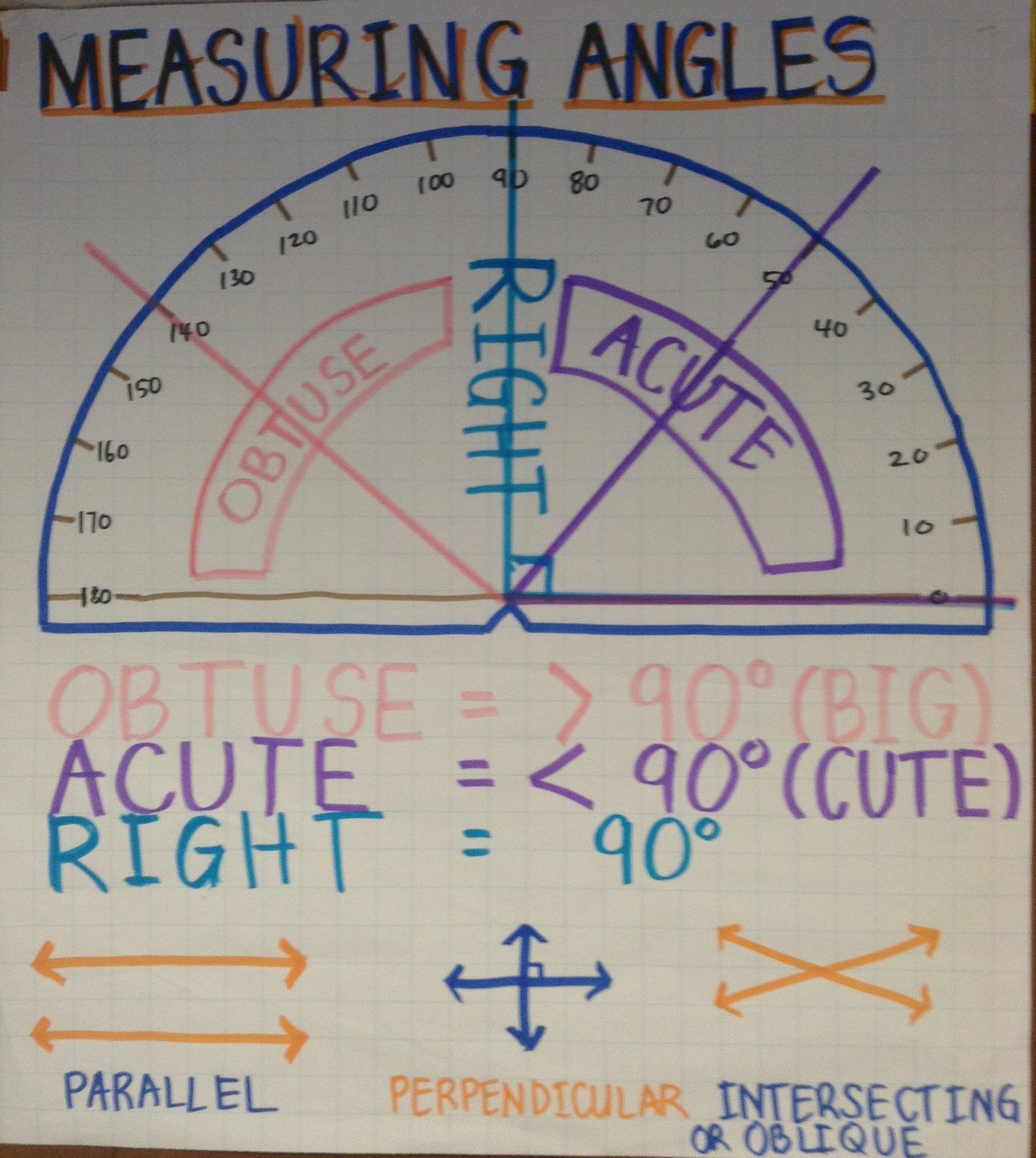
Angles are geometric figures formed by two rays, called the sides of the angle, sharing a common endpoint known as the vertex. The measurement of an angle is typically given in degrees, where one full rotation is equal to 360 degrees. In educational contexts, angles are often classified based on their degree measure:
- Acute Angles: Less than 90 degrees.
- Right Angles: Exactly 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Angles: Between 90 and 180 degrees.
- Straight Angles: Exactly 180 degrees.
- Reflex Angles: More than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
Benefits of Angle Measurement Worksheets
