5 Ways Food Stamps

Introduction to Food Stamps and Their Importance

The concept of food stamps has been around for several decades, serving as a vital component of social welfare programs aimed at reducing hunger and poverty. These programs, now more commonly referred to as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), provide eligible low-income individuals and families with financial assistance to purchase food. The significance of food stamps cannot be overstated, as they play a critical role in ensuring that vulnerable populations have access to nutritious food, thereby promoting health, well-being, and productivity.
History and Evolution of Food Stamps
The first food stamp program was initiated in the United States in the late 1930s as part of President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal. The program was designed to help farmers by providing them with a market for their surplus crops and to assist low-income families by enabling them to purchase food at a lower cost. Over the years, the program has undergone numerous changes, including its renaming to SNAP in 2008. These changes reflect efforts to modernize the program, making it more efficient and effective in serving its beneficiaries. The use of Electronic Benefit Transfer (EBT) cards has been a significant development, replacing traditional paper coupons and allowing for more discreet and convenient transactions.
Eligibility and Application Process
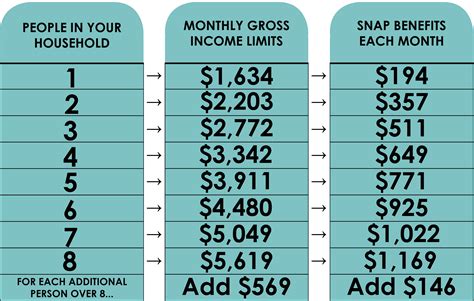
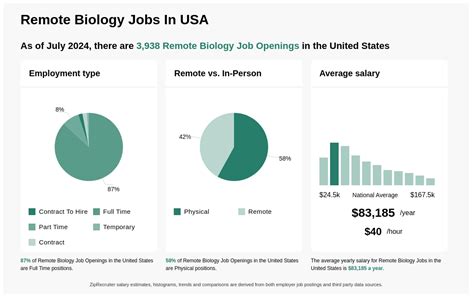
To be eligible for food stamps, individuals and families must meet specific income and resource requirements, which vary by state. Generally, applicants must have a limited income and few resources. The application process typically involves submitting an application to the local social services department, providing required documentation, and participating in an interview. Once eligibility is determined, beneficiaries receive an EBT card, which they can use to purchase food at participating retailers. It’s essential for applicants to understand that eligibility criteria can differ, so it’s crucial to check with the local authorities for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Benefits of the Food Stamp Program

The benefits of the food stamp program are multifaceted: - Nutritional Assistance: The most direct benefit is the provision of financial assistance to purchase food, helping to alleviate hunger and malnutrition. - Economic Stimulus: By providing low-income individuals and families with the means to purchase food, the program also acts as an economic stimulus, as the funds are spent within local communities. - Health Improvement: Access to nutritious food can lead to improved health outcomes, reducing the incidence of diet-related diseases and improving overall well-being. - Support for Vulnerable Populations: The program is particularly vital for vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and individuals with disabilities, who may face higher risks of food insecurity.
Challenges and Criticisms

Despite its importance, the food stamp program faces several challenges and criticisms: - Stigma: Many beneficiaries face stigma associated with using food stamps, which can be a barrier to participation. - Administrative Challenges: The application and eligibility determination process can be complex and time-consuming, potentially deterring eligible individuals from applying. - Funding Issues: The program is subject to federal and state funding, which can be unpredictable and may lead to benefit reductions or eligibility restrictions. - Nutritional Quality: There are concerns about the nutritional quality of foods that can be purchased with SNAP benefits, with some advocating for restrictions on the purchase of unhealthy foods.
📝 Note: Understanding the challenges faced by the food stamp program is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders seeking to improve its effectiveness and accessibility.
Future Directions and Reforms

Looking ahead, there are several potential reforms and directions that could enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of the food stamp program: - Simplification of Eligibility and Application Processes: Streamlining these processes could increase participation rates among eligible individuals and families. - Promotion of Healthy Eating: Initiatives to encourage the purchase of nutritious foods, such as incentives for buying fruits and vegetables, could improve the health outcomes of beneficiaries. - Technological Advancements: Further integration of technology, such as mobile applications for managing benefits and finding healthy recipes, could enhance the user experience and promote better nutrition. - Addressing Food Insecurity: Policies aimed at addressing the root causes of food insecurity, including poverty and lack of access to healthy food options, are essential for the long-term success of the program.
What is the primary purpose of the food stamp program?

+
The primary purpose of the food stamp program, now known as SNAP, is to provide financial assistance to low-income individuals and families to purchase food, thereby reducing hunger and poverty.
How do I apply for food stamps?

+
To apply for food stamps, you typically need to submit an application to your local social services department, provide required documentation, and participate in an eligibility interview. The specific process may vary by state, so it's best to contact your local office for detailed instructions.
What kinds of food can I buy with food stamps?

+
Food stamps, or SNAP benefits, can be used to purchase a wide variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, meats, dairy products, and bread. However, they cannot be used to buy non-food items, such as household supplies, or hot, ready-to-eat foods.
In summary, the food stamp program plays a vital role in supporting low-income individuals and families, providing them with the means to access nutritious food. Despite its challenges, the program remains a cornerstone of social welfare policy, aiming to reduce hunger, promote health, and stimulate local economies. As policymakers and stakeholders continue to navigate the complexities of food insecurity, understanding the program’s history, benefits, challenges, and potential for reform is essential for creating a more equitable and food-secure future for all.