Mastering Osmosis: Amoeba Sisters Worksheet Explained
Exploring the fundamentals of biology can be both fascinating and challenging. One of the key concepts in understanding cellular biology is osmosis. If you've stumbled upon the Osmosis Amoeba Sisters worksheet, you're likely seeking a deeper understanding of this process, or perhaps you're preparing for an upcoming exam. This comprehensive guide will take you through the worksheet, explain osmosis in detail, and provide tips on how to excel in this topic.
Understanding Osmosis

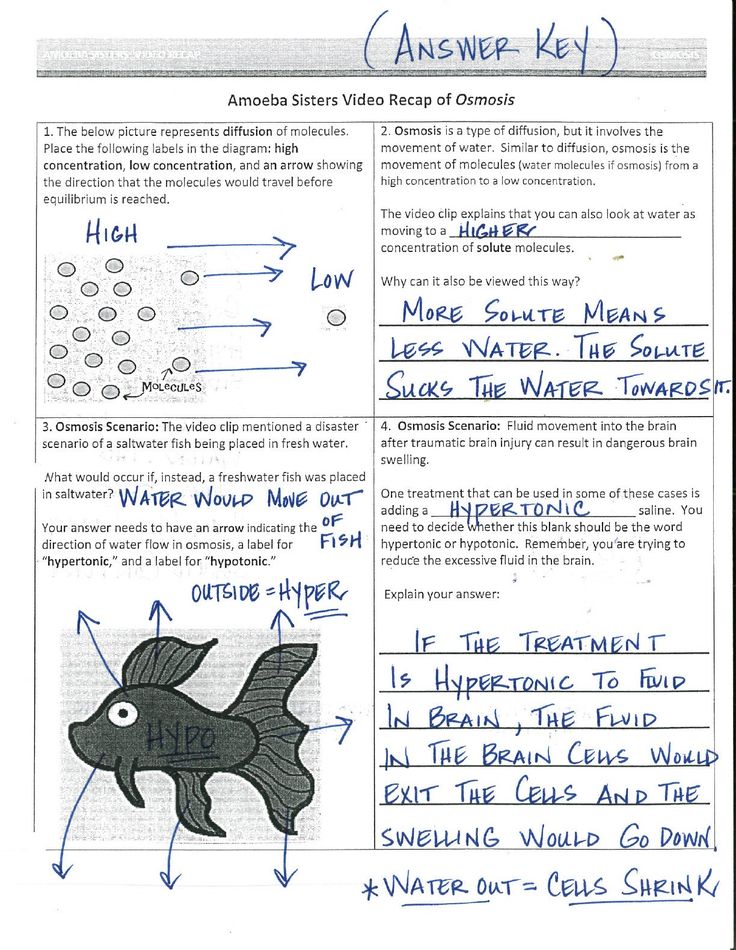
