5 Essential Tips for Solving Algebra 1b Inequalities

Algebra 1b introduces students to a more complex realm of algebraic equations, inequalities being one of the core components. Solving inequalities can seem daunting at first, but with the right strategies, it becomes an engaging puzzle to solve. Here, we'll delve into five essential tips that will not only make solving inequalities in Algebra 1b easier but also help you master this mathematical concept.
1. Understand the Concept of Inequalities
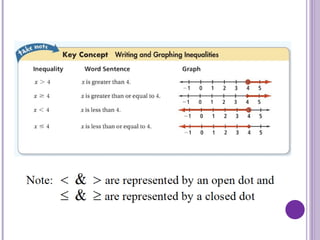
Before diving into solving inequalities, it’s crucial to grasp what they are. Unlike equations that seek to find exact values, inequalities aim to identify ranges of values that satisfy a given statement. Here’s a quick overview:
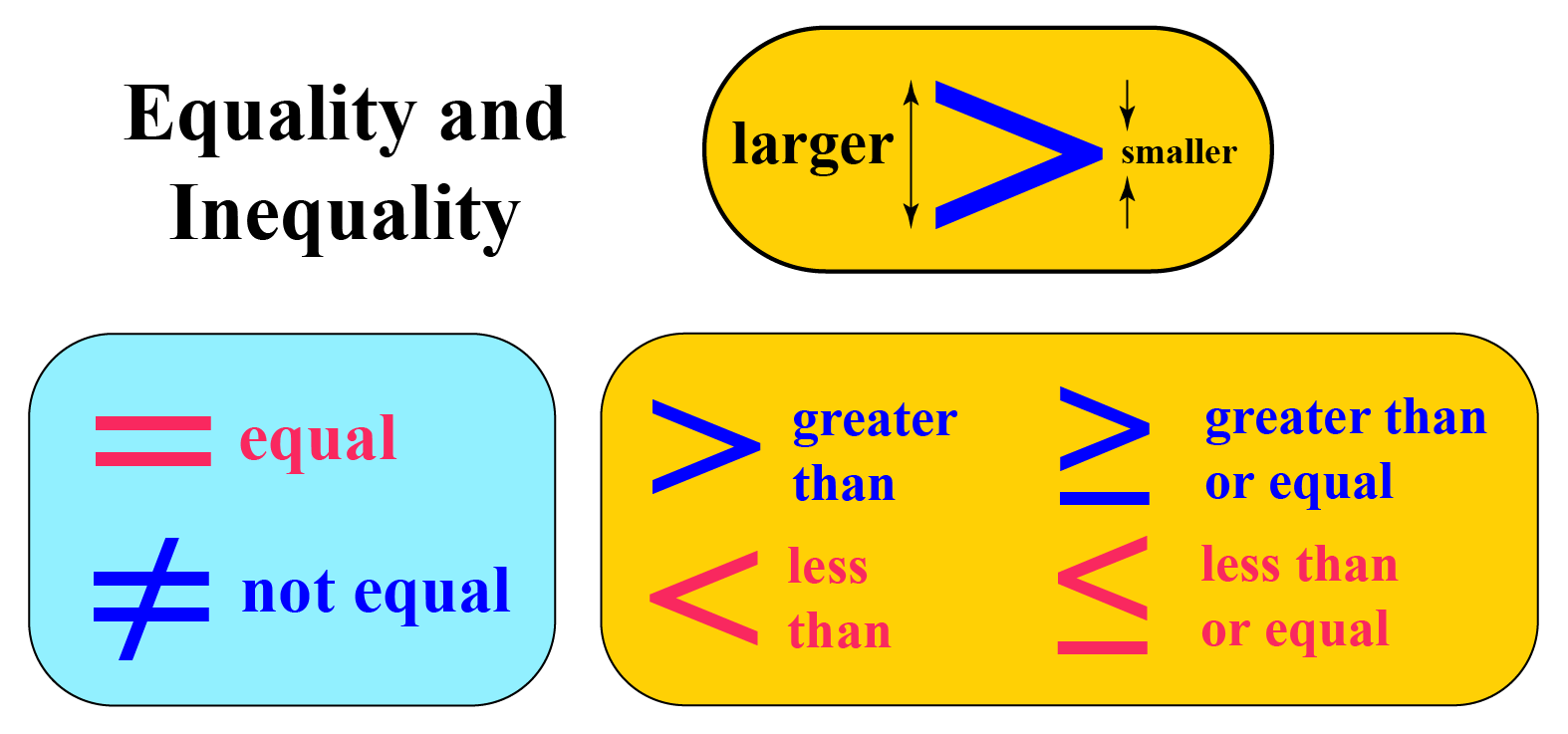
- Less than or less than or equal to (<, ≤)
- Greater than or greater than or equal to (>, ≥)
- Not equal to (≠)
🔍 Note: When an inequality includes variables, these variables represent the possible values that can make the inequality true.
2. Manipulate the Inequality Correctly

