5 Essential Pythagorean Theorem Worksheet Tips for Algebra 1

Algebra 1 introduces students to various mathematical concepts, and one of the fundamental principles they encounter is the Pythagorean Theorem. Here are some essential tips to enhance your understanding and application of Pythagorean Theorem through worksheets.
Understand the Basics

The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This can be mathematically expressed as:
- a2 + b2 = c2, where c is the hypotenuse.

Worksheet Tip 1: Visualize the Problem
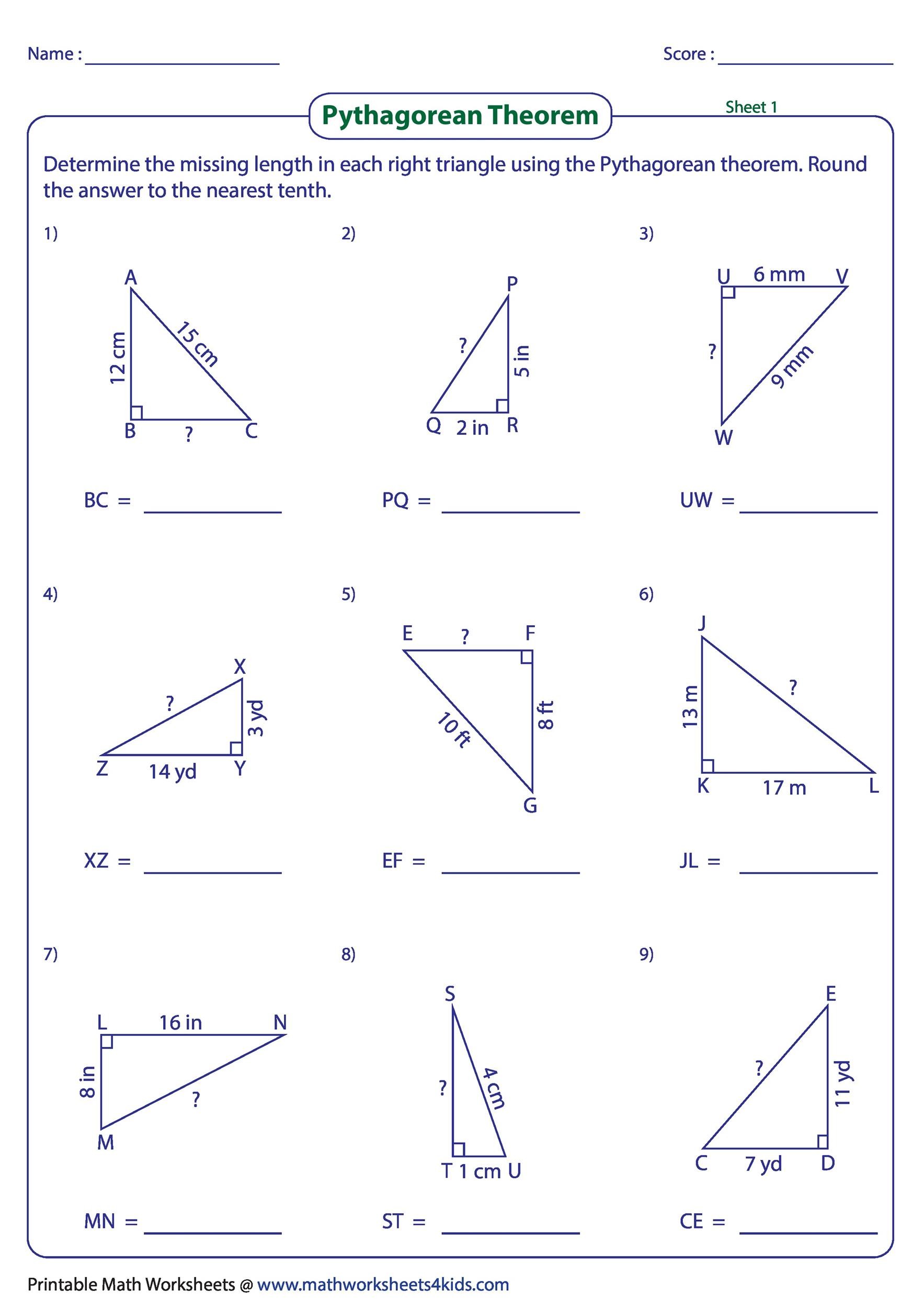
Before diving into calculations, sketching the triangle can significantly help:
