9 Air Force Commissioned Officer Ranks Explained

Understanding the Hierarchy: 9 Air Force Commissioned Officer Ranks Explained

The United States Air Force (USAF) is one of the most technologically advanced air forces in the world, with a vast array of aircraft, missiles, and other military equipment. To manage and operate these complex systems, the Air Force relies on a hierarchical structure of commissioned officers, each with their own distinct rank and responsibilities. In this article, we will explore the nine commissioned officer ranks in the Air Force, from the lowest to the highest, and provide an overview of their roles and responsibilities.
Second Lieutenant (2nd Lt, O-1)
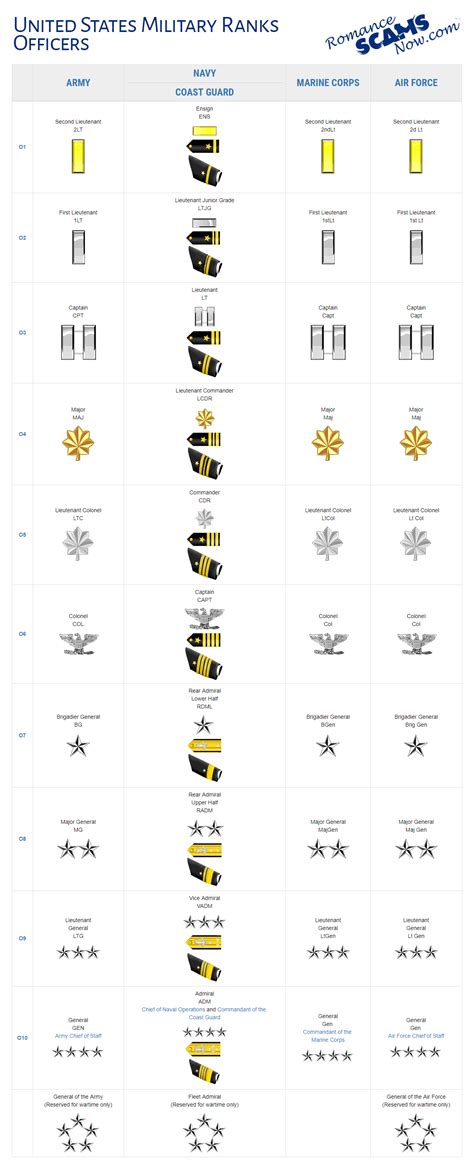
The second lieutenant is the most junior commissioned officer rank in the Air Force. Typically, this rank is held by new officers who have just graduated from the Air Force Academy, Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC), or Officer Training School (OTS). Second lieutenants usually serve as platoon leaders or executive officers in various units, where they are responsible for leading and training a small team of airmen.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and train a small team of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
First Lieutenant (1st Lt, O-2)

First lieutenants typically serve as executive officers or assistant operations officers in various units. They are responsible for leading and managing larger teams of airmen and are often involved in planning and executing unit operations.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and manage a team of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
Captain (Capt, O-3)

Captains are company-grade officers who typically serve as flight commanders or squadron executive officers. They are responsible for leading and managing large teams of airmen and are often involved in planning and executing unit operations.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and manage a large team of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
Major (Maj, O-4)

Majors are field-grade officers who typically serve as squadron commanders or executive officers. They are responsible for leading and managing large units of airmen and are often involved in planning and executing unit operations.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and manage a large unit of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col, O-5)

Lieutenant colonels are field-grade officers who typically serve as wing or group commanders. They are responsible for leading and managing large units of airmen and are often involved in planning and executing unit operations.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and manage a large unit of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
Colonel (Col, O-6)
Colonels are senior field-grade officers who typically serve as wing or group commanders. They are responsible for leading and managing large units of airmen and are often involved in planning and executing unit operations.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and manage a large unit of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
Brigadier General (Brig Gen, O-7)

Brigadier generals are one-star generals who typically serve as wing or group commanders. They are responsible for leading and managing large units of airmen and are often involved in planning and executing unit operations.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and manage a large unit of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
Major General (Maj Gen, O-8)
Major generals are two-star generals who typically serve as numbered air force commanders or deputy commanders. They are responsible for leading and managing large units of airmen and are often involved in planning and executing unit operations.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and manage a large unit of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
Lieutenant General (Lt Gen, O-9)

Lieutenant generals are three-star generals who typically serve as major command commanders or deputy commanders. They are responsible for leading and managing large units of airmen and are often involved in planning and executing unit operations.
Responsibilities:
- Lead and manage a large unit of airmen
- Assist in planning and executing unit operations
- Develop leadership and management skills
📝 Note: The responsibilities listed above are general in nature and may vary depending on the specific unit and mission.
In conclusion, the nine commissioned officer ranks in the Air Force are each unique and play a critical role in the success of the organization. From the junior second lieutenant to the senior lieutenant general, each rank brings its own set of responsibilities and challenges. By understanding the hierarchy and responsibilities of each rank, we can better appreciate the complexity and sophistication of the Air Force.
What is the lowest commissioned officer rank in the Air Force?

+
The lowest commissioned officer rank in the Air Force is second lieutenant (2nd Lt, O-1).
What is the highest commissioned officer rank in the Air Force?

+
The highest commissioned officer rank in the Air Force is lieutenant general (Lt Gen, O-9).
What are the responsibilities of a second lieutenant?

+
A second lieutenant is typically responsible for leading and training a small team of airmen, assisting in planning and executing unit operations, and developing leadership and management skills.
Related Terms:
- U S Air Force rank
- O1 officer
- Philippines air force rank
- Us air force academy ranks
- Us military rank charts
- British Military rank



