Amoeba Sisters Biomolecules Worksheet: Your Answer Guide

Understanding Biomolecules with the Amoeba Sisters
The Amoeba Sisters are well-known educators on YouTube who have mastered the art of breaking down complex biological concepts into digestible, engaging lessons. Their Biomolecules Worksheet, designed to complement their video content, offers students a comprehensive guide to understanding the four major types of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. In this post, we'll dive deep into each biomolecule category, providing detailed answers to the worksheet questions to help students grasp these fundamental components of life.
What Are Biomolecules?

Biomolecules, often referred to as biological macromolecules, are large molecules that are essential for life. They are made up of thousands of atoms arranged in very specific structures. Here's a quick overview:
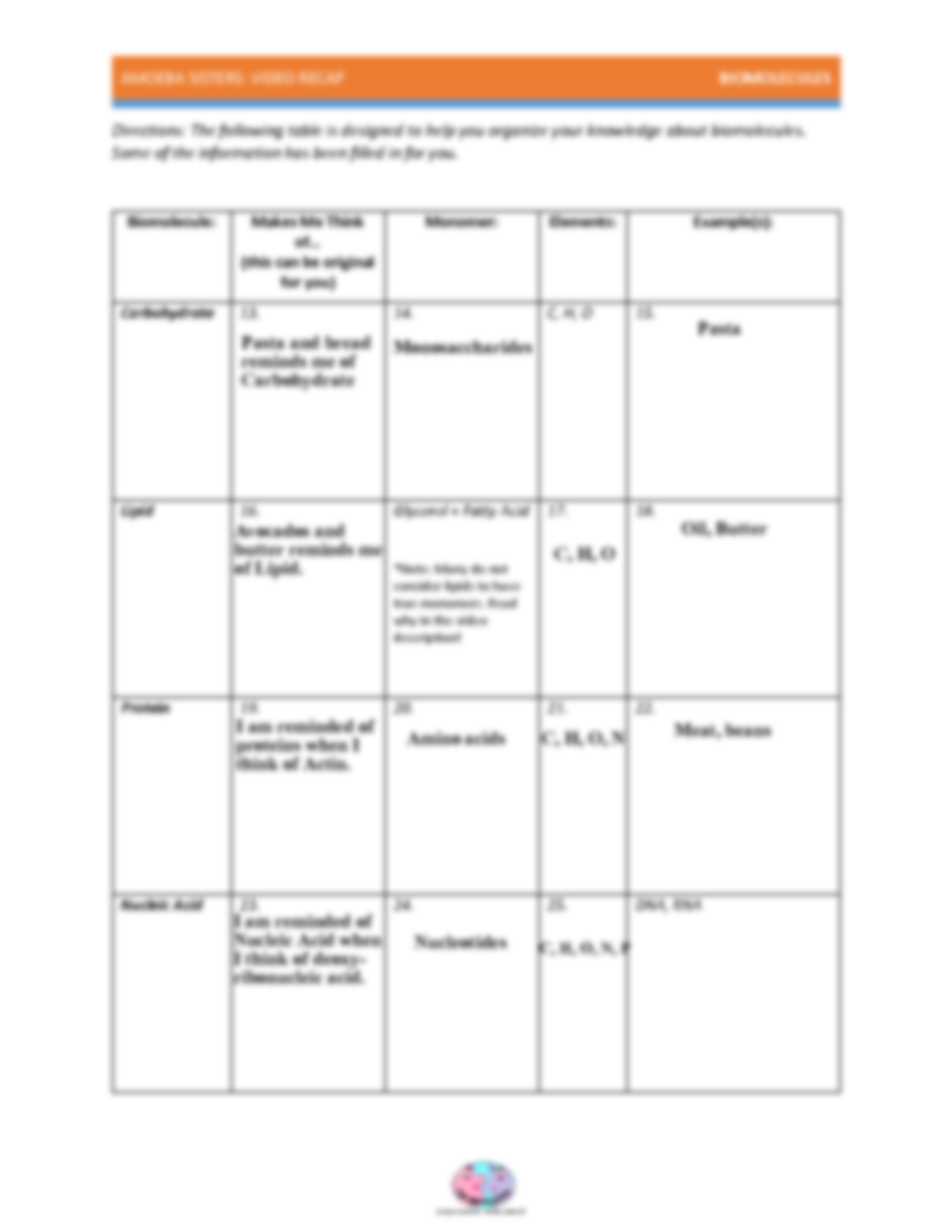
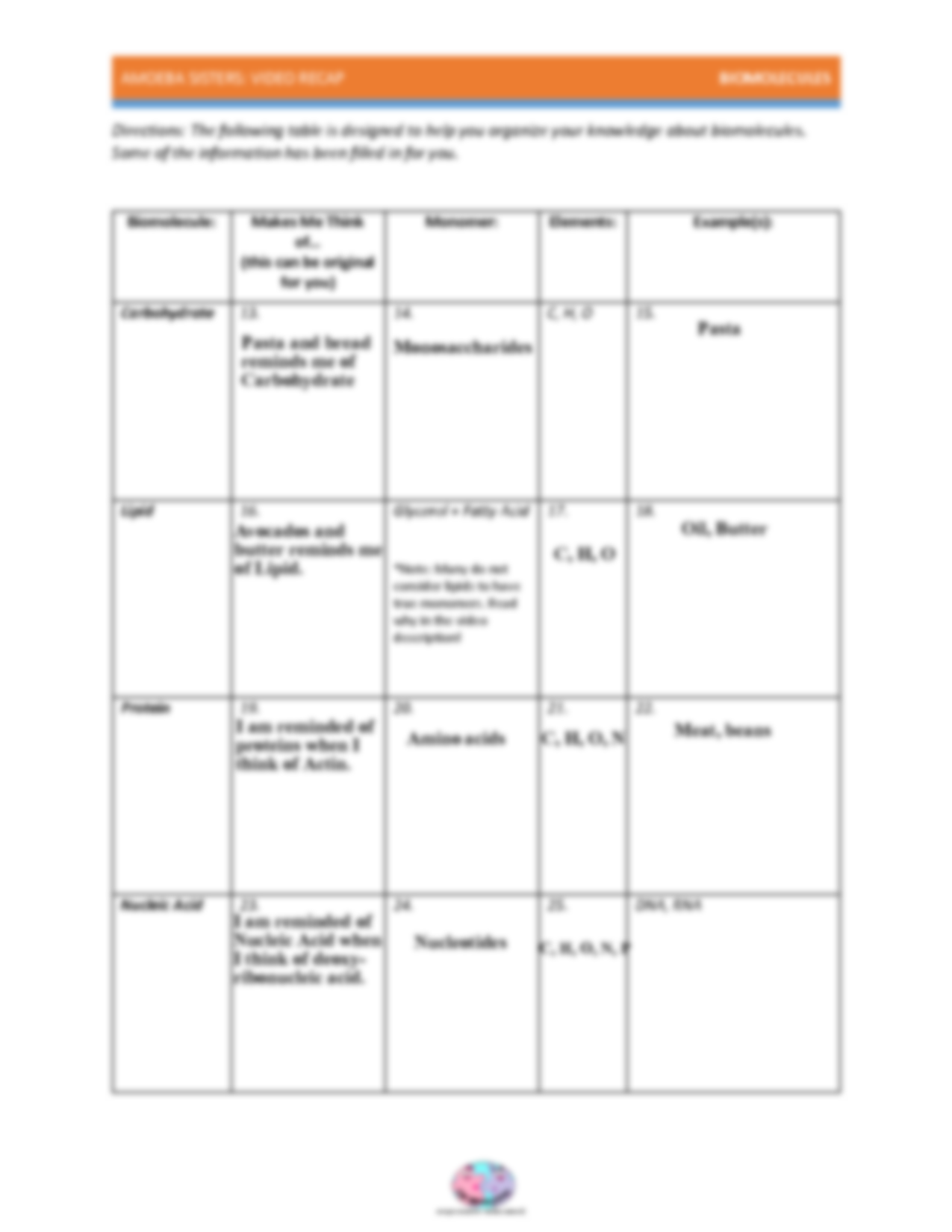
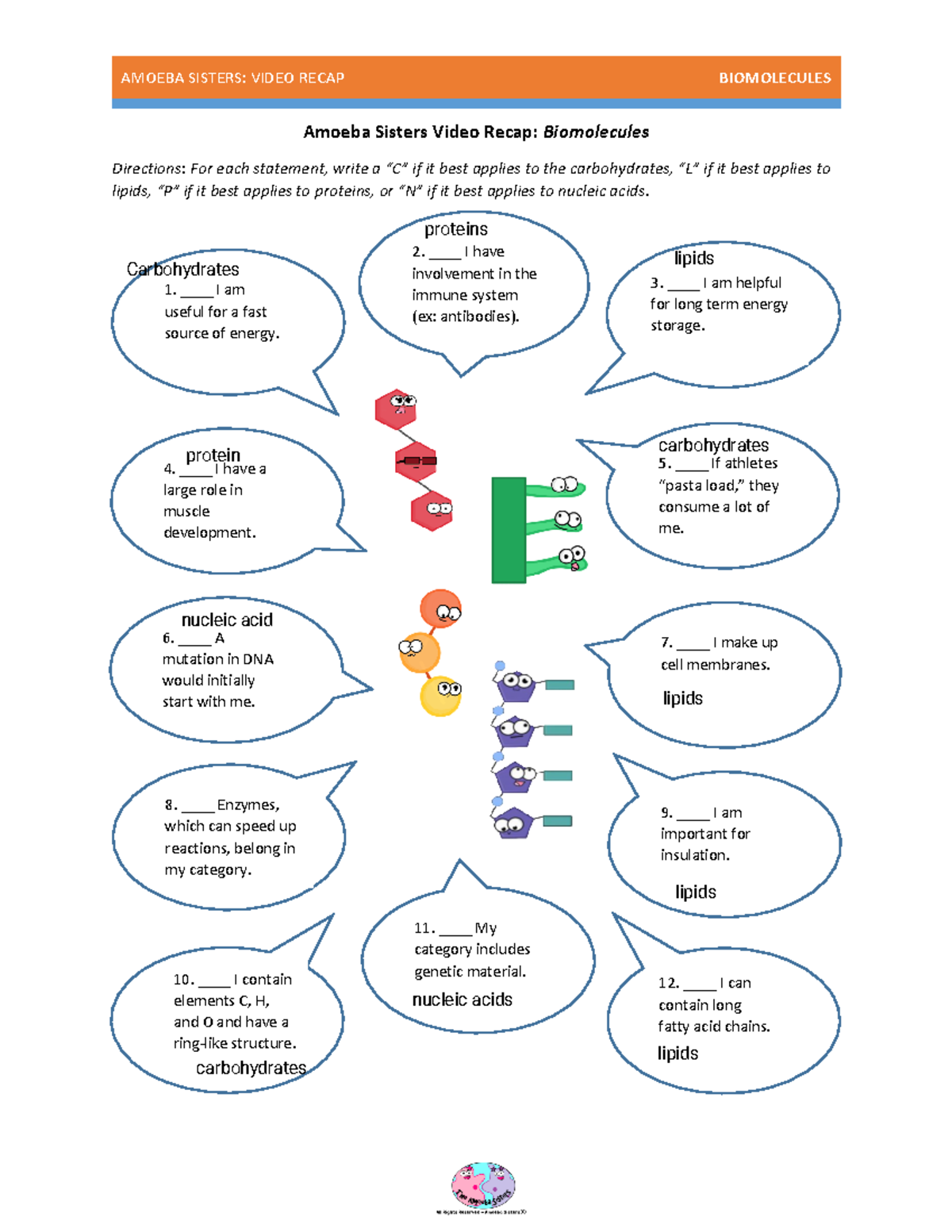
- Carbohydrates: Serve as the primary energy source for cells, and also play structural roles.
- Lipids: Key components of cell membranes, energy storage, and certain signaling molecules.
