5 USAF Warrant Officer Ranks Explained
USAF Warrant Officer Ranks: Understanding the Roles and Responsibilities
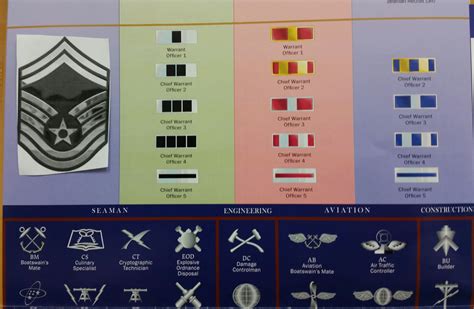
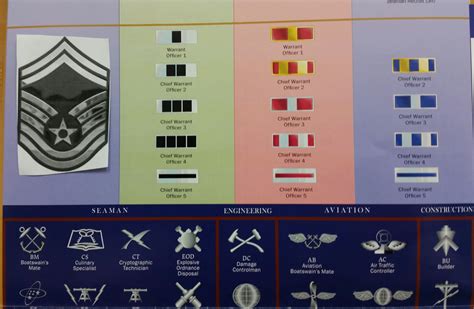
The United States Air Force (USAF) has a unique rank structure that includes warrant officers, who are technical experts in their field. Warrant officers play a crucial role in the USAF, providing critical support and guidance to airmen and officers. In this article, we will explore the five USAF warrant officer ranks, their roles, and responsibilities.
1. Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)

Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) is the entry-level warrant officer rank in the USAF. To become a WO1, an airman must have a minimum of 4 years of service, with 2 years in their current Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC). They must also have a bachelor’s degree or higher, and meet specific requirements for their AFSC.
WO1s serve as technical experts in their field and provide guidance and support to airmen and officers. They are responsible for leading small teams, analyzing problems, and developing solutions.
Key Responsibilities:
- Provide technical expertise in their AFSC
- Lead small teams and provide guidance to airmen and officers
- Analyze problems and develop solutions
- Participate in planning and decision-making processes
2. Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2)
Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) is the second warrant officer rank in the USAF. To become a CW2, a WO1 must have a minimum of 2 years in grade and meet specific requirements for their AFSC.
CW2s serve as senior technical experts in their field and provide guidance and support to airmen, officers, and other warrant officers. They are responsible for leading larger teams, developing policies, and making decisions that impact the unit.
Key Responsibilities:
- Provide senior technical expertise in their AFSC
- Lead larger teams and provide guidance to airmen, officers, and other warrant officers
- Develop policies and procedures
- Make decisions that impact the unit
3. Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3)
Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) is the third warrant officer rank in the USAF. To become a CW3, a CW2 must have a minimum of 2 years in grade and meet specific requirements for their AFSC.
CW3s serve as experts in their field and provide guidance and support to airmen, officers, and other warrant officers. They are responsible for leading units, developing strategic plans, and making decisions that impact the wing or base.
Key Responsibilities:
- Provide expert technical guidance in their AFSC
- Lead units and provide guidance to airmen, officers, and other warrant officers
- Develop strategic plans
- Make decisions that impact the wing or base
4. Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4)

Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) is the fourth warrant officer rank in the USAF. To become a CW4, a CW3 must have a minimum of 2 years in grade and meet specific requirements for their AFSC.
CW4s serve as senior experts in their field and provide guidance and support to airmen, officers, and other warrant officers. They are responsible for leading major commands, developing policy, and making decisions that impact the Air Force.
Key Responsibilities:
- Provide senior expert technical guidance in their AFSC
- Lead major commands and provide guidance to airmen, officers, and other warrant officers
- Develop policy
- Make decisions that impact the Air Force
5. Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5)
Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) is the highest warrant officer rank in the USAF. To become a CW5, a CW4 must have a minimum of 2 years in grade and meet specific requirements for their AFSC.
CW5s serve as master experts in their field and provide guidance and support to airmen, officers, and other warrant officers. They are responsible for leading Air Force-wide initiatives, developing policy, and making decisions that impact the Department of Defense.
Key Responsibilities:
- Provide master expert technical guidance in their AFSC
- Lead Air Force-wide initiatives and provide guidance to airmen, officers, and other warrant officers
- Develop policy
- Make decisions that impact the Department of Defense
In conclusion, the USAF warrant officer ranks play a critical role in the Air Force, providing technical expertise, guidance, and support to airmen and officers. Each rank has unique responsibilities and requirements, and understanding these roles is essential for success in the Air Force.
📝 Note: The requirements and responsibilities for each warrant officer rank may vary depending on the AFSC and unit.
What is the difference between a warrant officer and an officer in the USAF?

+
Warrant officers are technical experts in their field, while officers are leaders who have a broader range of responsibilities. Warrant officers provide guidance and support to airmen and officers, while officers lead units and make decisions that impact the Air Force.
How do I become a warrant officer in the USAF?
+
To become a warrant officer in the USAF, you must meet specific requirements for your AFSC, including education, training, and experience. You must also have a minimum of 4 years of service, with 2 years in your current AFSC.
What is the highest rank a warrant officer can achieve in the USAF?

+
The highest rank a warrant officer can achieve in the USAF is Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5).
Related Terms:
- Air Force warrant officer requirements
- USAF warrant officer
- Warrant officer Air Force pay
- Usaf warrant Officer jobs
- Air Force warrant officer pilot