Just like in equations, the rules for manipulating inequalities are quite straightforward but come with an important twist:
- Addition and Subtraction: You can add or subtract the same value on both sides of the inequality without changing the direction.
- Multiplication and Division: Multiplying or dividing both sides by a positive number also keeps the inequality sign the same. However, if you multiply or divide by a negative number, you must reverse the inequality sign to maintain the truth of the statement.
| Original Inequality | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 2x > 6 | Divide by 2 | x > 3 |
| -3x ≤ 9 | Divide by -3 and flip the sign | x ≥ -3 |

⚠️ Note: Reversing the sign when multiplying or dividing by a negative is crucial to keep the inequality logically consistent.
3. Use Sign Charts and Test Points

In more complex inequalities, using sign charts or test points can be a powerful strategy. Here’s how:
- Find all points where the inequality is equal to zero. These are potential boundary points.
- Choose test points from each interval created by these boundary points.
- Determine if the test points satisfy the inequality.
- Sketch the sign chart to visualize where the inequality holds true.
📊 Note: Test points provide a visual and systematic way to solve inequalities, making the process more tangible for learners.
4. Identify and Handle Absolute Value Inequalities
Absolute value inequalities involve the concept of distance from zero. Here are the steps to solve them:
- Formulate: Write the inequality in terms of two scenarios where the expression inside the absolute value is positive or negative.
- Solve Each Scenario: Treat each case as a regular inequality.
- Combine Results: Union or intersection of solutions depends on the inequality sign.
📦 Note: Absolute value inequalities often require you to consider both positive and negative values of the expression inside the absolute value symbol.
5. Practice, Practice, Practice

There’s no substitute for practice when mastering algebra, particularly with inequalities. Regularly solving different types of inequalities helps in:
- Recognizing patterns and common pitfalls.
- Improving speed and accuracy in solving.
- Developing an intuition for mathematical logic.
🔄 Note: Practice not only builds proficiency but also confidence in handling algebraic inequalities.
Mastering Algebra 1b inequalities involves understanding their basic principles, manipulating them with care, using strategic tools like sign charts, tackling absolute value inequalities, and engaging in constant practice. These tips, when applied, can significantly ease the learning curve, transforming inequality solving from a source of frustration into a rewarding challenge.
What are the differences between equations and inequalities?

+
Equations seek specific solutions where both sides balance out exactly. Inequalities, on the other hand, look for a range of solutions where one side can be greater than, less than, or equal to the other side.
Why do we flip the inequality sign when multiplying or dividing by a negative number?

+
Multiplying or dividing by a negative number reverses the order of numbers. Hence, to maintain the inequality’s truth, you must flip the sign to reflect this change in order.
Can inequalities have no solution?

+
Yes, sometimes inequalities might have no solution, especially when the conditions set up by the inequality are mutually exclusive, like x < 1 and x > 2 simultaneously.
How can absolute value affect the solution of an inequality?

+
Absolute value considers the distance from zero, thus requiring you to split the inequality into two parts: one for when the expression inside the absolute value is positive and one when it is negative, potentially doubling the number of solutions.