- Draw a right triangle.
- Label the sides you know, especially the hypotenuse if it’s given.
- Visualize the right angle to reinforce understanding.
Worksheet Tip 2: Substitute Known Values
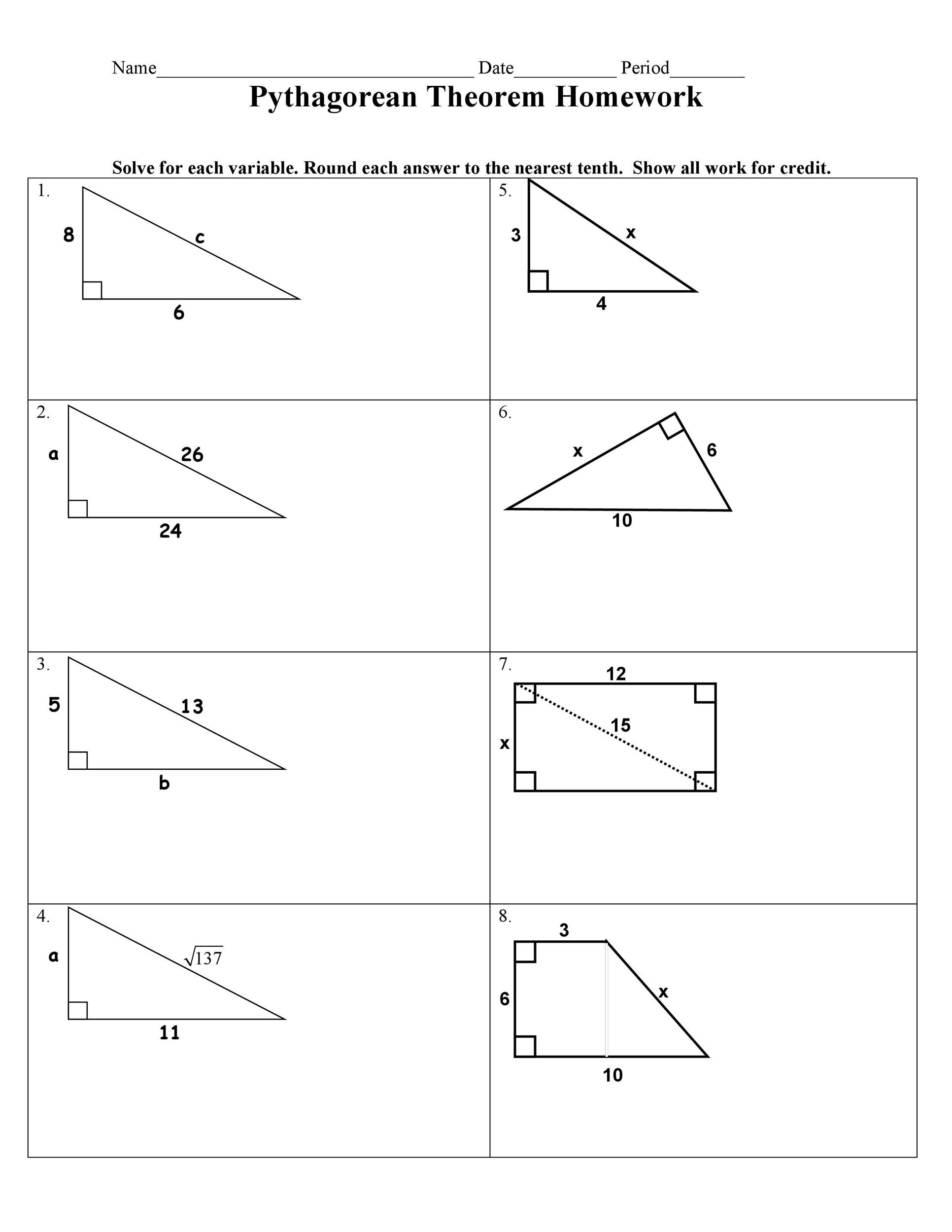
Once you have your triangle drawn, substitute the known values into the formula:
- If you’re finding the length of a side, identify which side you’re solving for (either ‘a’ or ‘b’) or the hypotenuse (‘c’).
- Plug in the known sides into the equation.
🔎 Note: Always double-check which value is ‘c’ in your equation. It’s common to mistake ‘a’ or ‘b’ for ‘c’ if not visualized correctly.
Worksheet Tip 3: Solve Step-by-Step