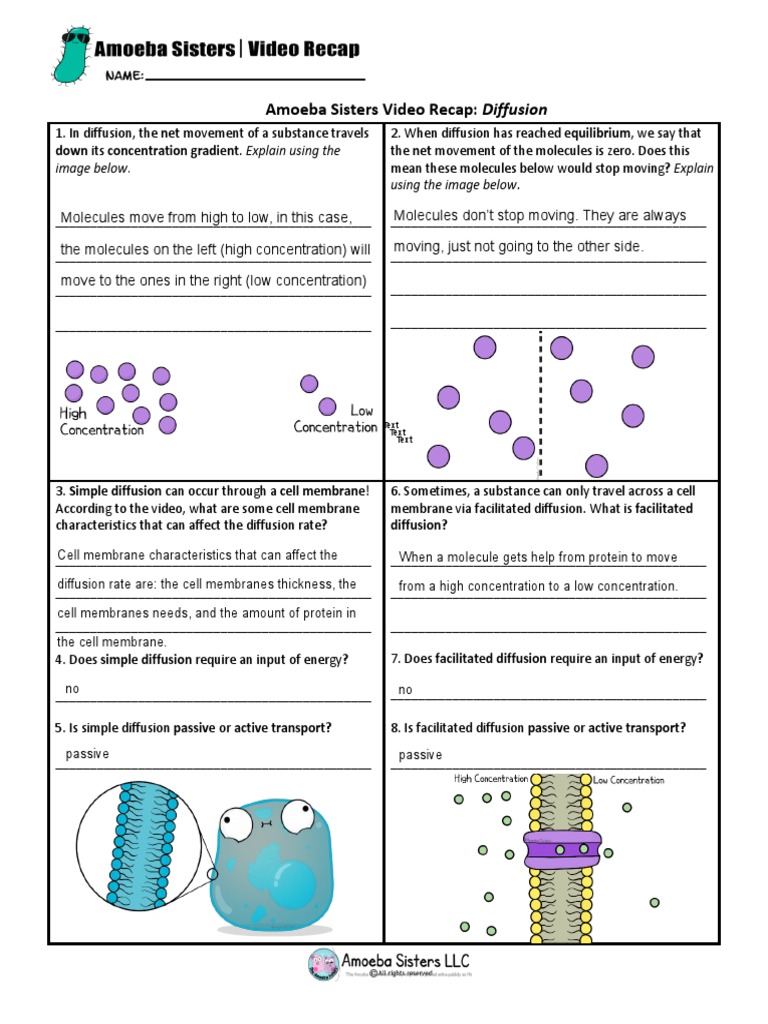
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Here’s how the Amoeba Sisters would break it down:
- Concentration Gradient: Water molecules will move to balance the concentration levels on both sides of the membrane.
- Membrane Permeability: Not all particles can pass through the membrane; only small molecules like water can go through freely.
Worksheet Analysis
The Amoeba Sisters worksheet on osmosis includes several key sections:
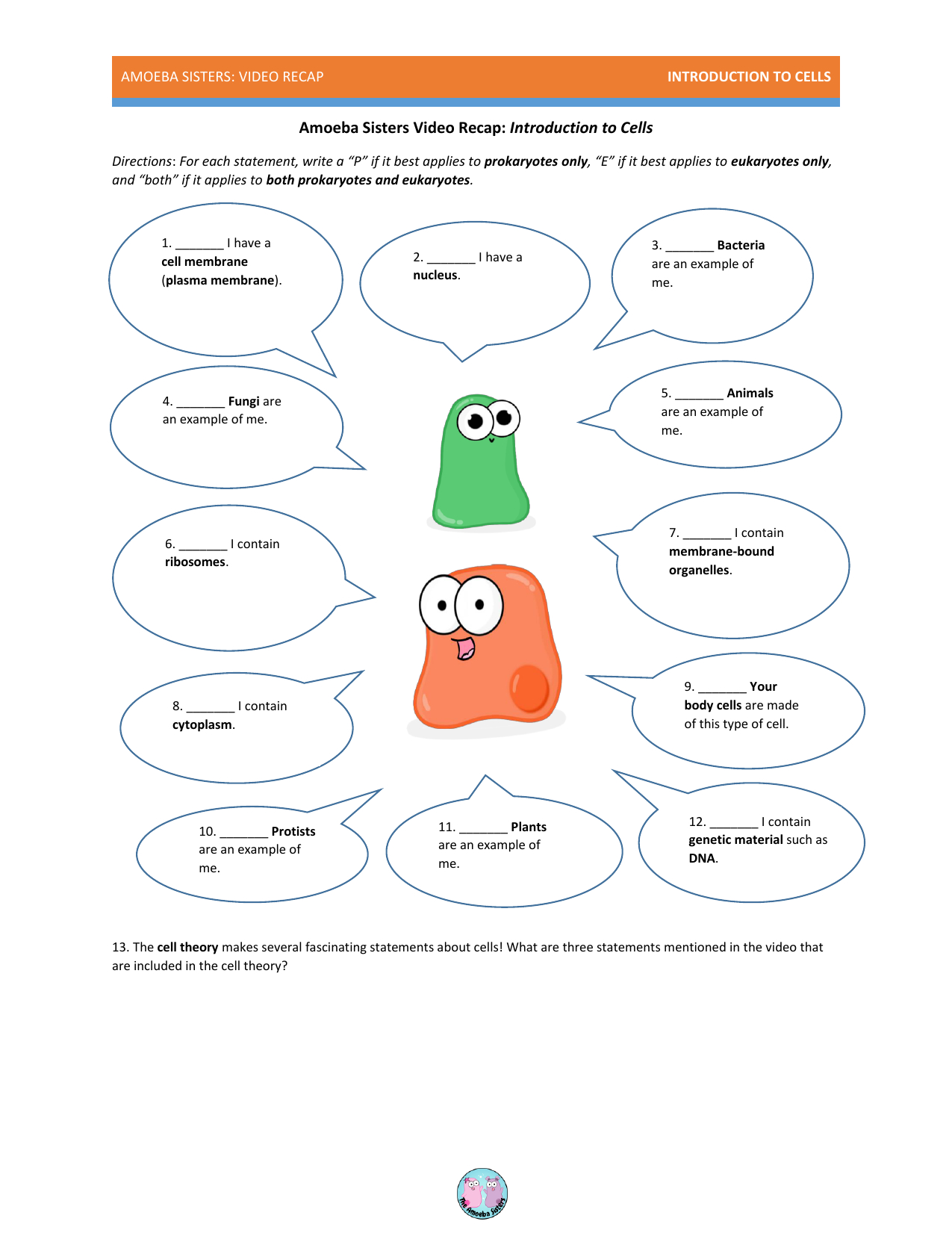
1. Terms to Know