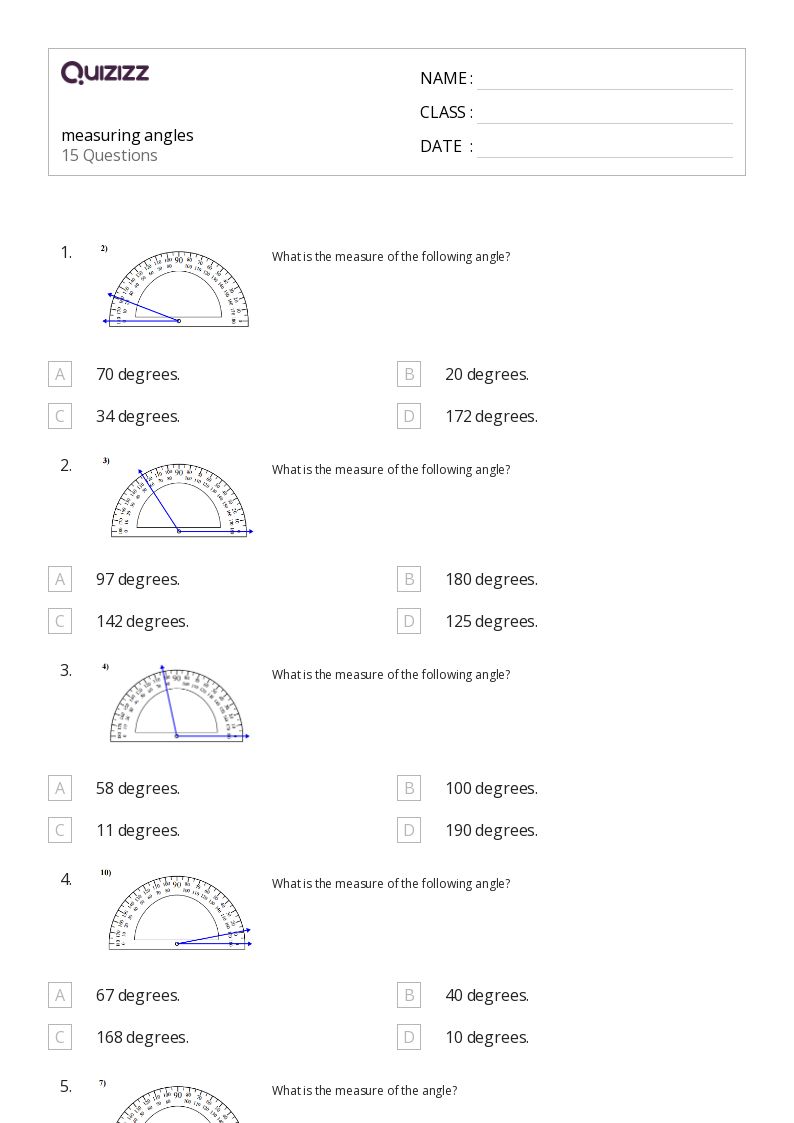
Utilizing angle measurement worksheets offers several advantages to students:
- Skill Development: Worksheets enable students to practice repeatedly, which is key to mastering the skill.
- Visual Learning: Visual representations of angles help in better understanding and retention.
- Real-World Application: Students learn to apply geometric concepts in scenarios they might encounter outside the classroom.
- Self-Assessment: Worksheets provide immediate feedback when solutions are provided, allowing students to evaluate their understanding.
How to Use Angle Measurement Worksheets
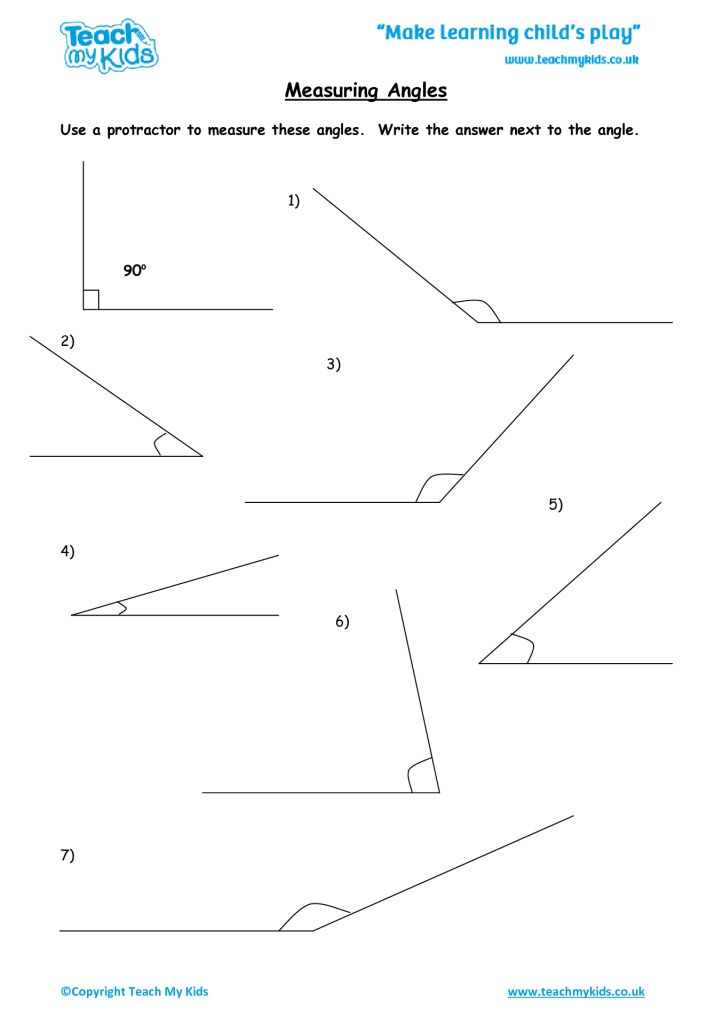

