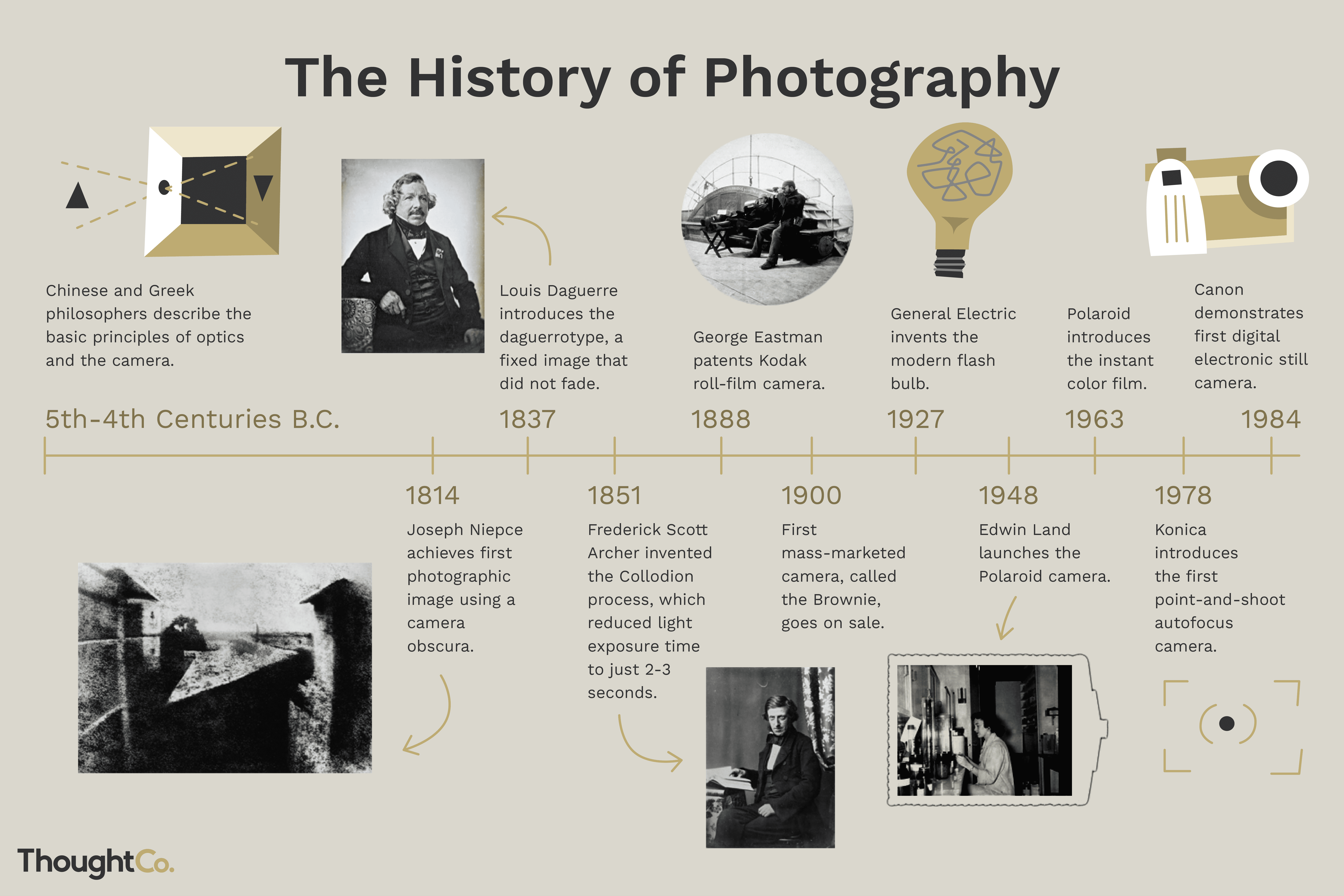
5 Key WWII Facts from America's Story

America's story during World War II is one of valor, strategic innovation, and a profound impact on the global stage. From the pivotal events leading to its involvement to the technological advancements and social changes that followed, the war shaped the U.S. and the world in numerous ways. Here are five key WWII facts that highlight America's role and the lasting legacy of the conflict:
1. The Attack on Pearl Harbor: A Turning Point

