5 Key Terms Every Anatomy Student Must Know
As you delve into the vast and intricate field of anatomy, understanding the fundamental terminology is akin to mastering the basic chords in music. These key terms serve as the language of anatomy, enabling students to describe, locate, and understand the complexity of human body structures. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into five key anatomical terms every student should know, to help navigate this fascinating study with confidence.
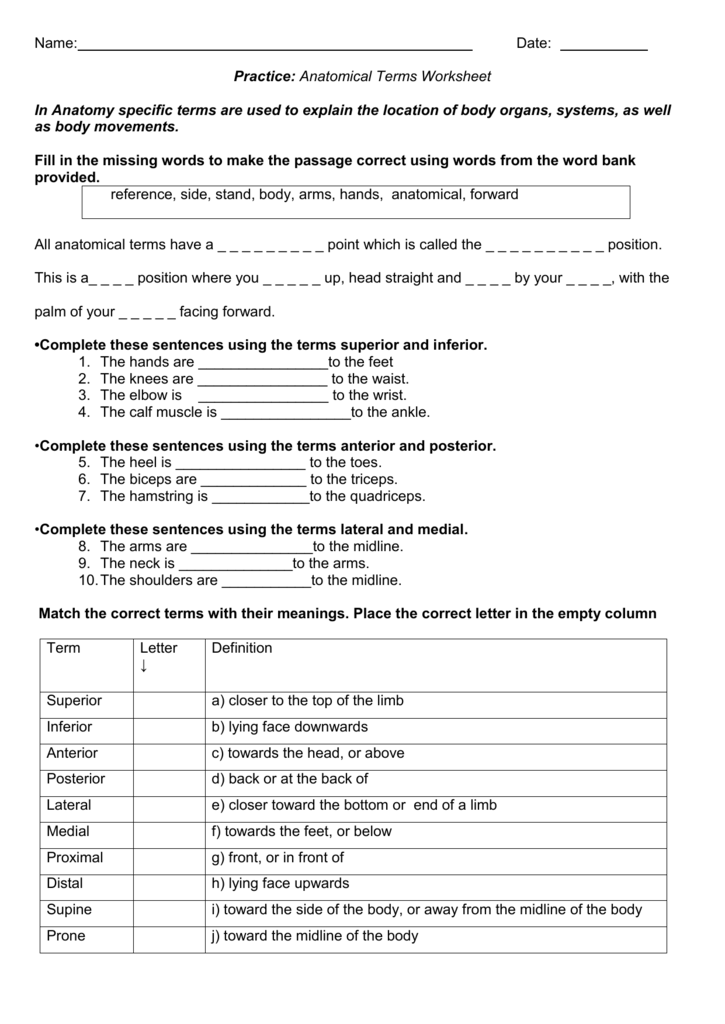
1. Anatomical Position


The anatomical position is the standardized stance for describing the human body. This position includes:
- Standing erect with feet together.
- Palms facing forward, with thumbs pointing away from the body.
- The head, eyes, and toes facing forward.
This universal reference point allows:
- Consistency: Ensures all anatomical descriptions are understood universally.
- Orientation: Provides a starting point from which to describe specific locations.
📚 Note: Anatomical descriptions must reference this position even if the body is in a different pose.
2. Planes of the Body

The human body is divided into several planes to facilitate the understanding of internal structures:
| Plane | Description | Examples of Use |
|---|---|---|
| Sagittal | Vertical plane dividing the body into left and right. | Cutting down the midline for body symmetry analysis. |
| Frontal (Coronal) | Vertical plane dividing the body into anterior and posterior. | Separating the front from the back to study muscle groups. |
| Transverse (Axial) | Horizontal plane dividing the body into superior and inferior parts. | Viewing internal organs like the liver or spleen at different levels. |

🌟 Note: Each plane provides a different perspective to visualize the internal anatomy.
3. Directional Terms

Directional terms help in locating and describing parts of the body in relation to other parts:
- Superior/Inferior: Superior refers to structures closer to the head, while inferior points to those nearer the feet.
- Anterior/Posterior: Anterior denotes the front (ventral) side, and posterior the back (dorsal).
- Medial/Lateral: Medial refers to the middle or near the midline, and lateral is further away from the midline.
- Proximal/Distal: Proximal means closer to the point of attachment, while distal means further from it.
📍 Note: Directional terms are key for clarity in anatomical descriptions, especially in clinical settings.
4. Body Cavities

The human body contains various cavities housing vital organs:
- Cranial Cavity: Housing the brain, it's the upper part of the dorsal body cavity.
- Spinal Cavity: Contains the spinal cord, extending from the skull to the vertebral column.
- Thoracic Cavity: Contains organs like the heart and lungs; divided by the mediastinum.
- Abdominopelvic Cavity: Includes the abdominal and pelvic cavities, housing digestive organs and reproductive structures.
📦 Note: Understanding body cavities aids in pathology as different diseases can affect different cavities.
5. Medical Imaging

Medical imaging techniques provide insights into the internal structure and function of organs:
- X-rays: Useful for detecting fractures or lung conditions like pneumonia.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): For detailed views of soft tissues, including muscles and organs.
- CT (Computed Tomography): Provides cross-sectional images, helpful for head injuries or cancer staging.
- Ultrasound: Non-invasive, often used to monitor fetal development or for abdominal assessments.
Each imaging modality has its strengths, making them invaluable tools in anatomical and medical study.
🧪 Note: Knowledge of medical imaging is crucial for interpreting diagnostic results and understanding anatomy in different contexts.
In summary, these five key terms form the cornerstone of anatomical language. They enable students to describe, locate, and understand the complex structures of the human body systematically. By mastering these terms, you'll unlock the ability to communicate effectively within the field of anatomy, fostering a clearer path to understanding how our bodies are interconnected, built, and function. This foundational knowledge is not only essential for academic success but is also instrumental in clinical settings, research, and further medical education. As you continue your journey in anatomy, remember that these terms are your guideposts, helping you navigate the intricate landscapes of human anatomy with precision and clarity.
Why is the anatomical position important?

+
The anatomical position provides a standardized reference point that ensures consistent anatomical descriptions across different individuals and studies.
How do the planes of the body help in anatomy?

+
By dividing the body into different planes, we can study internal organs and systems in cross-sections, providing a three-dimensional understanding.
What are some common directional terms in anatomy?

+
Terms like Superior/Inferior, Anterior/Posterior, Medial/Lateral, and Proximal/Distal are commonly used to describe the relative positions of body parts.
Can you explain the significance of medical imaging?

+
Medical imaging technologies enable visualization of internal anatomy, aiding in diagnosis, treatment planning, and research without invasive procedures.
What are the main body cavities and what organs do they contain?

+
The main body cavities include the cranial (brain), spinal (spinal cord), thoracic (heart, lungs, and mediastinum), and abdominopelvic (digestive organs and reproductive structures).