- Proteins: Fundamental in almost all cellular functions including catalysis, transport, and structural support.
- Nucleic Acids: Carry genetic information (DNA) and play a central role in protein synthesis (RNA).
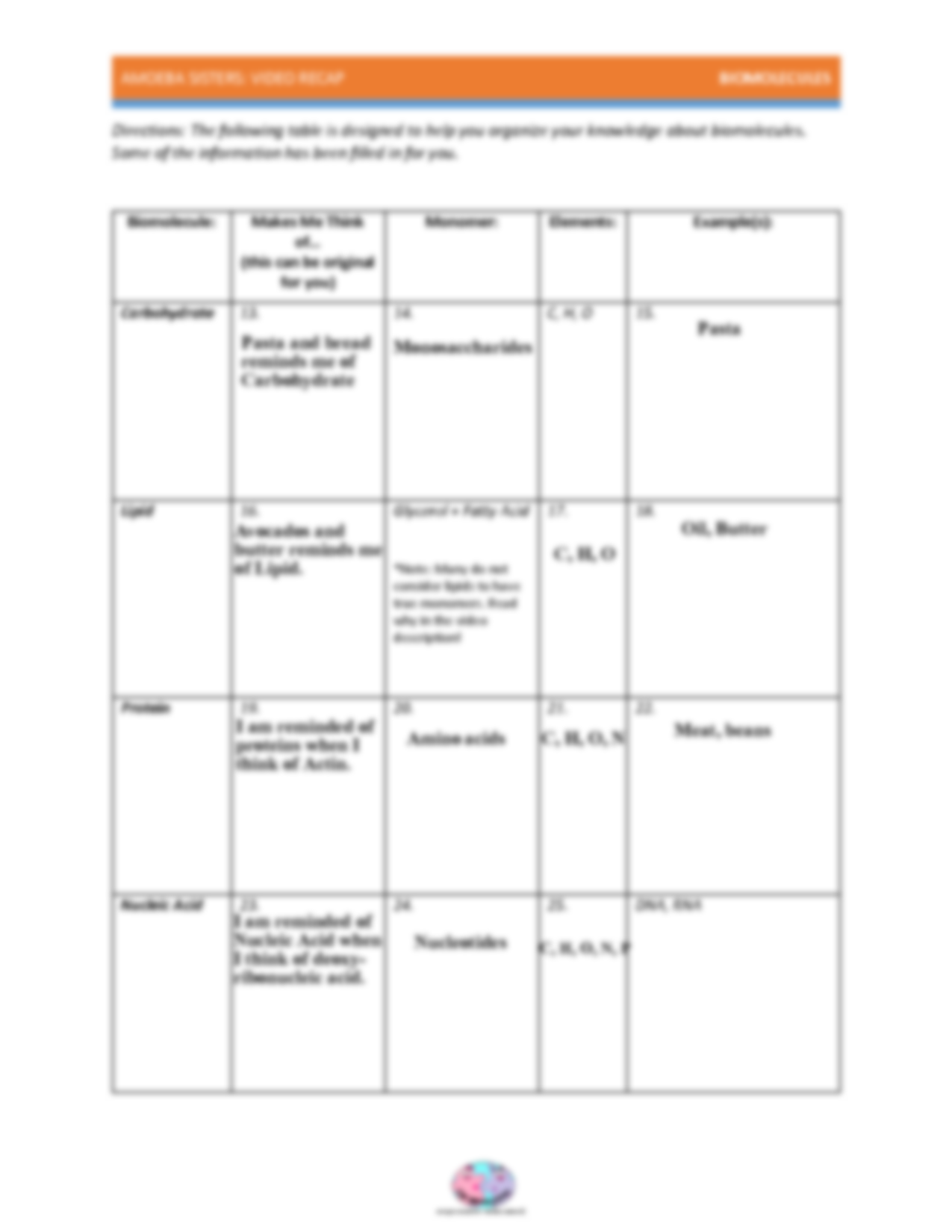
Carbohydrates: The Energy Powerhouses
Function and Importance
Carbohydrates are often referred to as sugars or saccharides. They:
- Provide quick energy due to their structure allowing for easy breakdown.
- Are critical in building cellular structures like the cell wall in plants (cellulose).
- Can be used as markers in cellular recognition.
| Carbohydrate Type | Example | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Monosaccharides | Glucose, Fructose | Energy source, building block for other carbohydrates |
| Disaccharides | Sucrose, Lactose | Energy storage, transport form of monosaccharides |
| Polysaccharides | Starch, Glycogen | Energy storage in plants/animals, structural support |
🌟 Note: The function of carbohydrates can vary significantly depending on their complexity and the type of organism they are found in.
Questions from the Worksheet

