Air Force JAG Salary Revealed

Understanding the Air Force JAG Salary Structure
The United States Air Force Judge Advocate General’s (JAG) Corps is a highly respected and elite group of lawyers who serve as the primary source of legal advice to the Air Force. As a JAG officer, one can expect a competitive salary, comprehensive benefits, and a unique opportunity to serve their country. But how much does an Air Force JAG officer actually earn? In this article, we will delve into the Air Force JAG salary structure, explore the factors that influence compensation, and provide insights into the overall compensation package.
Basic Pay: The Foundation of Air Force JAG Salary
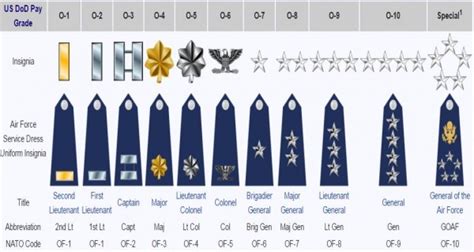
Air Force JAG officers are paid based on their rank and time in service, just like other Air Force personnel. The basic pay structure for JAG officers is identical to that of other Air Force officers, with some exceptions. Here is a breakdown of the basic pay for Air Force JAG officers:
| Rank | Basic Pay (per month) |
|---|---|
| Second Lieutenant (O-1) | $3,287.10 |
| First Lieutenant (O-2) | $3,787.70 |
| Captain (O-3) | $5,135.30 |
| Major (O-4) | $6,356.40 |
| Lieutenant Colonel (O-5) | $7,819.50 |
| Colonel (O-6) | $9,849.90 |
Note: These figures are based on 2022 pay rates and are subject to change.
Additional Forms of Compensation
In addition to basic pay, Air Force JAG officers may receive various forms of special compensation, including:
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): A monthly stipend to help cover the cost of housing, based on the officer’s rank, location, and family size.
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): A monthly stipend to help cover the cost of food.
- Special Duty Pay: Additional pay for officers assigned to special duty positions, such as recruiter or drill instructor.
- Hazardous Duty Pay: Additional pay for officers assigned to hazardous duty positions, such as combat zones.
- Flight Pay: Additional pay for officers who are certified to fly.
📝 Note: These forms of compensation can vary depending on the officer's specific circumstances and duty assignments.
Benefits and Perks
Air Force JAG officers enjoy a comprehensive benefits package, including:
- Health Insurance: Comprehensive medical, dental, and vision coverage for the officer and their family.
- Retirement Benefits: Eligibility for a pension after 20 years of service, with options for early retirement.
- Education Assistance: Access to the Air Force’s tuition assistance program, as well as the GI Bill.
- Paid Time Off: Generous paid vacation and holiday leave.
- Access to Base Facilities: Use of base facilities, including fitness centers, libraries, and shopping centers.
Factors That Influence Air Force JAG Salary

Several factors can influence an Air Force JAG officer’s salary, including:
- Rank: As with other Air Force personnel, JAG officers’ salaries increase with rank.
- Time in Service: The longer an officer serves, the higher their salary.
- Location: Officers assigned to high-cost areas, such as San Francisco or New York City, may receive higher allowances to help offset the cost of living.
- Specialty: JAG officers with specialized skills, such as those with experience in cyber law or international law, may be eligible for special pay.
Conclusion

The Air Force JAG salary structure is competitive and comprehensive, offering a range of benefits and perks in addition to basic pay. While salary can vary depending on rank, time in service, and location, Air Force JAG officers can expect a rewarding and challenging career with opportunities for growth and development.
How much does an Air Force JAG officer make?

+
Air Force JAG officers’ salaries vary based on rank and time in service, but the basic pay for a Second Lieutenant (O-1) is 3,287.10 per month, while a Colonel (O-6) can earn up to 9,849.90 per month.
What benefits do Air Force JAG officers receive?

+
Air Force JAG officers enjoy a comprehensive benefits package, including health insurance, retirement benefits, education assistance, paid time off, and access to base facilities.
How do I become an Air Force JAG officer?

+
To become an Air Force JAG officer, you must earn a law degree from an American Bar Association (ABA)-accredited law school, pass the bar exam, and receive a commission through the Air Force’s Judge Advocate General’s Corps.