Here’s a structured approach for effectively using these worksheets:
Choosing the Right Worksheet
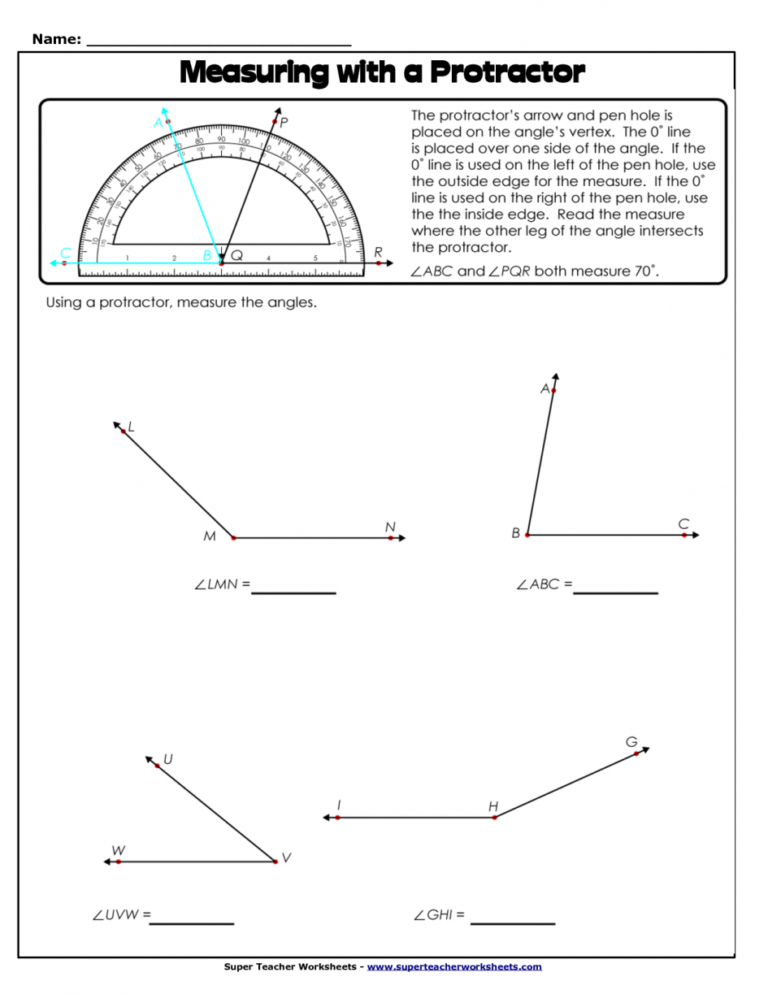
Select a worksheet that matches your current level of understanding. Beginners might start with identifying types of angles, while advanced students can tackle problems involving angle relationships in polygons or circles.
- Begin with identifying and naming angles.
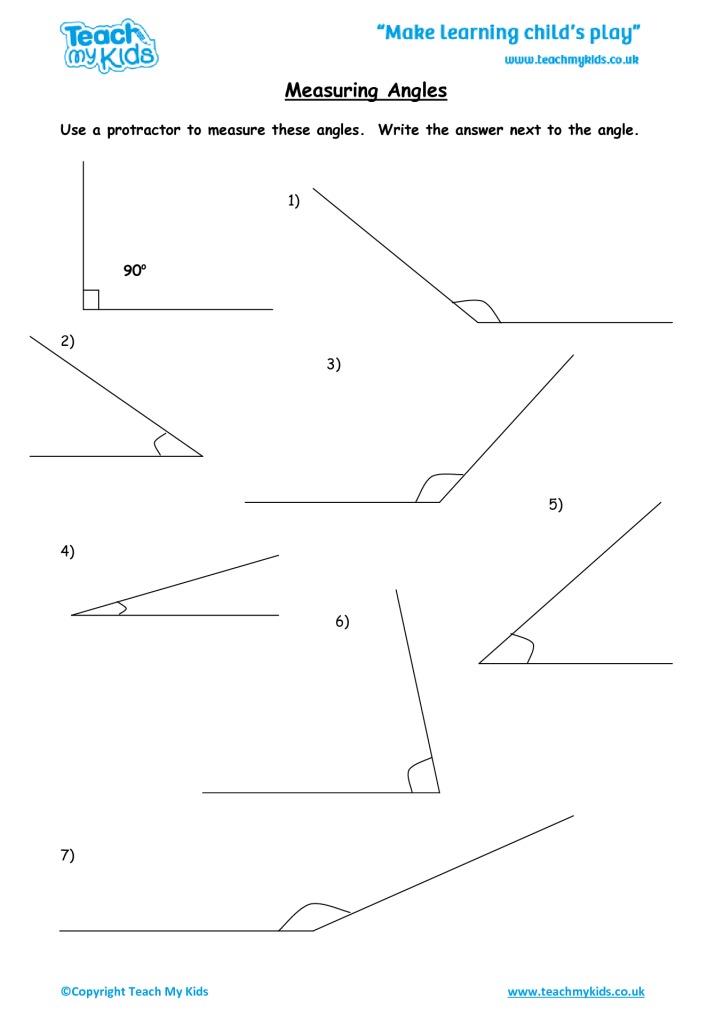
- Move on to measuring angles with a protractor.
- Progress to calculating angles using given data.
- Explore angle relationships like vertical, supplementary, or complementary angles.
Tools and Materials

