2 Digit by 1 Digit Multiplication Made Easy: Area Model Worksheets

Multiplication can often seem like a daunting task, especially when dealing with larger numbers. However, breaking down the process using visual models like the Area Model can significantly simplify the concept. In this blog, we will delve into 2 Digit by 1 Digit Multiplication using the area model method, providing step-by-step guidance and worksheets to practice, enhancing both understanding and proficiency in math for students and adults alike.
Why Use the Area Model for Multiplication?

The area model for multiplication visually represents the process, turning abstract arithmetic into a more intuitive and visual exercise. Here are some benefits:
- It breaks down large numbers into more manageable pieces.
- Enhances conceptual understanding by showing how multiplication works in terms of areas.
- Makes multiplication accessible for visual learners.
- It’s an excellent method for those who struggle with traditional long multiplication.
How to Perform 2 Digit by 1 Digit Multiplication Using the Area Model

Let’s walk through the process with an example: Multiplying 24 by 3.
Step 1: Draw the Rectangle
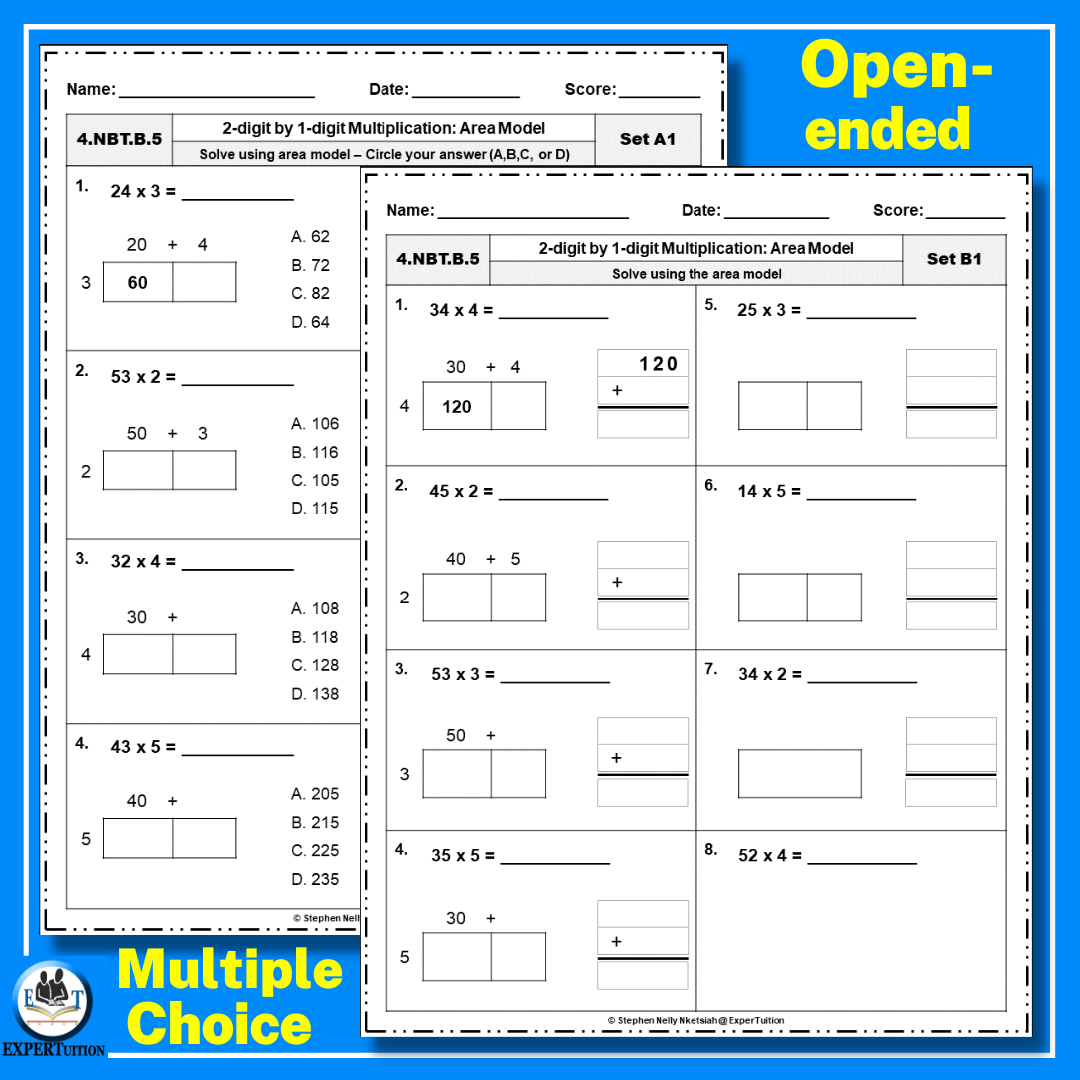
Imagine you have a rectangle. The width represents the tens place, and the length represents the ones place of the two-digit number, with the one-digit number being the height of the rectangle.
- On the base, write ‘20’ for the tens (24 - 4).
- On the height, write ‘3’.
- On the right side, write ‘4’ for the ones.
- Leave the top empty for now.
Step 2: Calculate the Areas

| Tens | Ones |
|---|---|
| 20 x 3 = 60 | 4 x 3 = 12 |

Now, you have two smaller rectangles. One is 20 by 3, and the other is 4 by 3.
Step 3: Sum the Areas

Add these areas together:
- 60 (from the tens column) + 12 (from the ones column) = 72
💡 Note: You can think of this visually as covering the area of the rectangle piece by piece, then summing those pieces to find the total area.
Practicing with Area Model Worksheets

Here are some exercises you can use for practicing 2 Digit by 1 Digit Multiplication:
- Multiply 15 by 2.
- Multiply 38 by 4.
- Multiply 67 by 9.
As you practice, remember the following:
- Always start by drawing the rectangle to visualize the problem.
- Divide the rectangle into sections based on the place values of the numbers.
- Calculate each section separately and sum them up at the end.
To further enhance your practice:
- Speed Up: Try to increase your speed without sacrificing accuracy.
- Challenge: Move to larger numbers or even introduce more digits to practice further.
Wrapping Up

By now, you've seen how the area model provides an intuitive way to approach 2 Digit by 1 Digit Multiplication. This method breaks down the multiplication into smaller, more manageable steps, turning a potentially complex calculation into a visual and logical process. Through regular practice, you or your students can gain confidence and proficiency in multiplying numbers, no matter the size, making math less of a challenge and more of an engaging puzzle to solve.
Why is the Area Model helpful for visual learners?

+
The Area Model for multiplication breaks down the numbers into visual components, making it easier to understand the relationship between the parts and the whole, which is particularly beneficial for those who learn better visually.
Can the Area Model be used for larger numbers?
+
Yes, the Area Model can be extended to handle larger numbers by simply increasing the number of sections in the visual representation, allowing for multi-digit multiplication to be broken down step-by-step.
Are there any limitations to using the Area Model?

+
The main limitation might be the time taken to draw and calculate the areas for very large numbers. Also, for some students, switching from visual methods to traditional algorithms can be challenging.