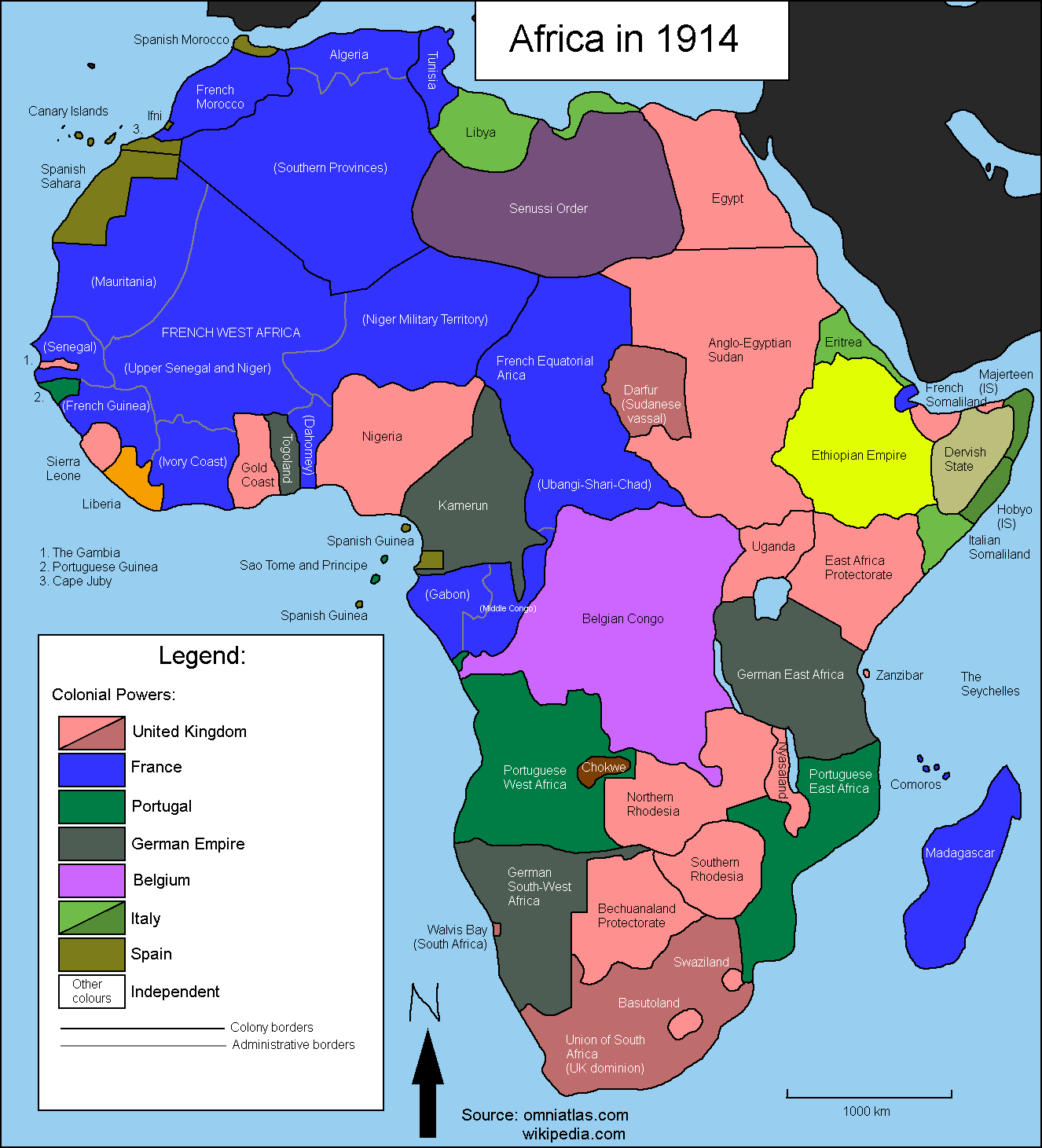
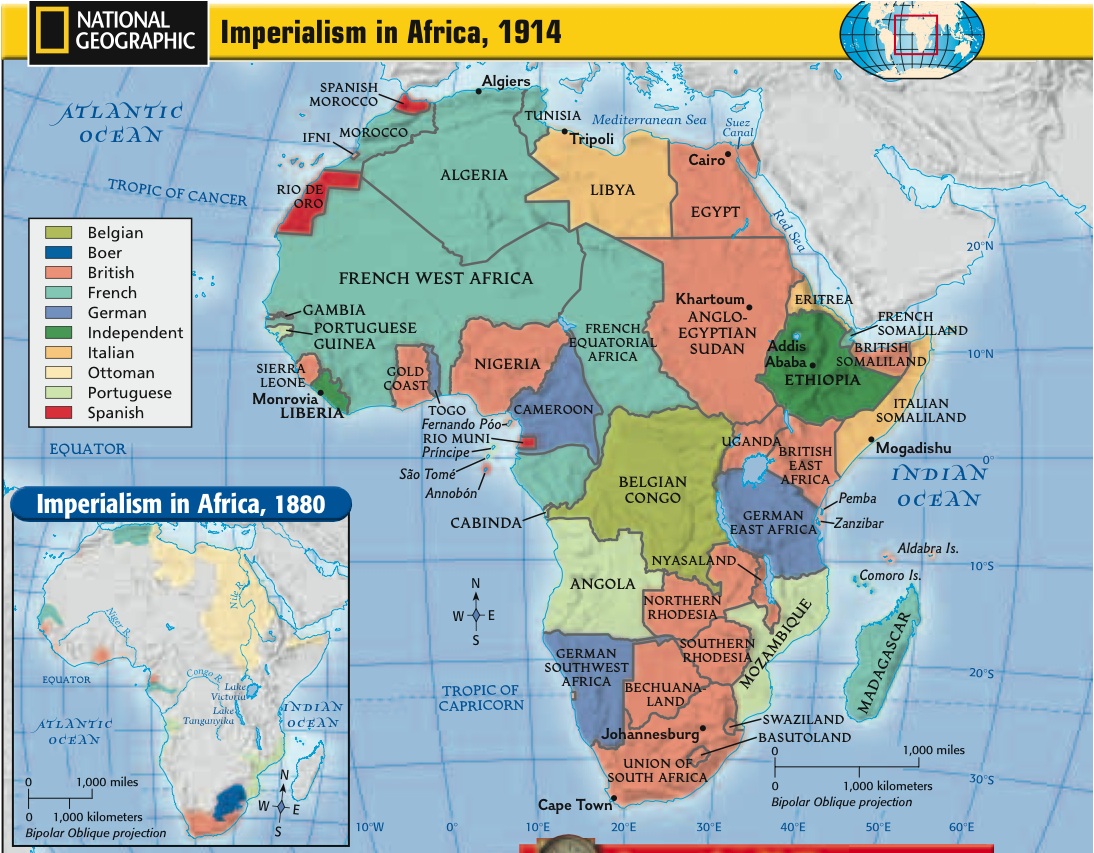
5 Fascinating Facts from the 1914 Africa Map Worksheet

