Air Force Aviation Mechanic: Keeping Jets Flying High

Introduction to Air Force Aviation Mechanic Career

As an integral part of the Air Force, aviation mechanics play a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation of military aircraft. These skilled technicians are responsible for maintaining, repairing, and inspecting various types of aircraft, including fighter jets, transport planes, and helicopters. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of Air Force aviation mechanics, exploring their responsibilities, requirements, and the steps to become one.
Responsibilities of an Air Force Aviation Mechanic

Air Force aviation mechanics, also known as aircraft maintenance specialists, are responsible for performing routine maintenance, repairs, and inspections on aircraft and their components. Their primary duties include:
- Performing routine maintenance: Conducting daily, weekly, and monthly checks on aircraft systems, including engines, landing gear, and flight controls.
- Repairing and replacing parts: Identifying and repairing or replacing damaged or malfunctioning parts, such as engines, propellers, and avionics systems.
- Inspecting aircraft: Conducting pre-flight, post-flight, and periodic inspections to ensure aircraft airworthiness and identify potential issues.
- Troubleshooting: Using diagnostic tools and techniques to identify and resolve complex problems with aircraft systems.
- Collaborating with pilots and other teams: Working with pilots, aircrew members, and other maintenance teams to ensure aircraft are airworthy and ready for flight.
Requirements to Become an Air Force Aviation Mechanic

To become an Air Force aviation mechanic, you’ll need to meet specific requirements, including:
- Age: You must be between 17 and 39 years old (with some exceptions for older candidates).
- Citizenship: You must be a U.S. citizen.
- Education: You’ll need a high school diploma or equivalent.
- Background check: You’ll undergo a thorough background check and security clearance process.
- Medical exam: You’ll need to pass a medical exam to ensure you’re fit for duty.
- Basic training: You’ll attend Basic Military Training (BMT) at Lackland Air Force Base in Texas.
- Technical training: After BMT, you’ll attend technical training at a designated Air Force base, where you’ll learn specific skills related to aircraft maintenance.
Steps to Become an Air Force Aviation Mechanic

If you’re interested in pursuing a career as an Air Force aviation mechanic, follow these steps:
- Meet the basic requirements: Ensure you meet the age, citizenship, education, and background check requirements.
- Take the ASVAB test: The Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test measures your aptitude in various subjects. You’ll need to score well in areas related to mechanics and technology.
- Enlist in the Air Force: Visit an Air Force recruiter and enlist, specifying your interest in becoming an aviation mechanic.
- Attend Basic Military Training (BMT): Complete BMT at Lackland Air Force Base in Texas.
- Attend technical training: After BMT, you’ll attend technical training at a designated Air Force base, where you’ll learn specific skills related to aircraft maintenance.
- Complete on-the-job training: After technical training, you’ll receive on-the-job training, where you’ll work alongside experienced mechanics to learn the skills and procedures specific to your unit.
💡 Note: The Air Force offers various types of training and certifications, including the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) certification, which can be beneficial for those interested in pursuing a civilian career in aviation maintenance.
Specializations and Career Advancement

As an Air Force aviation mechanic, you’ll have opportunities to specialize in specific areas, such as:
- Fighter jet maintenance: Working on high-performance fighter jets, such as the F-16 or F-35.
- Transport aircraft maintenance: Maintaining large transport planes, such as the C-130 or C-5.
- Helicopter maintenance: Working on various types of helicopters, including the UH-60 Black Hawk or TH-1H Iroquois.
With experience and advanced training, you can move up the ranks and take on leadership roles, such as:
- Shift leader: Supervising a team of mechanics and coordinating maintenance operations.
- Section chief: Leading a section of mechanics and overseeing maintenance activities.
- Maintenance superintendent: Overseeing maintenance operations across multiple units.
Conclusion

As an Air Force aviation mechanic, you’ll play a critical role in ensuring the airworthiness of military aircraft. With the right combination of technical skills, attention to detail, and teamwork, you’ll be an integral part of the Air Force’s mission to fly, fight, and win.
What is the typical salary for an Air Force aviation mechanic?

+
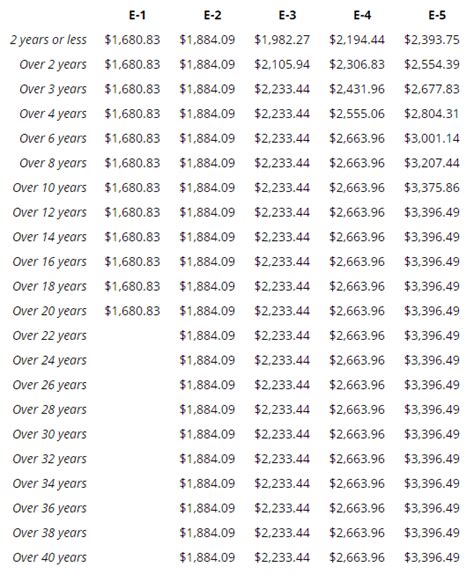
The salary for an Air Force aviation mechanic varies based on rank, experience, and location. On average, an Air Force aviation mechanic can expect to earn between 40,000 and 70,000 per year.
How long does technical training typically take?

+
Technical training for an Air Force aviation mechanic typically lasts around 3-6 months, depending on the specific job and location.
Can I pursue a civilian career in aviation maintenance after serving in the Air Force?

+
Yes, many Air Force aviation mechanics go on to pursue successful careers in civilian aviation maintenance. The skills and certifications you earn in the Air Force are highly transferable to the civilian sector.