When solving for a side length, follow these steps:
- If you’re solving for c, rearrange to c = √(a2 + b2).
- For ‘a’ or ‘b’, rearrange the equation to isolate the unknown variable:
- a = √(c2 - b2)
- b = √(c2 - a2)
- Calculate the result step-by-step, ensuring accuracy.
Worksheet Tip 4: Practice with Various Scenarios

To master the theorem, you need to practice with different types of problems:
- Finding the hypotenuse.
- Finding one of the other two sides when the hypotenuse and one side are known.
- Using the theorem to solve practical problems (like ladder placement).
Worksheet Tip 5: Common Mistakes to Avoid

Here are some typical mistakes to be cautious about:
- Confusing a, b, and c. Remember, ‘c’ is always the hypotenuse.
- Miscalculating square roots, especially when dealing with irrational numbers.
- Incorrectly rearranging the formula when solving for ‘a’ or ‘b’.
🔔 Note: Keep in mind, not all triangles are right triangles. Check for a 90-degree angle before applying the theorem.
Worksheets that focus on the Pythagorean Theorem are crucial in Algebra 1 for developing problem-solving skills. By following these tips, students can gain confidence in their ability to use this theorem accurately. Remember, practice makes perfect, and consistent application of these techniques will make the concept second nature, enhancing your algebraic journey.
Why is visualizing the problem helpful?
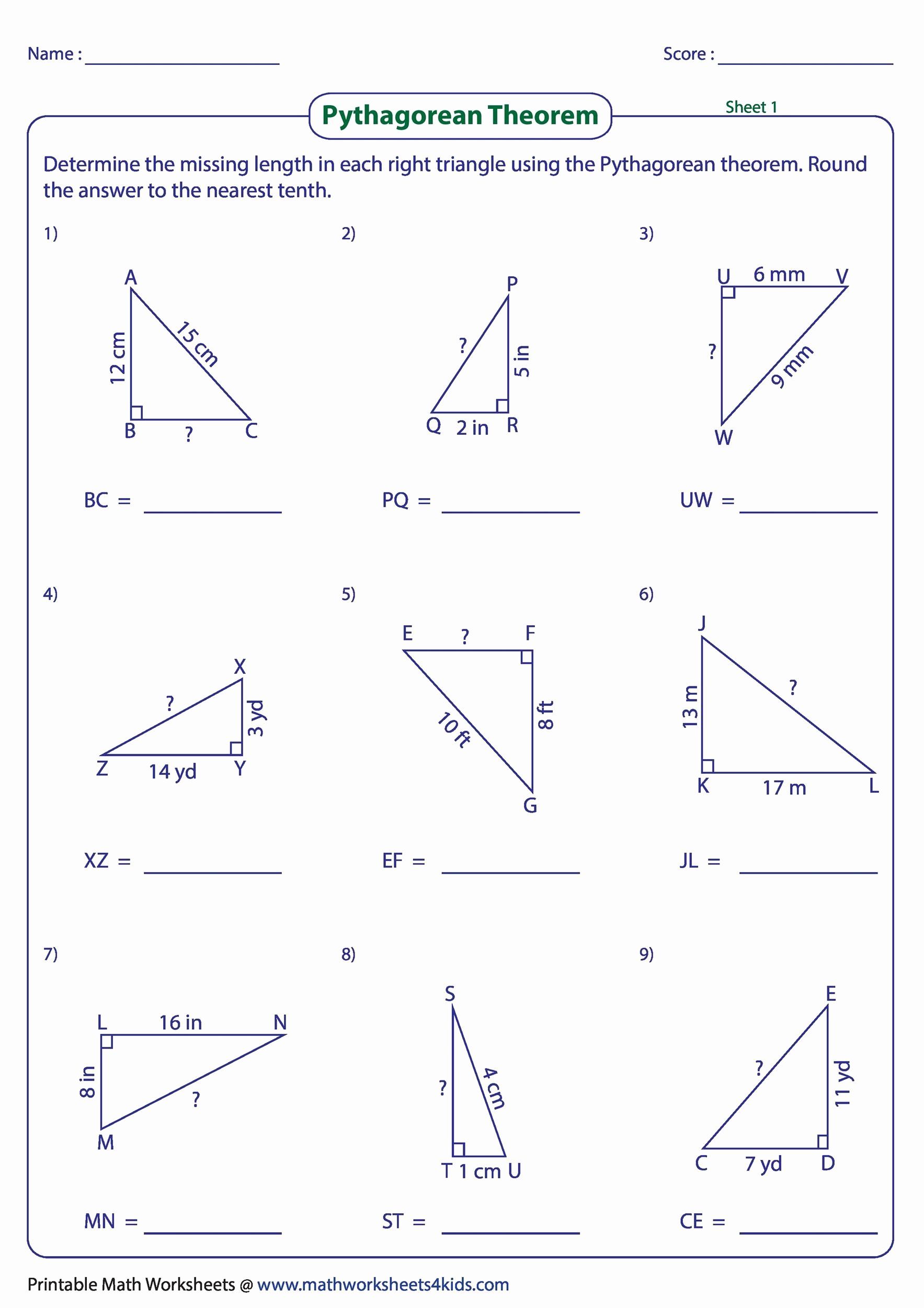
+
Visualizing helps to avoid common errors like misidentifying the hypotenuse, and it gives a geometric sense of how the numbers relate, making the problem more tangible.
How do I know if I need to use the Pythagorean Theorem?

+
If a problem mentions or involves a right triangle or the relationship between its sides, the Pythagorean Theorem is likely applicable.
Can I use the Pythagorean Theorem for any triangle?

+
No, it only applies to right triangles where one angle is 90 degrees.