In the world of history and cartography, 1914 marks a significant year due to the onset of the First World War. One of the less frequently discussed but equally important aspects of this era is the intricate mapping of Africa, reflecting the colonial ambitions and geopolitical tensions of the time. Here, we will delve into five fascinating facts derived from studying the 1914 Africa Map Worksheet, offering insights into the historical, political, and cultural landscape of the continent during this pivotal moment in history.
The Scramble for Africa


- Colonial Expansion: The 1914 Africa Map Worksheet vividly illustrates the “Scramble for Africa”, where European powers carved up the continent with little regard for pre-existing borders or cultures. By this time, nearly 90% of the African continent was under European control, showcasing the culmination of the Berlin Conference (1884-1885).
- Shifting Borders: The map reflects the fluid nature of colonial borders, with some areas still in dispute or not fully colonized. The lines drawn on maps were often subject to change due to treaties, wars, or administrative decisions, highlighting the dynamic nature of colonial rule.
Colonial Administrations and Their Impacts
| Country | Colonial Power | Notable Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Kenya | British | Introduction of cash crops like tea and coffee, which altered traditional agricultural practices. |
| Algeria | French | Massive settlement of French colons, leading to significant cultural and demographic changes. |
| Congo | Belgian | Exploitation under Leopold II, infamously known for the Congo Free State’s brutality and rubber plantations. |
💡 Note: The information presented here is an overview. For detailed historical context, refer to colonial records or academic studies.
The Influence of Missionaries

- Evangelization: Missionaries played a significant role in colonial Africa, not just in spreading Christianity but also in education and healthcare. The map might not show direct evidence, but their influence was pervasive across the colonies.
- Language and Culture: Missionaries often brought with them the culture and language of their home countries, significantly influencing local customs and languages.
Geopolitical Ripples

- The Morocco Crisis: The map alludes to tensions in North Africa, particularly the Tangier Crisis of 1911, which nearly sparked a war between France and Germany. Morocco became a focal point of European rivalry.
- African Independence Movements: While not evident on the 1914 map, the seeds of resistance and independence movements were sown in this period, which would eventually lead to the decolonization of Africa in the mid-20th century.
Cultural and Linguistic Divisions

- Language Influence: The map highlights how colonial powers imposed their languages, affecting communication, culture, and identity. English, French, Portuguese, and German became dominant in regions controlled by the respective colonial powers.
- Cultural Imposition: With colonization came not only political control but also cultural impositions, leading to a mix of traditional African and European cultural practices.
The exploration of the 1914 Africa Map Worksheet allows us to trace the geopolitical currents of the time, understand the colonial impacts on Africa, and appreciate the complexities that shaped modern African nations. The boundaries drawn in 1914 set the stage for many of the conflicts and challenges faced by African countries today. The map serves as both a historical document and a reminder of the enduring legacy of colonial rule, cultural shifts, and the beginnings of African resistance against foreign domination.
Why was 1914 a pivotal year in Africa’s history?

+
1914 marked the beginning of World War I, which had direct and indirect impacts on Africa. Colonial powers mobilized troops from their African colonies, and the war led to increased demand for African resources, shaping the continent’s geopolitical landscape.
What were the long-term effects of colonial boundaries?

+
Many modern-day conflicts in Africa can be traced back to the arbitrary borders drawn by colonial powers. These boundaries often ignored ethnic, linguistic, and cultural divisions, leading to post-independence disputes over territory and resources.
How did missionaries influence African societies?

+
Missionaries had profound effects on education, healthcare, and religious practices in Africa. While they introduced formal education and healthcare systems, they also contributed to cultural changes, often disrupting or altering local customs and beliefs.
What role did Africa play in World War I?

+
Africa played both direct and indirect roles in WWI. African troops from colonies like Senegal and Nigeria fought in Europe and Africa. Additionally, colonies were vital sources of raw materials, food, and soldiers for the war efforts.
How can studying historical maps benefit our understanding of current global politics?

+
Historical maps provide insight into the origins of current borders, conflicts, and alliances. Understanding the geopolitical decisions of the past can inform our perspective on contemporary issues like resource distribution, ethnic conflicts, and international relations.