You’ll need:
- A protractor to measure angles.
- A worksheet with various angle problems.
- A pen or pencil for your calculations.
- A ruler to draw straight lines if necessary.
Step-by-Step Guide

Here’s how you can work through an angle measurement worksheet:
- Read Instructions: Ensure you understand what each question is asking for.
- Set Up Your Workspace: Have your tools ready for quick reference.
- Measure or Calculate: Use your protractor or geometric formulas to solve each problem.
- For basic measuring, align the protractor base along one ray of the angle, with the vertex at the center mark.
- Read the degree measure where the other ray crosses the protractor’s scale.
- Check Your Work: Verify your measurements or calculations against provided answers or re-calculate to ensure accuracy.
- Reflect: Consider which problems were difficult and review the concepts involved.
Practice Tips

- Use Different Sheets: Variety helps in understanding different angle scenarios.
- Consistent Practice: Regularly tackle worksheets to build proficiency.
- Seek Help: If you encounter problems, ask for assistance from teachers or use online resources.
🔍 Note: Don't rush through worksheets; take your time to understand each problem and its solution.
Common Mistakes and Solutions

Here are some common pitfalls students face along with solutions:
- Proportion Error: Misalignment of the protractor when measuring.
📐 Note: Always ensure the base of the protractor aligns with the angle’s baseline, and the center mark of the protractor is at the vertex.
- Confusion with Angle Types: Mixing up types of angles, leading to incorrect calculations.
🌐 Note: Use clear definitions and visual cues to differentiate between angle types.
- Calculation Errors: Mistakes in arithmetic when calculating angles.
🔬 Note: Double-check your arithmetic, especially with more complex problems involving multiple angles.
Enhancing Your Learning Experience


Beyond worksheets, here are additional strategies to deepen your geometric understanding:
- Interactive Tools: Use software like GeoGebra for interactive angle measurements.
- Real-Life Application: Look for angles in your environment to relate classroom learning to everyday life.
- Peer Learning: Discuss with classmates to gain different perspectives on solving problems.
- Project-Based Learning: Work on projects that require geometric reasoning.
📚 Note: Combining traditional methods like worksheets with modern educational tools can significantly enhance learning.
To sum up, mastering geometry involves a combination of theoretical understanding, practical application, and consistent practice. Angle measurement worksheets provide an excellent platform for students to refine these skills. By engaging with these exercises, students not only improve their geometric proficiency but also cultivate a mindset geared towards precision, critical thinking, and problem-solving. As you progress in geometry, remember that every angle measured and every problem solved is a step closer to mastering this beautiful branch of mathematics.
Why are angle measurement worksheets important?

+
Angle measurement worksheets help students practice, understand, and apply geometric concepts, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
What tools do I need to complete these worksheets?
+
Essential tools include a protractor, a ruler, and a pen or pencil for calculations and sketches.
How often should I practice with angle measurement worksheets?
+
Regular practice is key. Aim for at least once or twice a week to build and retain proficiency.
What should I do if I find angles confusing?

+
Revisit basic angle definitions, engage with interactive tools, or seek guidance from educational resources or teachers.
Can angle measurement worksheets help in real-world scenarios?

+
Absolutely, understanding angles helps in fields like architecture, engineering, art, and even everyday tasks like navigation and construction.



