Amoeba Sisters Diffusion Recap: Worksheet Answers Revealed
The Amoeba Sisters, known for their educational videos on biology, have captivated audiences with their unique teaching style. Their "Diffusion" video, aimed at demystifying this crucial cell process, offers a comprehensive look into how substances move within cells and across membranes. Let's delve into the answers of their diffusion recap worksheet, ensuring clarity on these fundamental concepts.
Understanding Diffusion

Diffusion is a spontaneous process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, resulting in uniform distribution. This passive transport is fundamental for:
- Cell nourishment
- Waste removal
- Maintaining homeostasis
Here's how diffusion works:
- It occurs naturally without energy input
- It can happen in any medium: gas, liquid, or even across solid barriers
- It stops when the concentration gradient ceases to exist
🌍 Note: Remember that although we're focusing on diffusion in biological systems, it's a universal principle observed in various natural phenomena, like the scent of a flower traveling through air.
Key Concepts in Diffusion

Concentration Gradient: The change in concentration of a substance over a distance is key to understanding diffusion. Here's how it's broken down:
- High to Low: Substances move from where they're abundant to where they're scarce.
- Equilibrium: The point where molecules are evenly distributed; movement continues, but net movement stops.
Passive Transport: Diffusion falls under passive transport because:
- No ATP (energy) is required
- The process depends on the inherent kinetic energy of the molecules involved
Solubility: The molecule's ability to dissolve affects:
- Speed and efficiency of diffusion through a medium or barrier
- Can be influenced by factors like temperature and molecular size
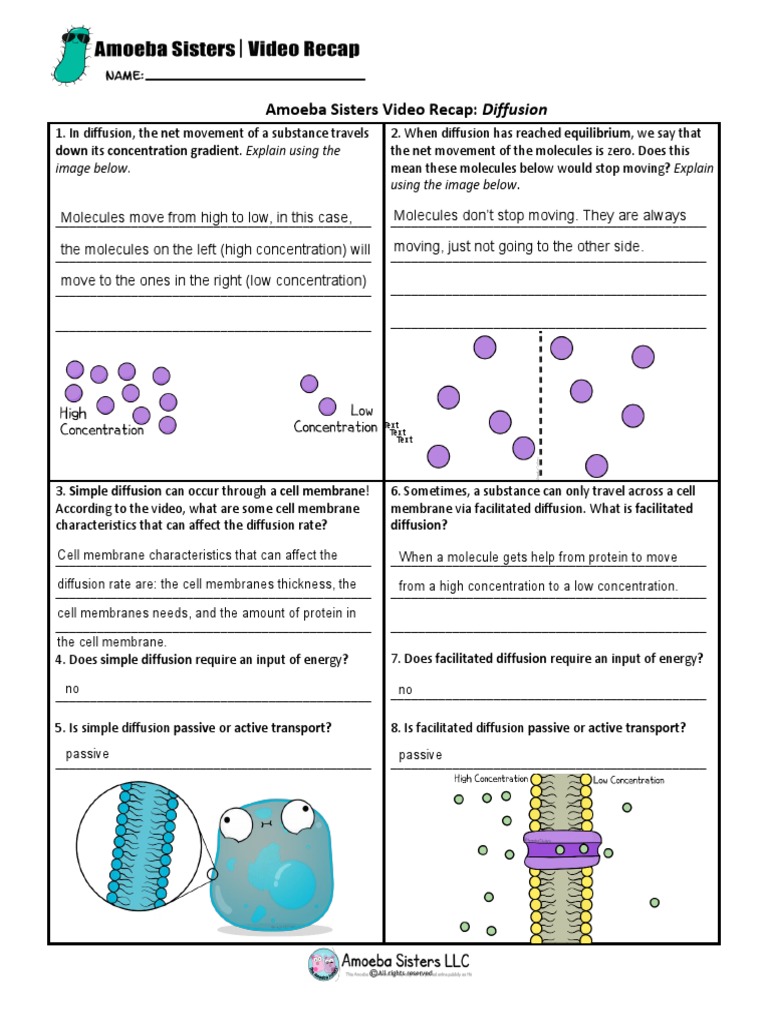
Answers to the Amoeba Sisters' Diffusion Recap Worksheet

Let's address the answers to the worksheet, ensuring that readers gain a firm grasp on the concepts:
- 1. What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the movement of substances from an area of high concentration to low concentration to achieve equilibrium.
- 2. How does diffusion relate to cellular respiration?
In cellular respiration, oxygen diffuses into cells, and carbon dioxide diffuses out, allowing for efficient gas exchange essential for energy production.
- 3. Explain passive transport.
Passive transport is the movement of molecules across a membrane without energy input, driven by concentration gradients.
- 4. Describe facilitated diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion involves the use of carrier proteins or channel proteins to assist the movement of specific substances across cell membranes.
- 5. What affects the rate of diffusion?
Factors include:
- Molecular size
- Temperature
- Concentration gradient
- Surface area and membrane thickness
Notes and Tips for Students

🧠 Note: When studying diffusion, visualize movement at the molecular level. Imagine how molecules spread out in a room when a perfume bottle is opened.
To master diffusion, consider:
- Drawing diagrams to illustrate diffusion in different scenarios
- Creating mnemonics for the steps involved
- Exploring real-life examples in everyday environments
Applications and Examples

Here are some practical examples of diffusion in biology:
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| Perfume | Diffuses through the air, moving from the bottle to your nose. |
| Oxygen Exchange in Lungs | Exchange of gases between alveoli and blood capillaries for respiration. |
| Nutrient Absorption in Small Intestine | Minerals and glucose diffuse into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body. |

Diffusion plays a critical role in maintaining life at every level, from single cells to complex organisms.
This comprehensive breakdown should leave you with a stronger understanding of diffusion, ensuring you can apply these concepts in various biological contexts. Diffusion is a cornerstone of passive transport, facilitating essential processes without the need for energy expenditure. It underscores the importance of concentration gradients in biological systems, driving substances to where they're needed most. Remember, diffusion doesn't just happen in textbooks; it's an active participant in your daily life, shaping how you breathe, eat, and thrive.
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?

+
Diffusion refers to the movement of any substance from an area of higher to lower concentration. Osmosis, however, is specifically the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane, driven by concentration differences in solutes.
Why is diffusion important for cells?

+
Diffusion is vital for cells because it allows for:
- Entry of essential nutrients and gases
- Removal of waste products
- Maintenance of cellular environment balance
Can diffusion happen in both directions?

+
Yes, diffusion can occur in both directions, but the net movement will always be from areas of high to low concentration. Equilibrium, where movement appears balanced, doesn’t stop movement, just the net flow.