The surprise attack by the Japanese Imperial Navy on December 7, 1941, at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, thrust the United States into World War II. This single event changed the course of history for the country:
- Immediate Impact: Over 2,400 American service members were killed, and significant damage was inflicted on U.S. naval vessels and aircraft.
- War Declaration: The next day, President Franklin D. Roosevelt delivered his famous “Infamy Speech” to Congress, leading to a declaration of war against Japan, with Germany and Italy declaring war on the U.S. shortly after.
- National Unity: The attack galvanized American public opinion and unified the country against the Axis powers, setting the stage for an unparalleled mobilization of resources.
💡 Note: Pearl Harbor remains a stark reminder of the importance of vigilance and preparedness in international relations.
2. Industrial Might and the Arsenal of Democracy

World War II showcased America’s industrial prowess, which turned the nation into the “Arsenal of Democracy”:
- Production Levels: The U.S. outproduced all other nations combined in terms of military hardware, including ships, aircraft, and vehicles.
- Economic Transformation: The war effort led to full employment, significantly lifting the country out of the Great Depression.
- Technological Innovations: The need for speed and efficiency fostered advancements in mass production, radar technology, and even the foundations for the computer age.

💡 Note: The industrial mobilization set the groundwork for America’s postwar economic dominance.
3. The D-Day Invasion: Operation Overlord

On June 6, 1944, the Allies, primarily American, British, and Canadian forces, executed the largest seaborne invasion in history:
- Normandy Beaches: D-Day involved over 156,000 troops landing on five beaches in Normandy, France, beginning the liberation of Western Europe.
- Strategic Significance: This operation opened a second front against Nazi Germany, hastening the end of the war in Europe.
- Human Cost: The initial invasion saw significant casualties, but it paved the way for victory in Europe, with Paris being liberated by August.
💡 Note: The success of D-Day underscored the importance of meticulous planning and international cooperation in warfare.
4. The Manhattan Project: A Scientific Endeavor

The Manhattan Project was a top-secret military initiative that led to the development of the first nuclear weapons:
- Development: Enlisted scientists worked in Los Alamos, New Mexico, to harness the power of nuclear fission.
- First Atomic Bomb Test: The Trinity Test on July 16, 1945, demonstrated the devastating potential of atomic bombs.
- Deployment: The bombs “Little Boy” and “Fat Man” were dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, effectively ending the war with Japan but introducing a new era of nuclear deterrence.
| Location | Date | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Hiroshima | August 6, 1945 | “Little Boy” detonated, resulting in approximately 140,000 deaths |
| Nagasaki | August 9, 1945 | “Fat Man” detonated, resulting in approximately 70,000 deaths |

💡 Note: The Manhattan Project’s ethical implications continue to be debated, influencing global discussions on nuclear weapons.
5. Social Changes and the Home Front

World War II also catalyzed significant social changes at home:
- Women in the Workforce: With men at war, “Rosie the Riveter” became an icon as women filled manufacturing and service roles, challenging gender norms.
- Racial Integration: Although segregation persisted, African Americans made significant contributions to the war effort, setting the stage for civil rights advancements.
- Cultural Shifts: The war led to mass migrations, cultural exchanges, and a redefinition of American identity, laying the foundation for the post-war boom.
The social changes initiated by the war continued to evolve, shaping America’s social landscape in the decades that followed.
💡 Note: The war's impact on society was as profound as its military significance, setting off a chain of events that would redefine America.
In reflecting on America's role during WWII, we see a nation that not only provided the material support necessary for victory but also underwent a profound transformation internally. The resilience shown in the face of adversity, the technological leaps made, and the societal shifts brought about continue to influence global politics, economics, and culture. These key facts remind us of the indelible mark World War II left on America, creating a legacy of both sacrifice and innovation that still resonates today.
What was the immediate consequence of the attack on Pearl Harbor?

+
The immediate consequence was the United States entering World War II on December 8, 1941, after declaring war on Japan, with subsequent declarations of war by Germany and Italy.
How did the D-Day invasion impact WWII?

+
The D-Day invasion opened a second front against Nazi Germany, hastening the end of the war in Europe by providing a platform for the liberation of occupied territories.
Why was the Manhattan Project considered a success?
+
The Manhattan Project was deemed a success because it led to the development of the atomic bomb, which was deployed to end the war with Japan and thus prevented further loss of life in a prolonged conflict.