1. What are the three main functions of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates mainly function as energy sources, structural components, and in some cases, for cell signaling and identification.
Lipids: The Building Blocks of Cellular Membranes

Types of Lipids

Lipids are a diverse group of molecules which include:
- Fats - serve as energy storage.
- Phospholipids - major components of cell membranes.
- Steroids - like cholesterol, critical for maintaining cell membrane fluidity.
- Waxes - protective coatings for plants and animals.
Questions from the Worksheet

2. Explain why lipids are considered hydrophobic?
Lipids contain non-polar hydrocarbon chains which do not interact well with water; this is because their molecular structure has regions that repel water, thus making them hydrophobic.
Proteins: The Workhorses of the Cell

Structure and Function
Proteins are incredibly versatile due to their:
- Primary structure: the sequence of amino acids.
- Secondary structure: local folding into α-helices or β-sheets.
- Tertiary structure: overall shape and function of the protein.
- Quaternary structure: arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains in multi-subunit proteins.
Questions from the Worksheet
3. What are the roles of proteins in cells?
Proteins can act as enzymes, structural components, transport molecules, hormones, receptors, antibodies, and more, showcasing their vast array of functions within cells.
Nucleic Acids: The Data Bank of Life

Role in Life Processes

Nucleic acids:
- Carry genetic information in the form of DNA.
- Help in protein synthesis through RNA.
- Ensure genetic information is passed from one generation to the next.
Questions from the Worksheet

4. How do nucleic acids relate to each other in terms of function?
DNA stores genetic information long-term, while RNA acts as a messenger, adaptor, and structural molecule during protein synthesis.
In wrapping up this guide to the Amoeba Sisters Biomolecules Worksheet, we’ve journeyed through the fascinating world of macromolecules that make life possible. From the quick energy bursts provided by carbohydrates, to the structural support and waterproofing from lipids, the diverse functionalities of proteins, to the crucial role of nucleic acids in maintaining life’s continuity – each biomolecule plays an integral part in biological systems. Understanding these biomolecules not only helps in acing biology classes but also in appreciating the intricate design of life itself.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
+
While both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, they differ in several key ways. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, contains deoxyribose sugar and stores genetic information in the form of a double helix. RNA, or ribonucleic acid, uses ribose sugar, often forms a single strand, and plays multiple roles in protein synthesis like messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
How do enzymes fit into the category of biomolecules?

+
Enzymes are a type of protein. Their unique structure allows them to act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction itself. They are vital for metabolism, allowing cells to perform necessary biochemical processes efficiently.
Why are lipids important for the structure of cell membranes?
+Lipids, specifically phospholipids, form a bilayer in the cell membrane. This structure is crucial because it provides a barrier between the cell’s internal environment and the external environment, controlling the passage of substances in and out of the cell. Additionally, lipids contribute to the membrane’s fluidity and flexibility.