Active Duty vs Reserve: Which Offers Better Benefits

Understanding the Difference Between Active Duty and Reserve

When it comes to serving in the military, there are several options to consider. Two of the most popular choices are active duty and reserve. While both options offer a sense of pride and fulfillment, they differ significantly in terms of benefits, lifestyle, and commitment. In this article, we will explore the differences between active duty and reserve, highlighting the benefits of each option to help you make an informed decision.
Active Duty: What to Expect

Active duty refers to full-time service in the military. When you enlist for active duty, you are committing to serve 24⁄7, 365 days a year. This means you will be required to relocate to a designated military base, either in the United States or abroad, and be prepared to deploy at a moment’s notice. Active duty members typically serve for a minimum of 4-6 years, although some careers may require longer commitments.
Benefits of Active Duty:
- Education Benefits: Active duty members are eligible for the GI Bill, which covers 100% of tuition and fees for in-state students at public colleges and universities.
- Healthcare Benefits: Active duty members and their families receive comprehensive healthcare coverage, including medical, dental, and pharmacy benefits.
- Housing Allowance: Active duty members receive a tax-free housing allowance, which helps cover the cost of living expenses.
- Career Advancement: Active duty members have opportunities for career advancement and professional development, including training and certifications.
- Travel Opportunities: Active duty members have the opportunity to travel and experience new cultures, both domestically and internationally.
Reserve: What to Expect

The reserve refers to part-time service in the military. When you enlist for the reserve, you are committing to serve one weekend a month and two weeks a year. Reserve members typically serve in their local communities and are not required to relocate. The reserve is a great option for those who want to serve their country while still maintaining a civilian career.
Benefits of Reserve:
- Flexibility: Reserve members have the flexibility to balance their military service with their civilian career and personal life.
- Education Benefits: Reserve members are eligible for the GI Bill, although the benefits are not as comprehensive as those offered to active duty members.
- Healthcare Benefits: Reserve members and their families receive healthcare coverage, although it may not be as comprehensive as that offered to active duty members.
- Career Advancement: Reserve members have opportunities for career advancement and professional development, although they may not be as extensive as those offered to active duty members.
- Retirement Benefits: Reserve members are eligible for retirement benefits, including a pension and healthcare coverage, after 20 years of service.
Comparing Benefits: Active Duty vs Reserve
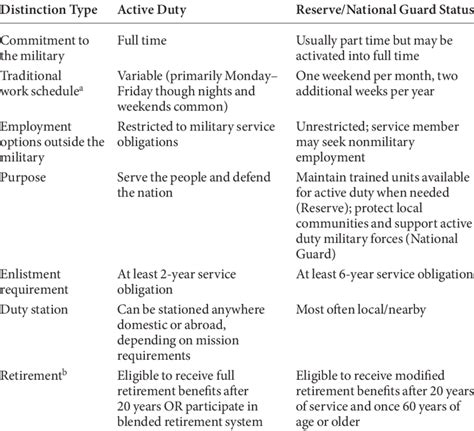
| Benefit | Active Duty | Reserve |
|---|---|---|
| Education Benefits | 100% tuition coverage | 50-100% tuition coverage |
| Healthcare Benefits | Comprehensive coverage | Limited coverage |
| Housing Allowance | Tax-free allowance | None |
| Career Advancement | Extensive opportunities | Limited opportunities |
| Travel Opportunities | Frequent travel | Limited travel |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility | Flexible schedule |
| Retirement Benefits | 20-year pension | 20-year pension |

📝 Note: The benefits listed above are subject to change and may vary depending on individual circumstances.
Making the Right Choice for You

Ultimately, the decision between active duty and reserve comes down to your personal preferences and priorities. If you value flexibility and want to balance your military service with your civilian career, the reserve may be the better choice. However, if you are willing to commit to full-time service and want comprehensive benefits, active duty may be the way to go.
Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Lifestyle: Are you willing to relocate and serve 24⁄7, or do you prefer a more flexible schedule?
- Career Goals: Are you looking for extensive career advancement opportunities, or do you prioritize flexibility and work-life balance?
- Financial Situation: Do you need comprehensive healthcare coverage and a housing allowance, or can you afford to cover these expenses yourself?
- Personal Preferences: Do you value the camaraderie and sense of community that comes with active duty, or do you prefer to serve in your local community?
By carefully considering these factors and weighing the benefits of each option, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your goals and priorities.
What is the difference between active duty and reserve?

+
Active duty refers to full-time service in the military, while reserve refers to part-time service. Active duty members serve 24⁄7, 365 days a year, while reserve members serve one weekend a month and two weeks a year.
Which option offers better benefits?

+
Active duty members typically receive more comprehensive benefits, including 100% tuition coverage, comprehensive healthcare coverage, and a tax-free housing allowance. However, reserve members may still be eligible for benefits, including education and healthcare coverage.
Can I switch from active duty to reserve?

+
Yes, it is possible to switch from active duty to reserve. However, this typically requires a new contract and may involve a change in job or location.