First, let’s define the essential terms used in osmosis:
- Hypotonic Solution: More solvent (water) outside the cell than inside, leading to water flowing into the cell.
- Hypertonic Solution: Less solvent outside the cell, causing water to exit the cell.
- Isotonic Solution: Equal solute concentration on both sides, so no net water movement.
- Semipermeable Membrane: A barrier that allows some particles to pass through.
- Diffusion: The movement of any molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
🧪 Note: Understanding these terms is crucial as they form the foundation for solving osmosis-related problems.
2. Diagram Interpretation

The worksheet includes diagrams to visually represent osmosis:
- Osmosis in Plant Cells: When placed in a hypotonic solution, plant cells take up water, which is crucial for turgor pressure. In a hypertonic solution, plant cells lose water, leading to plasmolysis.
- Osmosis in Animal Cells: Animal cells in a hypotonic environment swell and may burst (cytolysis), while in a hypertonic solution, they shrink (crenation).
Table to illustrate the effects:
| Solution Type | Plant Cells | Animal Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Hypotonic | Swells but limited by cell wall | Swells and might burst |
| Hypertonic | Shrinks (plasmolysis) | Shrinks (crenation) |
| Isotonic | Stays the same | Stays the same |

3. Problem Solving

The worksheet often involves problems where you must determine:
- Which direction will water move?
- What will be the effects on the cell?
- How can these effects be observed?
Key Takeaways from the Worksheet

Here are some general principles you should take away:
- Water moves towards areas of higher solute concentration through osmosis.
- Cells have different responses to osmotic changes based on their structure (plant vs. animal).
- The presence of solutes inside the cell changes the direction of water movement.
🔬 Note: Always read the questions carefully, as the correct answers hinge on understanding solute concentrations and membrane permeability.
As you delve into osmosis, remember that understanding the basic principles is key to mastering complex biological processes. This worksheet acts as both a teaching tool and a practice ground for students to engage with osmosis actively. When approached correctly, it provides a visual and conceptual understanding of how osmosis affects different cell types in various environments.
Final Thoughts

By working through the Amoeba Sisters’ Osmosis worksheet, students can enhance their grasp of one of biology’s most fundamental processes. This understanding isn’t just for passing exams but is crucial for anyone venturing into the fascinating world of biological sciences. The worksheet helps students visualize osmosis and its impacts, making it easier to recall during exams or when encountered in real-life scenarios. Remember, the key to mastering osmosis lies in understanding the movement of water and its consequences on cells.
What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?

+
Osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane, while diffusion refers to the spread of any substance (solutes or solvents) from high to low concentration. Osmosis is a type of diffusion but only for water.
Why do plant cells and animal cells react differently in hypotonic solutions?

+
Plant cells have a cell wall that provides structural support and prevents the cell from bursting when it takes in too much water. Animal cells lack this additional layer, so they can swell until they burst or lyse.
Can osmosis occur without a semipermeable membrane?

+
Osmosis, by definition, requires a semipermeable membrane. Without it, water would mix freely with the solute, which is closer to diffusion. However, the term “osmosis” generally implies selective permeability.
How can I solve osmosis problems?

+
Focus on understanding the initial and final concentrations of solutes on both sides of the membrane. Determine if the concentration gradient will cause water to enter or exit the cell, and then predict the cell’s response based on its type (plant or animal).
What is the role of turgor pressure in osmosis?
+
Turgor pressure occurs when water enters plant cells and causes them to swell, pushing against the cell wall. This pressure provides support to plants and helps maintain their shape and structure.