2 Force Member Analysis
Introduction to 2 Force Member Analysis
In the field of physics and engineering, particularly in mechanics, understanding the behavior of forces and their impact on objects is crucial. One fundamental concept in this area is the analysis of 2 force members, which are simple structures subjected to two forces. This analysis is essential for designing and analyzing more complex systems, ensuring they can withstand various loads without failing. The concept applies to a wide range of applications, from building design to mechanical engineering, where understanding the effects of forces on structural members is vital.
Understanding 2 Force Members

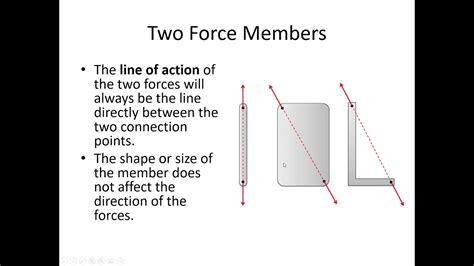
A 2 force member is a structural element that is subjected to two forces. These forces can act in any direction and can be either tensile (pulling the member apart) or compressive (pushing the member together). The analysis of such members involves determining the internal forces within the member due to the applied external forces. This is a basic yet critical step in understanding more complex structures, as these simple members are the building blocks of larger, more intricate systems.
Types of 2 Force Members

There are primarily two types of 2 force members based on how the forces act on them: - Tensile Members: These are members that are subjected to forces that tend to stretch or pull them apart. Examples include ropes, cables, and some types of beams. - Compressive Members: These members are subjected to forces that tend to compress or push them together. Examples include columns and some types of pillars.
Analysis of 2 Force Members
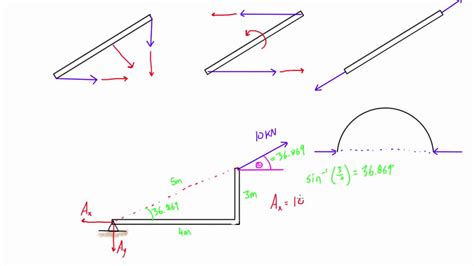
The analysis of 2 force members involves calculating the magnitude and direction of the internal force within the member due to the external forces applied. This analysis is based on the principle of equilibrium, which states that for an object to be at rest, the sum of all forces acting on it must be zero. In a 2 force member, if the two forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, the member is in equilibrium.
Steps for Analysis

The steps for analyzing a 2 force member include: - Identifying the external forces acting on the member. - Determining the direction and magnitude of these forces. - Applying the principles of equilibrium to calculate the internal force. - Deciding whether the member is in tension or compression based on the direction of the internal force.
Importance of 2 Force Member Analysis

The analysis of 2 force members is crucial in engineering and physics because it lays the foundation for understanding more complex structures. By understanding how simple members behave under different forces, engineers can design more complex systems that are safe, efficient, and reliable. This knowledge is applied in the design of buildings, bridges, mechanical devices, and many other structures.
Real-World Applications

The concept of 2 force members has numerous real-world applications: - Building Design: Understanding how beams and columns respond to forces is critical in building design to ensure structural integrity. - Mechanical Engineering: In mechanical systems, 2 force members are used in the design of linkages, gears, and other components. - Bridges: The cables and suspension systems in bridges are examples of 2 force members under tension.
Common Mistakes in Analysis

Common mistakes in the analysis of 2 force members include: - Incorrectly identifying the type of force (tensile or compressive) acting on the member. - Failing to consider all external forces acting on the member. - Not applying the principles of equilibrium correctly.
📝 Note: It is essential to meticulously follow the steps for analysis and to consider all forces acting on a 2 force member to ensure accurate calculations and design.
In summary, the analysis of 2 force members is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering that plays a critical role in designing and analyzing structural systems. Understanding how these simple structures behave under different forces is essential for creating safe, efficient, and reliable complex systems. By applying the principles of equilibrium and correctly identifying the types and directions of forces, engineers can ensure the structural integrity of a wide range of applications, from buildings and bridges to mechanical devices.
What is a 2 force member in physics and engineering?

+
A 2 force member is a structural element subjected to two forces, which can be either tensile or compressive, and is a fundamental concept in understanding the behavior of more complex systems.
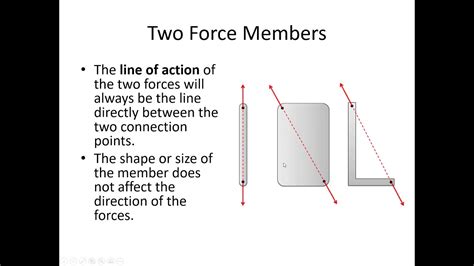
Why is the analysis of 2 force members important?
+
The analysis of 2 force members is crucial because it provides the foundation for understanding more complex structures and ensures the design of safe, efficient, and reliable systems in various engineering applications.
What are common applications of 2 force member analysis?

+
Common applications include building design, mechanical engineering, and the construction of bridges, where understanding the behavior of 2 force members under different loads is vital for structural integrity.