5 Ways to Sustainably Farm the Ocean

The Future of Ocean Farming: 5 Sustainable Practices

The world’s oceans cover over 70% of our planet, providing a vast array of ecosystem services, including food, livelihoods, and climate regulation. However, the ocean’s health is under threat from overfishing, pollution, and climate change. As the global population continues to grow, finding sustainable ways to farm the ocean is crucial to ensuring food security while protecting the marine environment. Here are five ways to sustainably farm the ocean:
1. Aquaculture: A Viable Alternative to Wild Catch

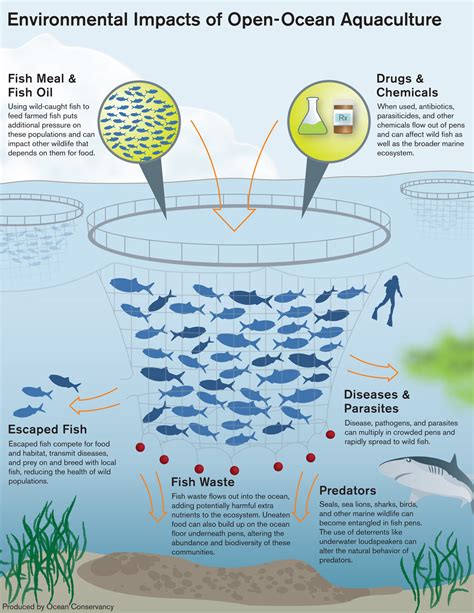
Aquaculture, or fish farming, is a rapidly growing industry that provides a viable alternative to wild catch fishing. By farming fish and other seafood in controlled environments, aquaculture reduces the pressure on wild fish populations and helps to maintain the health of marine ecosystems. However, traditional aquaculture practices can have negative environmental impacts, such as water pollution and habitat destruction.
To address these concerns, many aquaculture farms are adopting sustainable practices, such as:
- Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA): This approach involves farming multiple species together, such as fish, shellfish, and seaweed, to create a balanced ecosystem.
- Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS): RAS involves recycling water and waste to minimize the environmental impact of aquaculture.
🐟 Note: Aquaculture is not a replacement for wild catch fishing, but rather a supplement to help meet the global demand for seafood.
2. Kelp Farming: A Sustainable Solution for Seaweed Production

Kelp farming is a sustainable way to produce seaweed, which is used in a variety of products, from food to cosmetics. Kelp farming involves cultivating kelp in the ocean, where it absorbs nutrients and provides habitat for marine life. This approach:
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions: Kelp absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere, making it a valuable tool in the fight against climate change.
- Supports biodiversity: Kelp forests provide habitat for a diverse range of marine species, from fish to invertebrates.
| Species | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Kelp | Absorbs CO2, provides habitat for marine life |
| Dulse | Rich in vitamins and minerals, used in food and cosmetics |
| Irish Moss | Used in food and cosmetics, provides habitat for marine life |

3. Open Ocean Aquaculture: Farming the High Seas

Open ocean aquaculture involves farming fish and other seafood in the open ocean, away from coastal areas. This approach:
- Reduces environmental impact: By farming in the open ocean, the environmental impact of aquaculture is reduced, as there is less risk of water pollution and habitat destruction.
- Increases food production: Open ocean aquaculture can increase food production, helping to meet the global demand for seafood.
🌊 Note: Open ocean aquaculture requires careful planning and management to ensure that it does not harm the marine environment.
4. Restorative Aquaculture: Farming for Ecosystem Services
Restorative aquaculture involves farming seafood in a way that restores ecosystem services, such as water filtration and habitat creation. This approach:
- Enhances biodiversity: Restorative aquaculture can enhance biodiversity by providing habitat for marine species and promoting ecosystem services.
- Supports ecosystem health: By restoring ecosystem services, restorative aquaculture can help to maintain the health of marine ecosystems.
5. Offshore Wind Farms: A New Frontier for Ocean Farming

Offshore wind farms involve installing wind turbines in the ocean to generate electricity. This approach:
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions: Offshore wind farms can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by providing a renewable source of energy.
- Supports ocean farming: Offshore wind farms can provide a platform for ocean farming, such as aquaculture and seaweed production.
In conclusion, sustainable ocean farming is crucial to ensuring food security while protecting the marine environment. By adopting practices such as aquaculture, kelp farming, open ocean aquaculture, restorative aquaculture, and offshore wind farms, we can help to maintain the health of our oceans and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
What is sustainable ocean farming?

+
Sustainable ocean farming involves farming seafood in a way that maintains the health of marine ecosystems and ensures a sustainable future for generations to come.
How can aquaculture be sustainable?

+
Aquaculture can be sustainable by adopting practices such as integrated multi-trophic aquaculture, recirculating aquaculture systems, and restorative aquaculture.
What are the benefits of kelp farming?
+
Kelp farming provides habitat for marine life, absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere, and supports biodiversity.
Related Terms:
- Department of Agriculture head Office
- Department of Agriculture news
- Department of Agriculture Minister
- Ministers of Agriculture
- Department of Agriculture divisions
- Previous Agriculture Minister



